Sunday Poster Session
Category: Colon
P0445 - Eosinophilic Gastrointestinal Disorders (EGID): A Case of Eosinophilic Ascites
Sunday, October 26, 2025
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Keon Karimabady, DO
University of Chicago, NorthShore Internal Medicine
Evanston, IL
Presenting Author(s)
Keon Karimabady, DO1, Mitchelle Zolotarvesky, MD2, Jeremy Van, DO1, Madhav Patel, DO1, Kadir Isidan, MD3, David Labowitz, DO4
1University of Chicago, NorthShore Internal Medicine, Evanston, IL; 2University of Chicago, Northshore University Healthsystem, Chicago, IL; 3University of Chicago Northshore, Evanston, IL; 4University of Chicago, NorthShore Gastroenterology, Evanston, IL
Introduction: Eosinophilic (Eos) gastrointestinal (GI) disorders (EGID) are characterized by Th2 immune response to foods and environmental exposures with Eos infiltration of the GI tract. A history of (h/o) atopy and genetic predisposition has been well described. We present an interesting case of EGID with Eos ascites.
Case Description/
Methods: A 22 year old male with h/o allergic rhinitis presented with nausea, vomiting and post prandial right lower quadrant abdominal pain one week after a road-trip dirt biking and eating from a farm. Initial labs noted WBC 8.0 K/uL, Hgb 15.0 g/dL, platelets 202 K/uL, absolute eosinophil count 2.0 x 1000 /uL. LFT’s, lipase, and creatinine were normal. CT abdomen and pelvis revealed distal esophageal wall thickening, gastritis, jejunal submucosal edema, hepatosplenomegaly, and small-moderate ascites. A diagnostic paracentesis demonstrated low serum-ascites-albumin-gradient, high protein and Eos (2700 eosinophils) ascites. Stool enteric PCR, ova/parasite, giardia/cryptosporidium ag, and fecal calprotectin were negative. Serum ascaris/toxocara/strongyloides serologies, HIV ag/ab, tryptase, quantitative immunoglobulins, ANA, and ANCA were negative. EGD showed normal esophagus and erythematous mucosa in the gastric body/antrum, and duodenum. Biopsies (bx) demonstrated eosinophil-rich esophagitis ( >40 eosinophils per high-powered field) and were normal in the stomach and duodenum. Ileocolonoscopy was grossly normal with unrevealing bx in the terminal ileum. Numerous aggregate forming eosinophils with preserved architecture were found throughout the colon on bx. EGID with Eos ascites was diagnosed.
Discussion: EGIDs are a group of chronic immune mediated conditions characterized by GI symptoms and Eos infiltration of any layer of the GI tract: mucosa (70% of cases), muscularis (20% of cases), and serosa (10% of cases). Three diagnostic criteria are proposed: GI symptoms, bx proven Eos infiltration (alongside peripheral eosinophilia or Eos ascitic fluid), and exclusion of other secondary causes including parasitic infections, IBD and hypereosinophilic syndrome. This rare case underscores the importance of maintaining a high level of suspicion for EGIDs in patients with unexplained ascites and GI symptoms as making diagnosis can often be challenging. Early recognition and accurate diagnosis are critical to initiate appropriate therapy and prevent prolonged morbidity and long term complications related to this chronic inflammatory disorder.
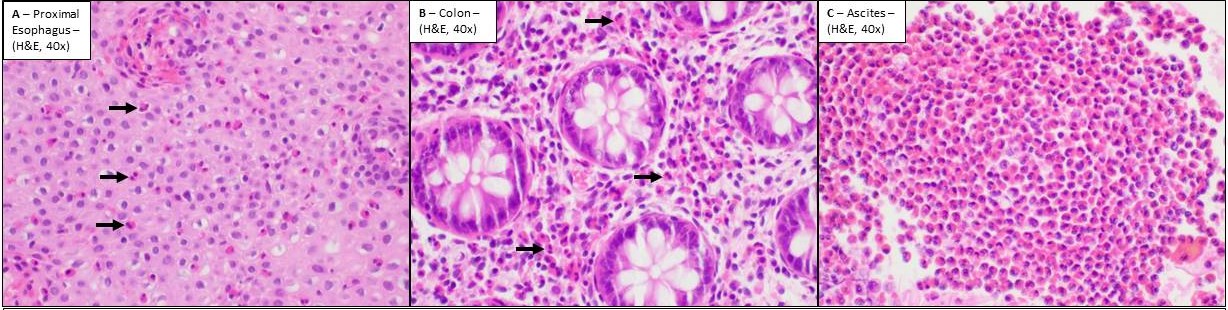
Figure: Figure 1; Computed Tomography Abdomen and Pelvis demonstrating (A) gastritis and (B) jejunal submucosal edema. EGD demonstrating erythematous mucosa in the (C, D) duodenal bulb
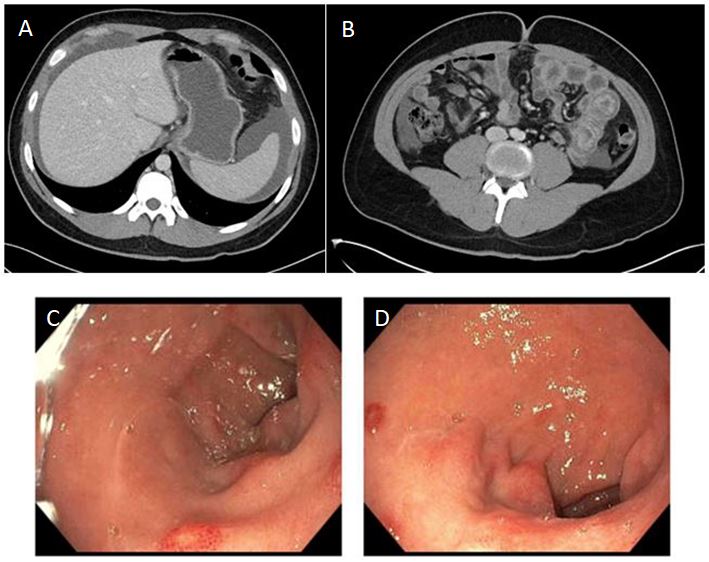
Figure: Figure 2; Histopathological images. A: Proximal esophagus biopsy showing numerous intraepithelial eosinophils (>40 per high power field). B: Random colonic biopsy showing numerous eosinophils filling the lamina propria and forming aggregates in places. C: A cell block made from ascites fluid showing large amount of eosinophils with only rare mesothelial cells, consistent with eosinophilic effusion.
