Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Biliary/Pancreas
P4478 - Backed It up and Burned It Down: A Case of Durvalumab-Induced Cholestasis and Cholangitis
Tuesday, October 28, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall
- AM
Ahmad Mardini, MD
Advocate Christ Medical Center
Oak Lawn, IL
Presenting Author(s)
Ahmad Mardini, MD, Krishna Shah, MD, Matthew Posen, DO, Samee Farooqi, DO, Imad Elkhatib, MD
Advocate Christ Medical Center, Oak Lawn, IL
Introduction: Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) side effects are called immune related adverse events. Some gastrointestinal IRAEs are recognized in literature but there is scarce material on ICI induced cholangiopathy. Here we present a unique case of this pathology due to durvalumab.
Case Description/
Methods: A 64 year old male on mesalamine for ulcerative colitis presented for epigastric pain and jaundice. Labs were notable for elevated aspartate transaminase (AST) 703 units/liter (units/l), alanine transaminase (ALT) 868 units/l, alkaline phosphatase (ALP) 985 units/l, and total bilirubin (T Bil) 5.7 milligram/deciliter. Computed tomography abdomen pelvis (CT AP) showed liver lesions, intra and extrahepatic biliary duct dilation, common bile duct (CBD) narrowing and a pancreatic head mass . He underwent endoscopic ultrasound and endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP). CBD brushing was positive for adenocarcinoma. Liver biopsy showed poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma. Pancreatic mass biopsy was unremarkable. Carbohydrate Antigen 19-9 was elevated: 6401 units/milliliter. He was diagnosed with stage IV metastatic cholangiocarcinoma. He was started on cisplatin and gemcitabine. Labs and imaging were