Sunday Poster Session
Category: IBD
P1104 - Real-World Effectiveness of Risankizumab on Clinical and Patient-Reported Outcomes in Patients With Moderate-to-Severe Crohn’s Disease in the PPD CorEvitas Inflammatory Bowel Disease Registry
Sunday, October 26, 2025
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Raymond Cross, MD, MS, FACG
The Melissa L. Posner Institute for Digestive Health & Liver Disease, Mercy Medical Center
Baltimore, MD
Presenting Author(s)
Raymond K. Cross, MD, MS, FACG1, Jenny M. Griffith, PharmD2, Alicia Beeghly, MPH, PhD3, Margaux Crabtree, MPH3, Jae Rok Kim, PharmD, MS4, Marie Gurrola, MPH3
1The Melissa L. Posner Institute for Digestive Health & Liver Disease, Mercy Medical Center, Baltimore, MD; 2AbbVie Inc, North Chicago, IL; 3Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA; 4AbbVie Inc, Irvine, CA
Introduction: Risankizumab (RZB) is an interleukin-23A inhibitor approved for treatment of moderate-to-severe Crohn’s disease (CD); however, real-world evidence on RZB use is limited. This study investigated the impact of RZB on clinical and patient-reported outcomes (PROs) among patients with CD in a real-world setting.
Methods: This prospective cohort study included patients with CD who enrolled in the PPDTM CorEvitasTM Inflammatory Bowel Diseases Registry and initiated RZB at or after a Registry visit from 05/03/2017 – 03/01/2025. Disease activity (Harvey Bradshaw Index [HBI]), PRO Measurement Information System measures (PROMIS), and Work Productivity and Activity Impairment (WPAI) questionnaire scores were assessed at RZB initiation (baseline) and 6-month follow-up visits; mean changes were calculated and significance was assessed using paired Student’s t-tests.
Results: Of 127 patients who initiated RZB, 55.1% were female, the mean (standard deviation [SD]) age was 44.7 (15.6) years, and time since diagnosis was 15.3 (13.1) years. At baseline, 20.5% of patients were naive to advanced therapy, 21.3% had 1 and 58.3% had ≥2 prior advanced therapies. Mean (SD) HBI significantly decreased (p=0.014) from 5.3 (5.0) at baseline to 4.2 (4.3) at 6 months and more patients were in remission (HBI < 5) at 6 months (67.0%, 61/91) than at baseline (56.0%, 51/91) (Figure 1). Specifically, patients reporting general well-being as very well and no abdominal pain increased from 32.0% (40/125) to 49.6% (62/125; p< 0.001) and 44.0% (55/125) to 61.6% (77/125; p=0.009), respectively. At 6 months, mean (SD) fatigue (N=123) and pain interference (N=124) scores decreased from 54.6 (11.9) to 51.6 (12.2; p< 0.001) and 53.0 (11.1) to 50.4 (10.7; p=0.004), respectively. At baseline, 56.9% (n=70) and 48.4% (n=60) of patients had above normal (≥55) fatigue and pain levels, which decreased to 45.5% (n=56, p=0.011) and 33.9% (n=42, p=0.002) at 6 months, respectively (Figure 2). Among RZB initiators, 65.1% were employed (82/126); reductions in WPAI impairment while working (81.5% [53/65] to 63.1% [41/65]; p=0.003), WPAI absenteeism (28.8% [19/66] to 15.2% [10/66]; p=0.052) and WPAI activity impairment (76.6% [95/124] to 64.5% [80/124]; p=0.009) were observed from baseline to 6 months.
Discussion: This real-world analysis found RZB significantly reduced disease activity and improved PROs 6 months after initiation, indicating that RZB is an effective treatment in patients with CD who were predominantly advanced-therapy experienced.