Disclosures:
Keon Karimabady indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mitchelle Zolotarvesky indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jeremy Van indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Madhav Patel indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kadir Isidan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
David Labowitz indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Keon Karimabady, DO1, Mitchelle Zolotarvesky, MD2, Jeremy Van, DO1, Madhav Patel, DO1, Kadir Isidan, MD3, David Labowitz, DO4. P0445 - Eosinophilic Gastrointestinal Disorders (EGID): A Case of Eosinophilic Ascites, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1University of Chicago, NorthShore Internal Medicine, Evanston, IL; 2University of Chicago, Northshore University Healthsystem, Chicago, IL; 3University of Chicago Northshore, Evanston, IL; 4University of Chicago, NorthShore Gastroenterology, Evanston, IL
Introduction: Eosinophilic (Eos) gastrointestinal (GI) disorders (EGID) are characterized by Th2 immune response to foods and environmental exposures with Eos infiltration of the GI tract. A history of (h/o) atopy and genetic predisposition has been well described. We present an interesting case of EGID with Eos ascites.
Case Description/
Methods: A 22 year old male with h/o allergic rhinitis presented with nausea, vomiting and post prandial right lower quadrant abdominal pain one week after a road-trip dirt biking and eating from a farm. Initial labs noted WBC 8.0 K/uL, Hgb 15.0 g/dL, platelets 202 K/uL, absolute eosinophil count 2.0 x 1000 /uL. LFT’s, lipase, and creatinine were normal. CT abdomen and pelvis revealed distal esophageal wall thickening, gastritis, jejunal submucosal edema, hepatosplenomegaly, and small-moderate ascites. A diagnostic paracentesis demonstrated low serum-ascites-albumin-gradient, high protein and Eos (2700 eosinophils) ascites. Stool enteric PCR, ova/parasite, giardia/cryptosporidium ag, and fecal calprotectin were negative. Serum ascaris/toxocara/strongyloides serologies, HIV ag/ab, tryptase, quantitative immunoglobulins, ANA, and ANCA were negative. EGD showed normal esophagus and erythematous mucosa in the gastric body/antrum, and duodenum. Biopsies (bx) demonstrated eosinophil-rich esophagitis ( >40 eosinophils per high-powered field) and were normal in the stomach and duodenum. Ileocolonoscopy was grossly normal with unrevealing bx in the terminal ileum. Numerous aggregate forming eosinophils with preserved architecture were found throughout the colon on bx. EGID with Eos ascites was diagnosed.
Discussion: EGIDs are a group of chronic immune mediated conditions characterized by GI symptoms and Eos infiltration of any layer of the GI tract: mucosa (70% of cases), muscularis (20% of cases), and serosa (10% of cases). Three diagnostic criteria are proposed: GI symptoms, bx proven Eos infiltration (alongside peripheral eosinophilia or Eos ascitic fluid), and exclusion of other secondary causes including parasitic infections, IBD and hypereosinophilic syndrome. This rare case underscores the importance of maintaining a high level of suspicion for EGIDs in patients with unexplained ascites and GI symptoms as making diagnosis can often be challenging. Early recognition and accurate diagnosis are critical to initiate appropriate therapy and prevent prolonged morbidity and long term complications related to this chronic inflammatory disorder.

Figure: Figure 1; Computed Tomography Abdomen and Pelvis demonstrating (A) gastritis and (B) jejunal submucosal edema. EGD demonstrating erythematous mucosa in the (C, D) duodenal bulb

Figure: Figure 2; Histopathological images. A: Proximal esophagus biopsy showing numerous intraepithelial eosinophils (>40 per high power field). B: Random colonic biopsy showing numerous eosinophils filling the lamina propria and forming aggregates in places. C: A cell block made from ascites fluid showing large amount of eosinophils with only rare mesothelial cells, consistent with eosinophilic effusion.
Disclosures:
Keon Karimabady indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mitchelle Zolotarvesky indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jeremy Van indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Madhav Patel indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kadir Isidan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
David Labowitz indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Keon Karimabady, DO1, Mitchelle Zolotarvesky, MD2, Jeremy Van, DO1, Madhav Patel, DO1, Kadir Isidan, MD3, David Labowitz, DO4. P0445 - Eosinophilic Gastrointestinal Disorders (EGID): A Case of Eosinophilic Ascites, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
