Sunday Poster Session
Category: Biliary/Pancreas
P0055 - Endoscopic Papillary Balloon Dilation versus Sphincterotomy for Common Bile Duct Stones: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Sunday, October 26, 2025
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Faizan ul Hussain Mohammed, MBBS (he/him/his)
Osmania Medical College
Farmington Hills, MI
Presenting Author(s)
Faizan ul Hussain Mohammed, MBBS1, Chandana Tadigotla, MBBS2, Afreen Begum, MBBS3, Diksha Mahadeva Gowda, MBBS4, Dheeraj Kumar Maheshwari, MBBS5, Adarsh Gande, MBBS6, Omer Farooq Mohammed, MBBS7, Binay Panjiyar, MD8, Adi Prasad Bodapati, MD9, Ashwith Reddy Gaddam, MD10, Sri Lakshmi Ananya Bokka, MBBS11, Siddhi P. Shah, MBBS12
1Osmania Medical College, Karimnagar, Telangana, India; 2PES INSTITUTE OF MEDICAL SCIENCES AND RESEARCH, Ananthapur, Andhra Pradesh, India; 3ESIC Medical College and Hospital, Washington, DC; 4Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN; 5Liaquat University of Medical and Health Science, Pensacola, FL; 6JIPMER, Pondicherry, India, Southlake, TX; 7Osmania General Hospital and Medical College, Hyderabad, Telangana, India; 8NorthShore University Hospital, Manhasset, NY; 9Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center, Odessa, TX; 10NYMC at St. Mary’s General hospital amd st clares health, Parsippany, NJ; 11Gandhi Medical College & Hospital, Hyderabad, Telangana, India; 12HBT Medical College and Dr. R.N. Cooper Municipal General Hospital, Thane, Maharashtra, India
Introduction: Endoscopic sphincterotomy (EST) and endoscopic papillary balloon dilation (EPBD) are widely used techniques for the management of common bile duct (CBD) stones. Despite their widespread use, comparative safety and efficacy remain debated. This meta-analysis aimed to evaluate and compare the outcomes of EPBD and EST.
Methods: A systematic review and meta-analysis were conducted to compare endoscopic papillary balloon dilation (EPBD) and endoscopic sphincterotomy (EST) in the management of common bile duct (CBD) stones. A comprehensive literature search of PubMed, Google Scholar, Cochrane Library, and PLOS databases was performed from 2000 to the present. Only randomized controlled trials (RCTs) involving adult patients were included. The risk of bias was assessed using the Cochrane Risk of Bias (RoB) tool.
Results: Nineteen randomized controlled trials were included. EPBD and EST demonstrated comparable efficacy in stone clearance at first attempt (OR = 1.02; 95% CI, 0.65–1.60; P = 0.94) and requirement for mechanical lithotripsy (OR = 1.00; 95% CI, 0.80–1.24; P = 0.98). However, a borderline statistically significant trend favored EST for overall stone clearance (OR = 0.65; 95% CI, 0.43–1.00; P = 0.05). Notably, EPBD was associated with a significantly higher risk of post-ERCP pancreatitis (OR = 1.70; 95% CI, 1.22–2.37; P = 0.002), though overall short-term complications did not differ between the groups (OR = 1.00; 95% CI, 0.66–1.52; P = 0.99).
Discussion: Both EPBD and EST demonstrate similar efficacy in terms of first-attempt stone clearance and need for mechanical lithotripsy. However, EST appears to offer a modest advantage in overall stone clearance and is associated with a significantly lower risk of post-ERCP pancreatitis. These findings suggest that while EPBD remains a viable alternative, EST may be the preferred approach, particularly when minimizing the risk of pancreatitis is a clinical priority.