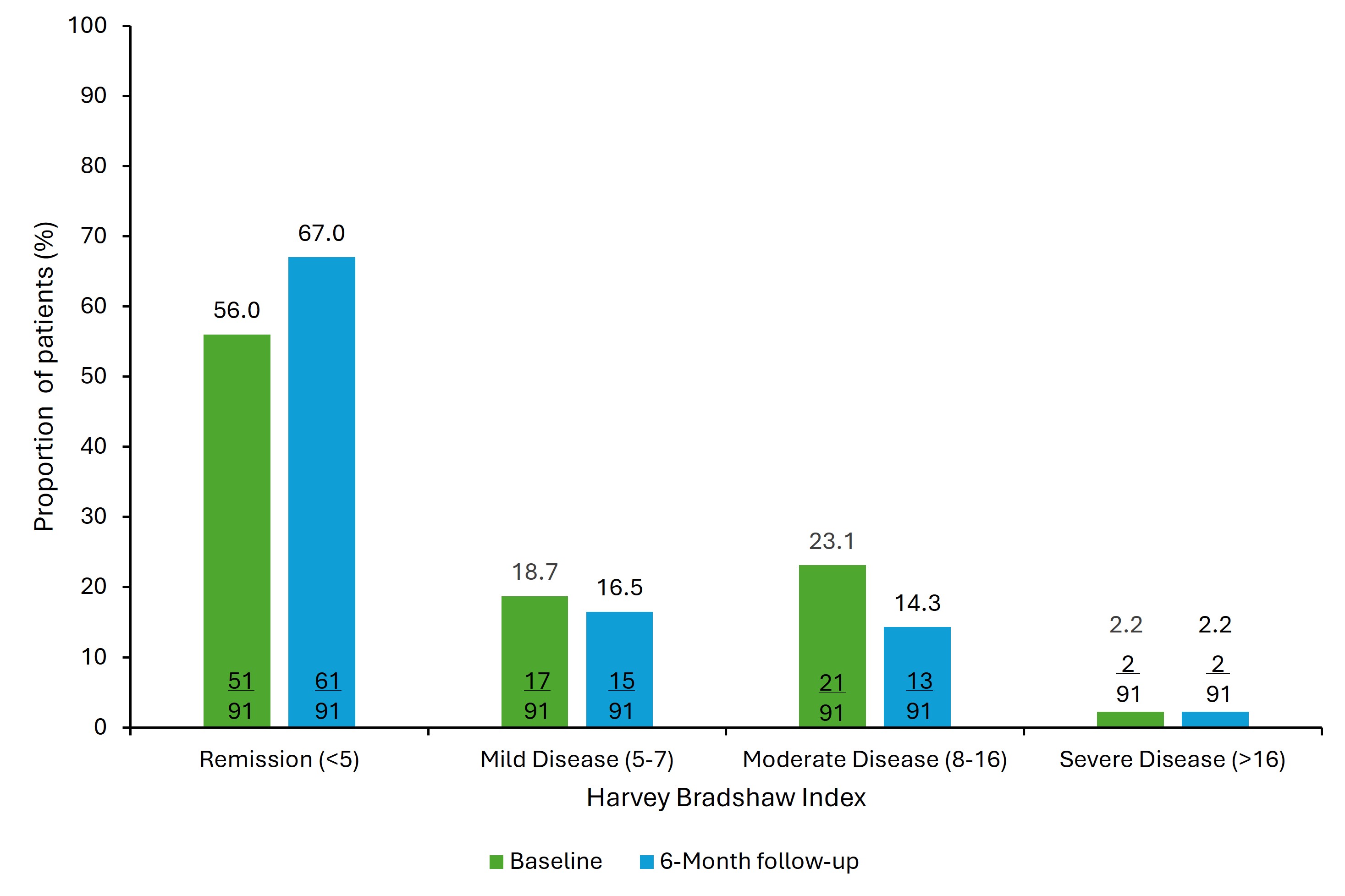
Figure: Figure 1
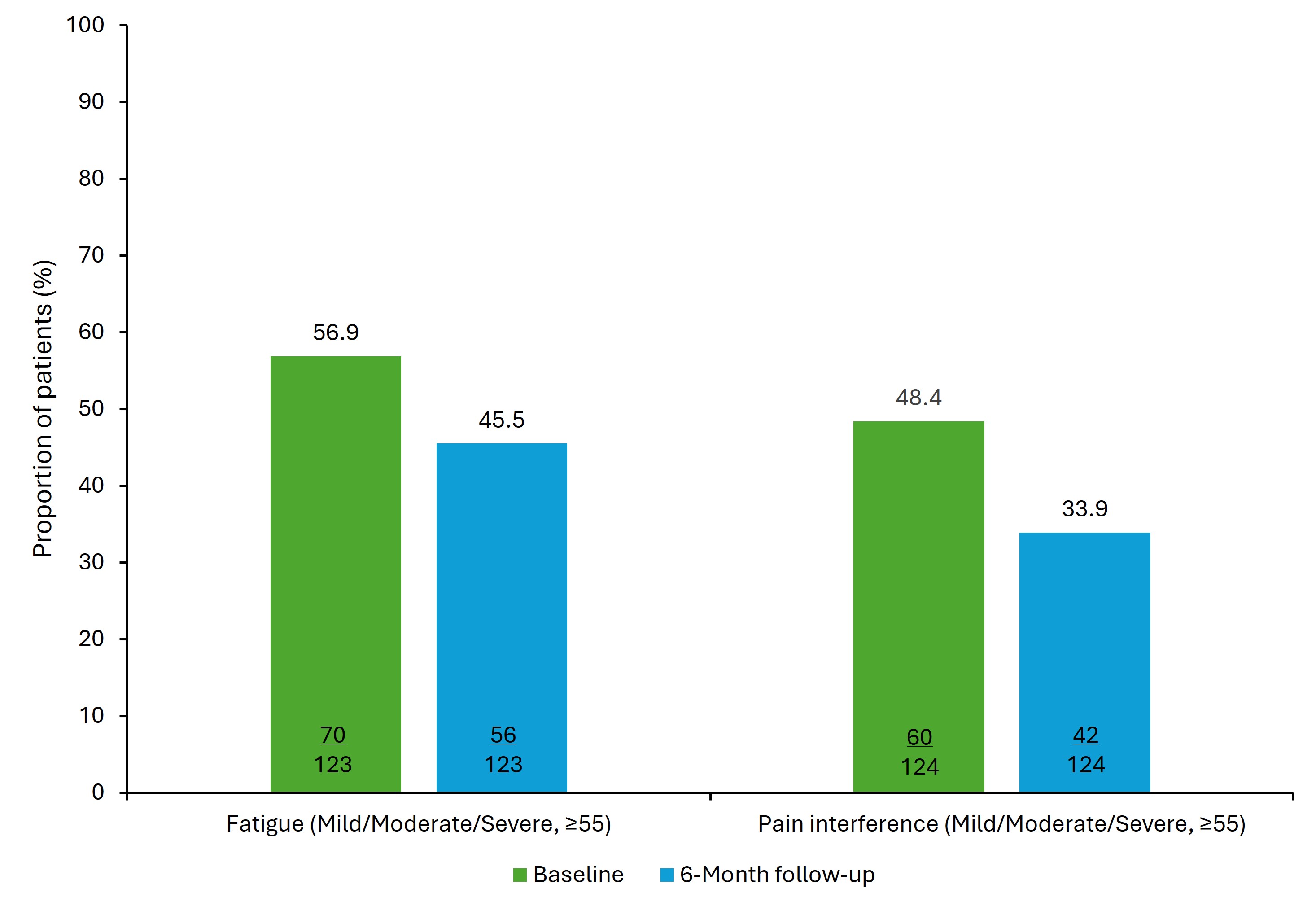
Figure: Figure 2
Disclosures:
Raymond K. Cross: Abbvie – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Consultant, Speakers Bureau. BMS – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Consultant, Speakers Bureau. CorEvitas – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Fresenius Kabi – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Genetech – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Gilead – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. IBD Education Group – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Janssen – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Magellan Health – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Option Care – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Pfizer – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Pharmacosmos – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Samsung Bioepis – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Sandoz – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Takeda – Grant/Research Support.
Jenny M. Griffith: AbbVie – Employee, Stock Options.
Alicia Beeghly: Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc – Employee, Stock-publicly held company(excluding mutual/index funds).
Margaux Crabtree: Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc – Employee, Stock-publicly held company(excluding mutual/index funds).
Jae Rok Kim: AbbVie – Employee, Stock Options.
Marie Gurrola: Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc – Employee.
