Sunday Poster Session
Category: Colon
P0370 - Cannabis and the Colon: A Case Report of Ileocolonic Nodular Lymphoid Hyperplasia with Symptomatic Improvement Following Discontinuation of Cannabis
- LC
Lorraine I. Chong Tai, MD (she/her/hers)
Broward Health Medical Center
Allentown, PA
Presenting Author(s)
Broward Health Medical Center, Fort Lauderdale, FL
Introduction:
Ileocolonic lymphonodular hyperplasia (ILNH) is an uncommon but notable condition characterized by numerous small polypoid nodules predominantly affecting the ileum and colon. Though commonly seen in pediatric populations, ILNH can occasionally present in adults, often mimicking symptoms of inflammatory bowel disease or gastrointestinal infections.
Case Description/
Methods:
A 19-year-old male with no medical history presented to our clinic for worsening nausea, vomiting, weight loss, and loose bowel movements for 1 year. Symptoms were associated with early satiety, that ultimately resulted in a weight loss of 35 kg. Prior CT scan of the abdomen/pelvis with contrast showed sigmoid and descending colitis along with mild reactive adenitis for which he was prescribed antibiotics with no improvement. Allergy testing confirmed allergy to peanut, wheat, soybean, sesame, hazelnut. He also reported smoking cannabis once a week. Colonoscopy revealed multiple polyps in the terminal ileum (Figure 1). Pathology of the terminal ileum polyps showed lymphoid aggregates and congestion with no evidence of malignancy or parasites. Rectosigmoid polyp pathology showed lymphoid aggregates and congestion as well with no granulomas, cryptitis, increased intraepithelial lymphocytes, or viral cytopathic changes consistent with Ileocolonic lymphonodular hyperplasia. At one month follow-up his symptoms were significantly improved after cannabis cessation.
Discussion:
The pathophysiology of ILNH is not well understood but is thought to involve an increase in lamina propria T cells resulting in enhanced local immune responses causing gastrointestinal symptoms. Associations with food hypersensitivities, infections, and immune dysregulation have been documented. In this case, we suggest the patient’s confirmed multiple food allergies and potential contribution of cannabis likely played a role in symptom exacerbation. Although benign, management of ILNH involves addressing underlying triggers and providing symptomatic relief. In this case, cessation of cannabis use resulted in significant symptom improvement. Dietary modifications to avoid allergens may also be beneficial, though their role in ILNH still remains unclear. Long-term outcomes are favorable, with most patients experiencing resolution or significant improvement of symptoms. Although there are no definitive treatment guidelines, addressing underlying etiologies and avoiding potential triggers may help alleviate symptoms in affected individuals.
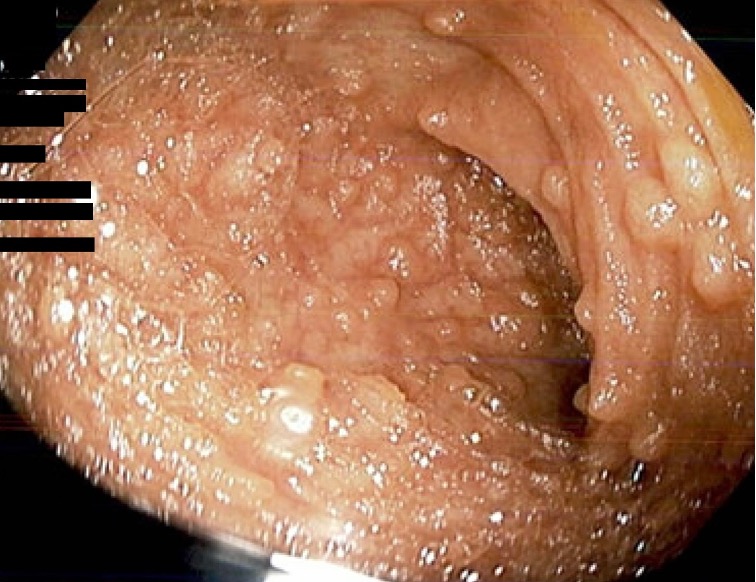
Figure: Colonoscopy showing nodular lymphoid hyperplasia of the terminal ileum
Disclosures:
Lorraine Chong Tai indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ivana Rubenstein indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Lorraine Chong Tai, MD, Ivana Rubenstein, DO. P0370 - Cannabis and the Colon: A Case Report of Ileocolonic Nodular Lymphoid Hyperplasia with Symptomatic Improvement Following Discontinuation of Cannabis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