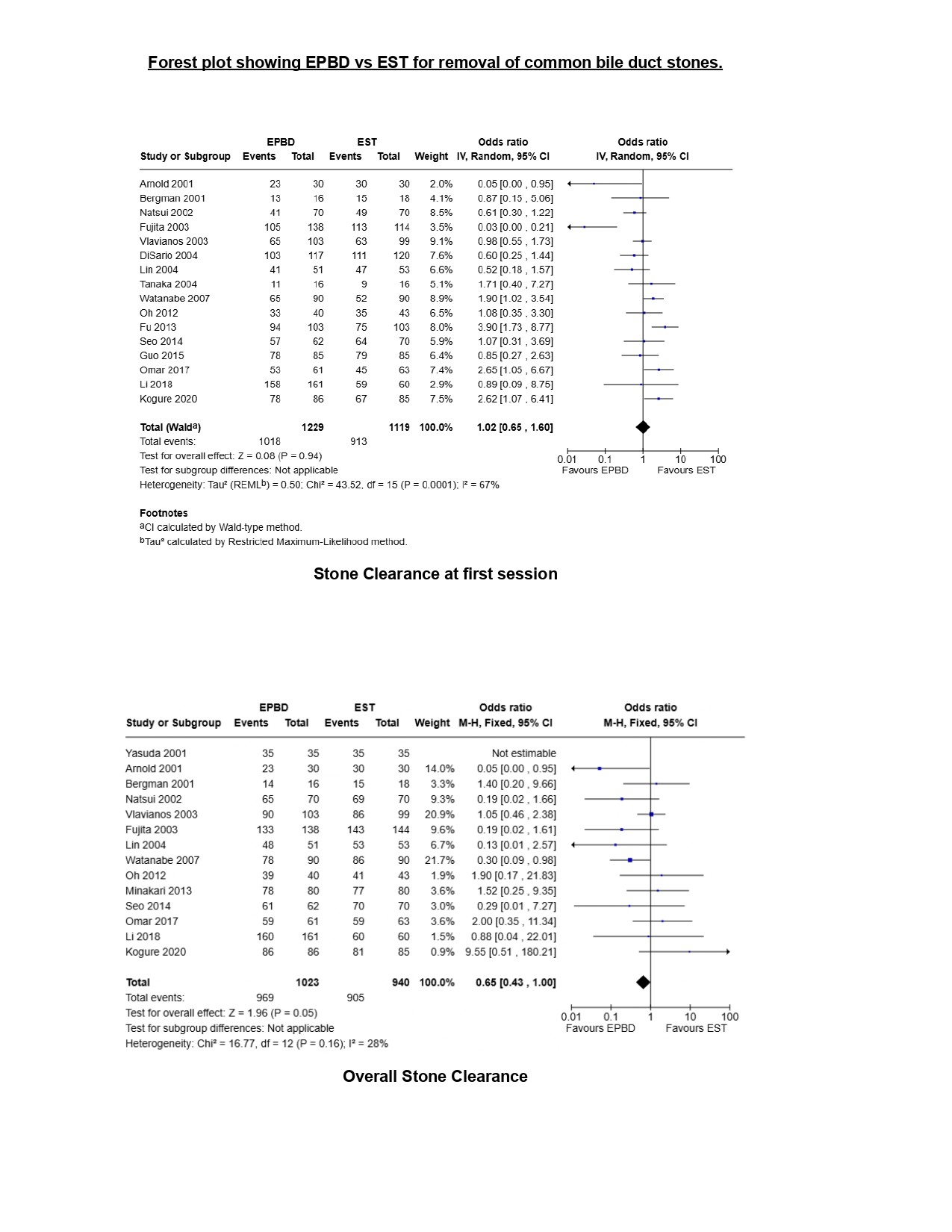
Figure: Forest plot showing EPBD vs EST for removal of common bile duct stones-stone clearance at first session; overall stone clearance
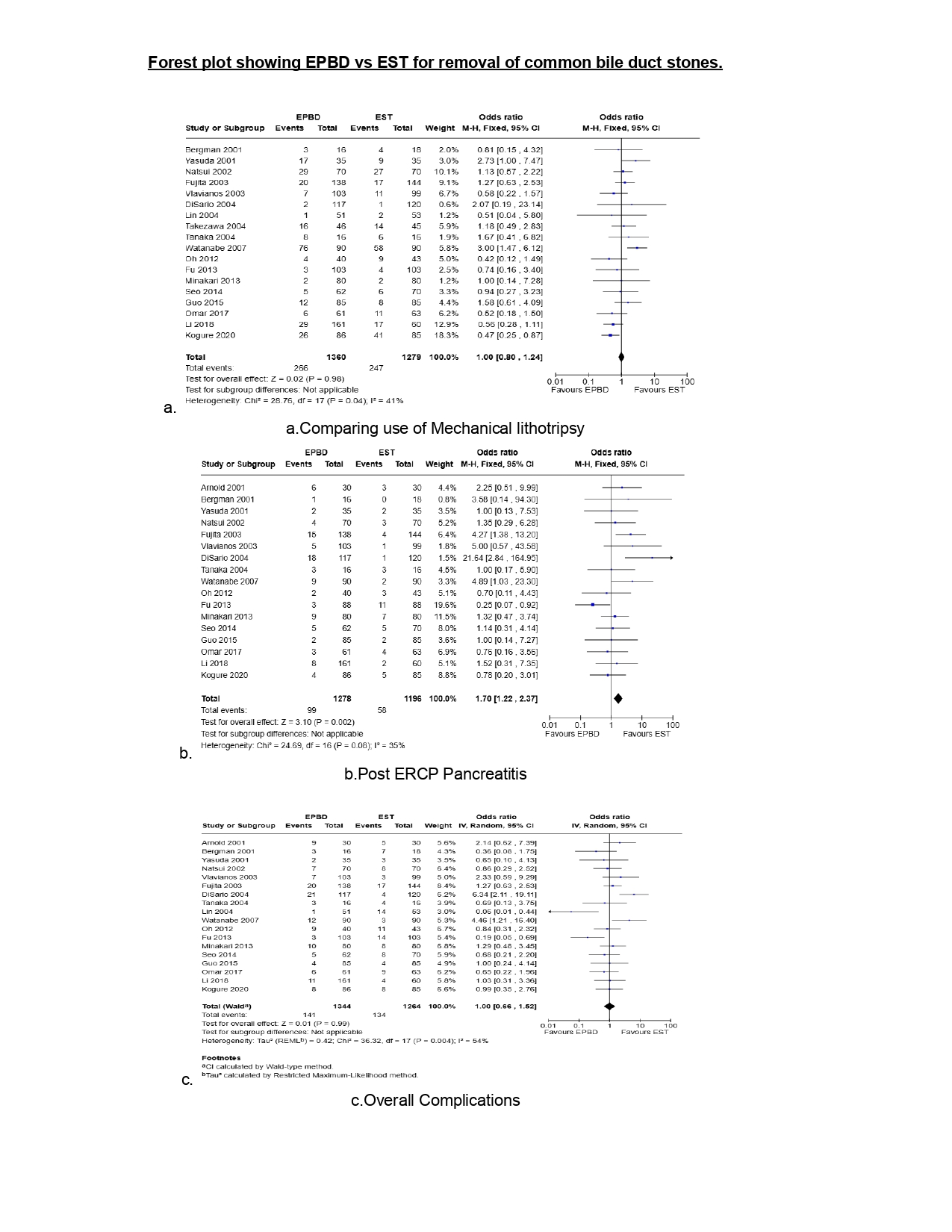
Figure: Forest plot showing EPBD vs EST for removal of common bile duct stones
a.Comparing use of Mechanical lithotripsy
b.Post ERCP Pancreatitis
c.Overall Complications
Disclosures:
Faizan ul Hussain Mohammed indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Chandana Tadigotla indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Afreen Begum indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Diksha Mahadeva Gowda indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Dheeraj Kumar Maheshwari indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Adarsh Gande indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Omer Farooq Mohammed indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Binay Panjiyar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Adi Prasad Bodapati indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ashwith Reddy Gaddam indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sri Lakshmi Ananya Bokka indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Siddhi Shah indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Faizan ul Hussain Mohammed, MBBS1, Chandana Tadigotla, MBBS2, Afreen Begum, MBBS3, Diksha Mahadeva Gowda, MBBS4, Dheeraj Kumar Maheshwari, MBBS5, Adarsh