Sunday Poster Session
Category: General Endoscopy
P0834 - Burden of Gastrointestinal and Systemic Comorbidities in Patients Diagnosed With GIST During EGD: A Multi-Center Propensity-Matched Study
Sunday, October 26, 2025
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall
- MA
Mohammed Aloqaily, MD (he/him/his)
University of Maryland Medical Center Midtown Campus
Baltimore, MD
Presenting Author(s)
Mohammed Aloqaily, MD1, Omar Abureesh, MD2, Ahmad Abdulraheem, MD3, Pinghsin Hsieh, MD4, Alexander Rabadi, MD5, Ra'Ed Ababneh, MD6, Zaid Al-Fakhouri, MD7, Abdulla Massad, MD8, Bara Abujaber, MBBS9, Qusai Al Zureikat, MD10, Ibrahim Alfarrajin, MD11
1University of Maryland Medical Center Midtown Campus, Baltimore, MD; 2Staten Island University Hospital, Northwell Health, Staten Island, NY; 3MedStar Washington Hospital Center, Washington, DC; 4University of Maryland Medical Center midtown campus, Baltimore, MD; 5McLaren Flint Hospital, Flint, MI; 6MD, Amman, 'Amman, Jordan; 7Case Western Reserve University / MetroHealth, Cleveland, OH; 8University of Texas Medical Branch, Galveston, TX; 9MedStar Washington Hospital Center-Georgetown University, Washington, DC; 10MedStar Heath-Georgetown/Washington Hospital Center, Washington DC, DC; 11Saint Agnes Medical Center, Baltimore, MD
Introduction: Gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs) are uncommon subepithelial tumors often detected incidentally during upper endoscopy. The broader clinical burden of GIST, particularly in relation to gastrointestinal, metabolic, and cardiovascular comorbidities, remains unclear. We aimed to characterize the prevalence of key comorbid conditions among patients diagnosed with GIST during esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) compared to matched controls without GIST.
Methods: This is a retrospective, multi-institutional cohort study, conducted using the TriNetX research network, which aggregates real-time electronic medical records from over 100 healthcare organizations. Adult patients (≥18 years) who underwent esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) between October 1, 2015, and October 1, 2024, were included.
The exposure cohort comprised patients diagnosed with (GIST) within one year of EGD. The control cohort included patients with no GIST diagnosis during the same period. 1:1 propensity score matching was performed based on age, sex, race, and ethnicity, yielding 2,143 patients per group. Baseline prevalence of gastrointestinal, metabolic, cardiovascular, and systemic conditions was assessed using structured diagnosis codes. Between-group differences were evaluated using two-sided statistical tests, with significance defined as p < 0.05.
Results: Following propensity score matching, demographic characteristics were well-balanced between the GIST and non-GIST groups (n=2,143 each). The mean age was 65.0 ± 13.2 years in the GIST group and 64.1 ± 14.9 years in the non-GIST group, with 53.1% female and 58.6% White in both cohorts. GIST patients had higher rates of several upper GI disorders, including GERD, gastritis/duodenitis, peptic ulcers, and constipation. Conversely, patients without GIST were more likely to have systemic comorbidities such as diabetes, hyperlipidemia, hypertension, ischemic heart disease, cerebrovascular disease, and chronic kidney disease (Table 1).
Discussion: Patients diagnosed with GIST during EGD exhibit a higher burden of upper gastrointestinal disorders at baseline, while non-GIST patients have a greater prevalence of systemic cardiometabolic conditions. These distinct comorbidity patterns may inform risk stratification and long-term management strategies following incidental GIST detection during endoscopy.