used to monitor disease progression and treatment response. After 4 cycles of chemotherapy, durvalumab was started and he received radiation therapy. He completed 8 cycles of chemotherapy and continued Durvalumab for maintenance. On 4/2024 he had elevated liver enzymes. Durvalumab was held and prednisone was started for autoimmune hepatitis. On 6/2024 he was admitted for fevers and chills. CT AP showed CBD dilation. He had elevated T Bil, AST, ALT, ALP, and white blood cell count. He received ceftriaxone and metronidazole and underwent ERCP to treat cholangitis. The fully occluded stent was removed and replaced by another. Labs worsened so he had another ERCP to replace his again occluded stent. He improved and was discharged. Durvalumab was resumed on 8/2024. On 9-10/2024, he underwent ERCP twice given obstructive pattern transaminitis. Both times he had a significant amount of amorphous gelatinous material encasing his stents and obstructing flow. Labs improved after stent replacements.
Discussion: Sparse articles associate ICIs with cholangiopathy. With the recent approval of durvalumab for treating biliary tract cancer, it’s important to be aware of this side effect. The frequent stent replacements in this case due to an unusual gelatinous biliary sludge emphasizes this.
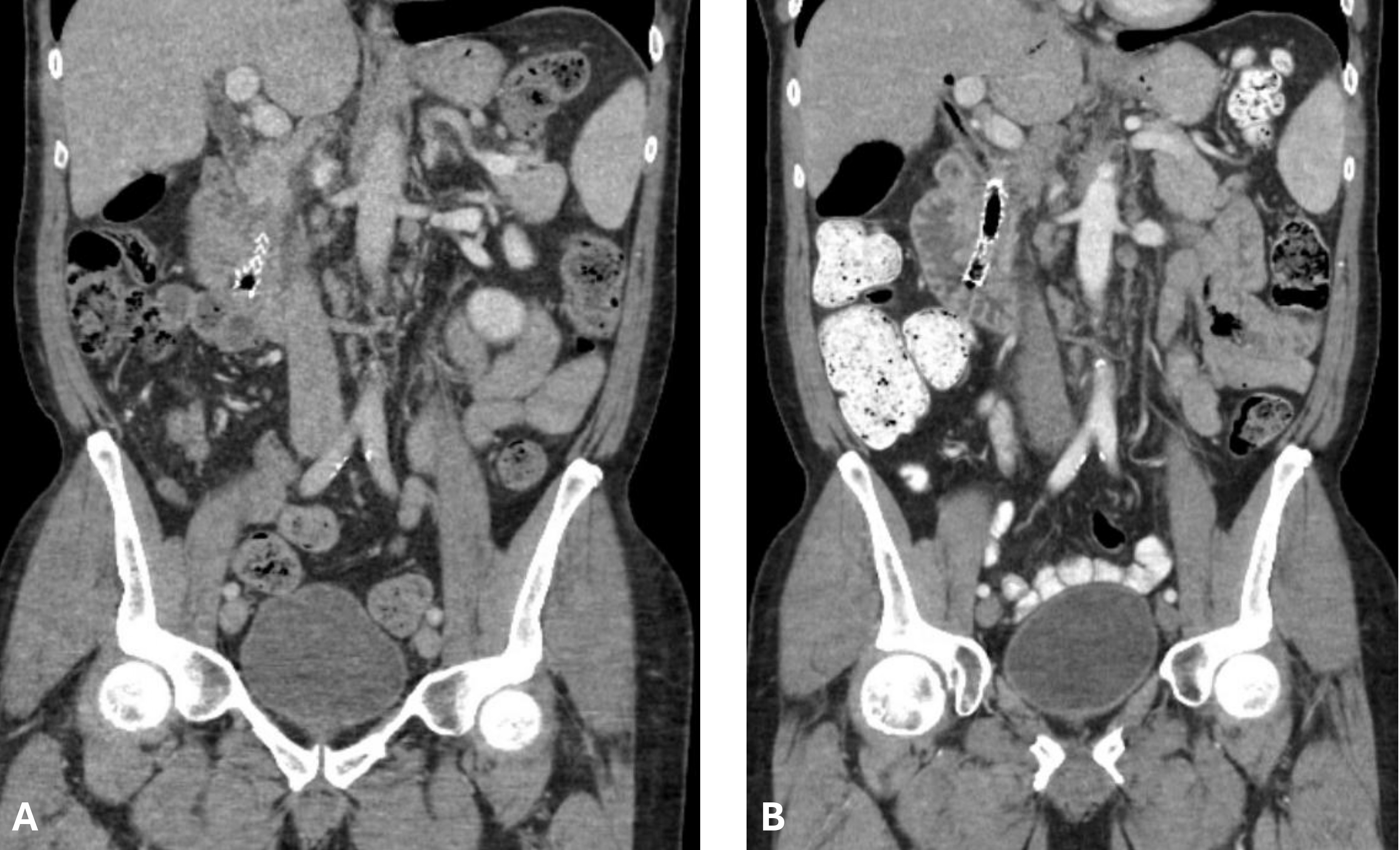
Figure: A: CT AP obtained during admission on 6/2024 showing stent within CBD. CBD is measuring 13.6 mm. Significant biliary sludge present within CBD.
B: CT AP obtained on 5/2024 while durvalumab was held. Stent within CBD. CBD is measuring 6.9 mm.
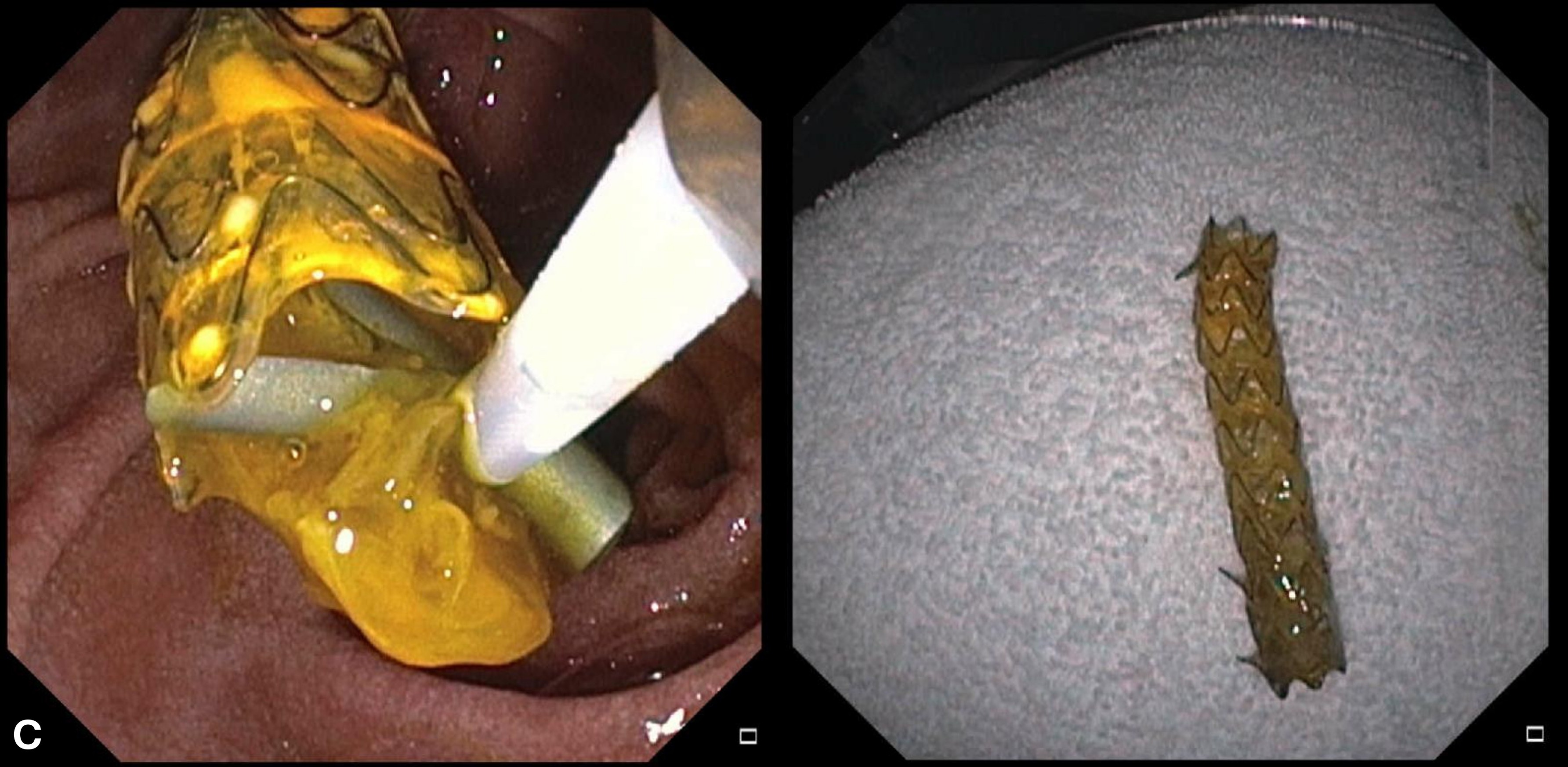
Figure: C: ERCP performed with extraction of metallic stent fully covered with significant amount of gelatinous amorphous material.