Gande, MBBS6, Omer Farooq Mohammed, MBBS7, Binay Panjiyar, MD8, Adi Prasad Bodapati, MD9, Ashwith Reddy Gaddam, MD10, Sri Lakshmi Ananya Bokka, MBBS11, Siddhi P. Shah, MBBS12. P0055 - Endoscopic Papillary Balloon Dilation versus Sphincterotomy for Common Bile Duct Stones: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Osmania Medical College, Karimnagar, Telangana, India; 2PES INSTITUTE OF MEDICAL SCIENCES AND RESEARCH, Ananthapur, Andhra Pradesh, India; 3ESIC Medical College and Hospital, Washington, DC; 4Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN; 5Liaquat University of Medical and Health Science, Pensacola, FL; 6JIPMER, Pondicherry, India, Southlake, TX; 7Osmania General Hospital and Medical College, Hyderabad, Telangana, India; 8NorthShore University Hospital, Manhasset, NY; 9Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center, Odessa, TX; 10NYMC at St. Mary’s General hospital amd st clares health, Parsippany, NJ; 11Gandhi Medical College & Hospital, Hyderabad, Telangana, India; 12HBT Medical College and Dr. R.N. Cooper Municipal General Hospital, Thane, Maharashtra, India
Introduction: Endoscopic sphincterotomy (EST) and endoscopic papillary balloon dilation (EPBD) are widely used techniques for the management of common bile duct (CBD) stones. Despite their widespread use, comparative safety and efficacy remain debated. This meta-analysis aimed to evaluate and compare the outcomes of EPBD and EST.