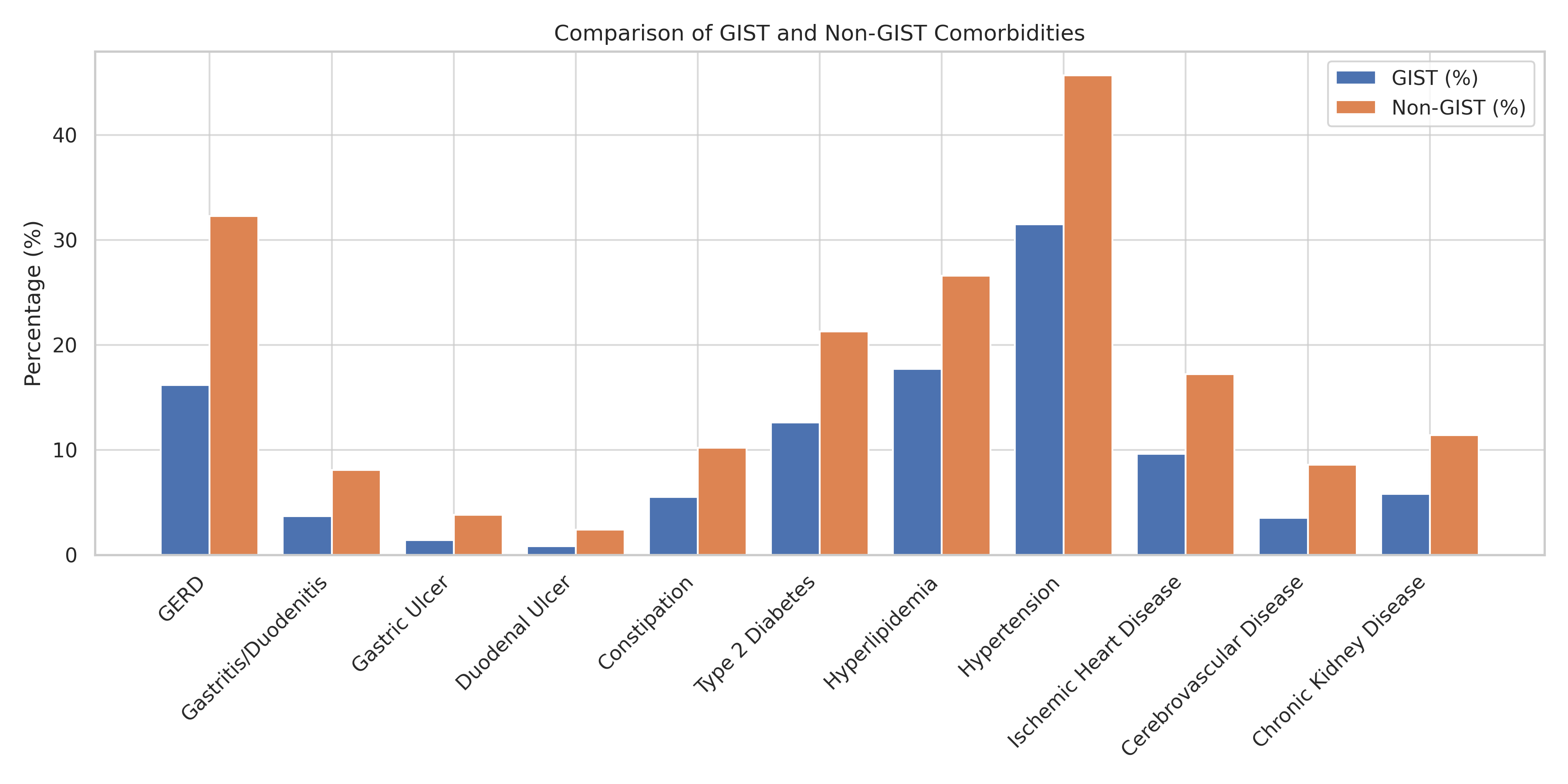
Figure: Table 1. Baseline Gastrointestinal and Systemic Comorbidities in Patients With and Without GIST
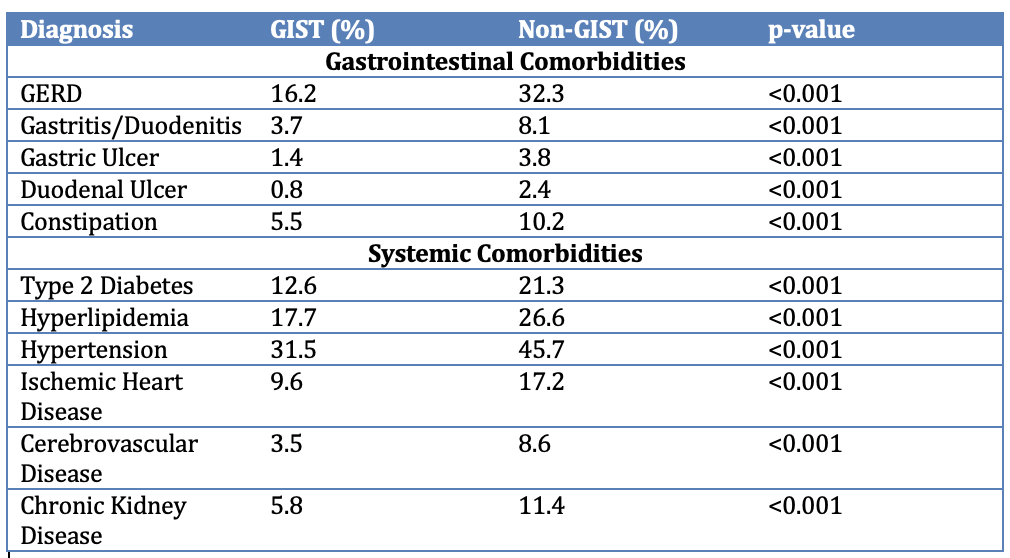
Figure: Figure 1. Distribution of Comorbidities Among Patients With and Without GIST
Disclosures:
Mohammed Aloqaily indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Omar Abureesh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ahmad Abdulraheem indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Pinghsin Hsieh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Alexander Rabadi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ra'Ed Ababneh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Zaid Al-Fakhouri indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Abdulla Massad indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Bara Abujaber indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Qusai Al Zureikat indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ibrahim Alfarrajin indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohammed Aloqaily, MD1, Omar Abureesh, MD2, Ahmad Abdulraheem, MD3, Pinghsin Hsieh, MD4, Alexander Rabadi, MD5, Ra'Ed Ababneh, MD6, Zaid Al-Fakhouri, MD7, Abdulla Massad, MD8, Bara Abujaber, MBBS9, Qusai Al Zureikat, MD10, Ibrahim Alfarrajin, MD11. P0834 - Burden of Gastrointestinal and Systemic Comorbidities in Patients Diagnosed With GIST During EGD: A Multi-Center Propensity-Matched Study, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1University of Maryland Medical Center Midtown Campus, Baltimore, MD; 2Staten Island University Hospital, Northwell Health, Staten Island, NY; 3MedStar Washington Hospital Center, Washington, DC; 4University of Maryland Medical Center midtown campus, Baltimore, MD; 5McLaren Flint Hospital, Flint, MI; 6MD, Amman, 'Amman, Jordan; 7Case Western Reserve University / MetroHealth, Cleveland, OH; 8University of Texas Medical Branch, Galveston, TX; 9MedStar Washington Hospital Center-Georgetown University, Washington, DC; 10MedStar Heath-Georgetown/Washington Hospital Center, Washington DC, DC; 11Saint Agnes Medical Center, Baltimore, MD
Introduction: Gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs) are uncommon subepithelial tumors often detected incidentally during upper endoscopy. The broader clinical burden of GIST, particularly in relation to gastrointestinal, metabolic, and cardiovascular comorbidities, remains unclear. We aimed to characterize the prevalence of key comorbid conditions among patients diagnosed with GIST during esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) compared to matched controls without GIST.
Methods: This is a retrospective, multi-institutional cohort study, conducted using the TriNetX research network, which aggregates real-time electronic medical records from over 100 healthcare organizations. Adult patients (≥18 years) who underwent esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) between October 1, 2015, and October 1, 2024, were included.