Disclosures:
Ahmad Mardini indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Krishna Shah indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Matthew Posen indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Samee Farooqi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Imad Elkhatib indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ahmad Mardini, MD, Krishna Shah, MD, Matthew Posen, DO, Samee Farooqi, DO, Imad Elkhatib, MD. P4478 - Backed It up and Burned It Down: A Case of Durvalumab-Induced Cholestasis and Cholangitis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
Advocate Christ Medical Center, Oak Lawn, IL
Introduction: Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) side effects are called immune related adverse events. Some gastrointestinal IRAEs are recognized in literature but there is scarce material on ICI induced cholangiopathy. Here we present a unique case of this pathology due to durvalumab.
Case Description/
Methods: A 64 year old male on mesalamine for ulcerative colitis presented for epigastric pain and jaundice. Labs were notable for elevated aspartate transaminase (AST) 703 units/liter (units/l), alanine transaminase (ALT) 868 units/l, alkaline phosphatase (ALP) 985 units/l, and total bilirubin (T Bil) 5.7 milligram/deciliter. Computed tomography abdomen pelvis (CT AP) showed liver lesions, intra and extrahepatic biliary duct dilation, common bile duct (CBD) narrowing and a pancreatic head mass . He underwent endoscopic ultrasound and endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP). CBD brushing was positive for adenocarcinoma. Liver biopsy showed poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma. Pancreatic mass biopsy was unremarkable. Carbohydrate Antigen 19-9 was elevated: 6401 units/milliliter. He was diagnosed with stage IV metastatic cholangiocarcinoma. He was started on cisplatin and gemcitabine. Labs and imaging were used to monitor disease progression and treatment response. After 4 cycles of chemotherapy, durvalumab was started and he received radiation therapy. He completed 8 cycles of chemotherapy and continued Durvalumab for maintenance. On 4/2024 he had elevated liver enzymes. Durvalumab was held and prednisone was started for autoimmune hepatitis. On 6/2024 he was admitted for fevers and chills. CT AP showed CBD dilation. He had elevated T Bil, AST, ALT, ALP, and white blood cell count. He received ceftriaxone and metronidazole and underwent ERCP to treat cholangitis. The fully occluded stent was removed and replaced by another. Labs worsened so he had another ERCP to replace his again occluded stent. He improved and was discharged. Durvalumab was resumed on 8/2024. On 9-10/2024, he underwent ERCP twice given obstructive pattern transaminitis. Both times he had a significant amount of amorphous gelatinous material encasing his stents and obstructing flow. Labs improved after stent replacements.
Discussion: Sparse articles associate ICIs with cholangiopathy. With the recent approval of durvalumab for treating biliary tract cancer, it’s important to be aware of this side effect. The frequent stent replacements in this case due to an unusual gelatinous biliary sludge emphasizes this.

Figure: A: CT AP obtained during admission on 6/2024 showing stent within CBD. CBD is measuring 13.6 mm. Significant biliary sludge present within CBD.
B: CT AP obtained on 5/2024 while durvalumab was held. Stent within CBD. CBD is measuring 6.9 mm.

Figure: C: ERCP performed with extraction of metallic stent fully covered with significant amount of gelatinous amorphous material.
Disclosures:
Ahmad Mardini indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Krishna Shah indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Matthew Posen indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Samee Farooqi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Imad Elkhatib indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ahmad Mardini, MD, Krishna Shah, MD, Matthew Posen, DO, Samee Farooqi, DO, Imad Elkhatib, MD. P4478 - Backed It up and Burned It Down: A Case of Durvalumab-Induced Cholestasis and Cholangitis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