Methods: A systematic review and meta-analysis were conducted to compare endoscopic papillary balloon dilation (EPBD) and endoscopic sphincterotomy (EST) in the management of common bile duct (CBD) stones. A comprehensive literature search of PubMed, Google Scholar, Cochrane Library, and PLOS databases was performed from 2000 to the present. Only randomized controlled trials (RCTs) involving adult patients were included. The risk of bias was assessed using the Cochrane Risk of Bias (RoB) tool.
Results: Nineteen randomized controlled trials were included. EPBD and EST demonstrated comparable efficacy in stone clearance at first attempt (OR = 1.02; 95% CI, 0.65–1.60; P = 0.94) and requirement for mechanical lithotripsy (OR = 1.00; 95% CI, 0.80–1.24; P = 0.98). However, a borderline statistically significant trend favored EST for overall stone clearance (OR = 0.65; 95% CI, 0.43–1.00; P = 0.05). Notably, EPBD was associated with a significantly higher risk of post-ERCP pancreatitis (OR = 1.70; 95% CI, 1.22–2.37; P = 0.002), though overall short-term complications did not differ between the groups (OR = 1.00; 95% CI, 0.66–1.52; P = 0.99).
Discussion: Both EPBD and EST demonstrate similar efficacy in terms of first-attempt stone clearance and need for mechanical lithotripsy. However, EST appears to offer a modest advantage in overall stone clearance and is associated with a significantly lower risk of post-ERCP pancreatitis. These findings suggest that while EPBD remains a viable alternative, EST may be the preferred approach, particularly when minimizing the risk of pancreatitis is a clinical priority.

Figure: Forest plot showing EPBD vs EST for removal of common bile duct stones-stone clearance at first session; overall stone clearance

Figure: Forest plot showing EPBD vs EST for removal of common bile duct stones
a.Comparing use of Mechanical lithotripsy
b.Post ERCP Pancreatitis
c.Overall Complications
Disclosures:
Faizan ul Hussain Mohammed indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Chandana Tadigotla indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Afreen Begum indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Diksha Mahadeva Gowda indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Dheeraj Kumar Maheshwari indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Adarsh Gande indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Omer Farooq Mohammed indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Binay Panjiyar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Adi Prasad Bodapati indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ashwith Reddy Gaddam indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sri Lakshmi Ananya Bokka indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Siddhi Shah indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Faizan ul Hussain Mohammed, MBBS1, Chandana Tadigotla, MBBS2, Afreen Begum, MBBS3, Diksha Mahadeva Gowda, MBBS4, Dheeraj Kumar Maheshwari, MBBS5, Adarsh Gande, MBBS6, Omer Farooq Mohammed, MBBS7, Binay Panjiyar, MD8, Adi Prasad Bodapati, MD9, Ashwith Reddy Gaddam, MD10, Sri Lakshmi Ananya Bokka, MBBS11, Siddhi P. Shah, MBBS12. P0055 - Endoscopic Papillary Balloon Dilation versus Sphincterotomy for Common Bile Duct Stones: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