The exposure cohort comprised patients diagnosed with (GIST) within one year of EGD. The control cohort included patients with no GIST diagnosis during the same period. 1:1 propensity score matching was performed based on age, sex, race, and ethnicity, yielding 2,143 patients per group. Baseline prevalence of gastrointestinal, metabolic, cardiovascular, and systemic conditions was assessed using structured diagnosis codes. Between-group differences were evaluated using two-sided statistical tests, with significance defined as p < 0.05.
Results: Following propensity score matching, demographic characteristics were well-balanced between the GIST and non-GIST groups (n=2,143 each). The mean age was 65.0 ± 13.2 years in the GIST group and 64.1 ± 14.9 years in the non-GIST group, with 53.1% female and 58.6% White in both cohorts. GIST patients had higher rates of several upper GI disorders, including GERD, gastritis/duodenitis, peptic ulcers, and constipation. Conversely, patients without GIST were more likely to have systemic comorbidities such as diabetes, hyperlipidemia, hypertension, ischemic heart disease, cerebrovascular disease, and chronic kidney disease (Table 1).
Discussion: Patients diagnosed with GIST during EGD exhibit a higher burden of upper gastrointestinal disorders at baseline, while non-GIST patients have a greater prevalence of systemic cardiometabolic conditions. These distinct comorbidity patterns may inform risk stratification and long-term management strategies following incidental GIST detection during endoscopy.

Figure: Table 1. Baseline Gastrointestinal and Systemic Comorbidities in Patients With and Without GIST

Figure: Figure 1. Distribution of Comorbidities Among Patients With and Without GIST
Disclosures:
Mohammed Aloqaily indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Omar Abureesh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ahmad Abdulraheem indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Pinghsin Hsieh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Alexander Rabadi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ra'Ed Ababneh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Zaid Al-Fakhouri indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Abdulla Massad indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Bara Abujaber indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Qusai Al Zureikat indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ibrahim Alfarrajin indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohammed Aloqaily, MD1, Omar Abureesh, MD2, Ahmad Abdulraheem, MD3, Pinghsin Hsieh, MD4, Alexander Rabadi, MD5, Ra'Ed Ababneh, MD6, Zaid Al-Fakhouri, MD7, Abdulla Massad, MD8, Bara Abujaber, MBBS9, Qusai Al Zureikat, MD10, Ibrahim Alfarrajin, MD11. P0834 - Burden of Gastrointestinal and Systemic Comorbidities in Patients Diagnosed With GIST During EGD: A Multi-Center Propensity-Matched Study, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