Raymond K. Cross, MD, MS, FACG1, Jenny M. Griffith, PharmD2, Alicia Beeghly, MPH, PhD3, Margaux Crabtree, MPH3, Jae Rok Kim, PharmD, MS4, Marie Gurrola, MPH3. P1104 - Real-World Effectiveness of Risankizumab on Clinical and Patient-Reported Outcomes in Patients With Moderate-to-Severe Crohn’s Disease in the PPD CorEvitas Inflammatory Bowel Disease Registry, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1The Melissa L. Posner Institute for Digestive Health & Liver Disease, Mercy Medical Center, Baltimore, MD; 2AbbVie Inc, North Chicago, IL; 3Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA; 4AbbVie Inc, Irvine, CA
Introduction: Risankizumab (RZB) is an interleukin-23A inhibitor approved for treatment of moderate-to-severe Crohn’s disease (CD); however, real-world evidence on RZB use is limited. This study investigated the impact of RZB on clinical and patient-reported outcomes (PROs) among patients with CD in a real-world setting.
Methods: This prospective cohort study included patients with CD who enrolled in the PPDTM CorEvitasTM Inflammatory Bowel Diseases Registry and initiated RZB at or after a Registry visit from 05/03/2017 – 03/01/2025. Disease activity (Harvey Bradshaw Index [HBI]), PRO Measurement Information System measures (PROMIS), and Work Productivity and Activity Impairment (WPAI) questionnaire scores were assessed at RZB initiation (baseline) and 6-month follow-up visits; mean changes were calculated and significance was assessed using paired Student’s t-tests.
Results: Of 127 patients who initiated RZB, 55.1% were female, the mean (standard deviation [SD]) age was 44.7 (15.6) years, and time since diagnosis was 15.3 (13.1) years. At baseline, 20.5% of patients were naive to advanced therapy, 21.3% had 1 and 58.3% had ≥2 prior advanced therapies. Mean (SD) HBI significantly decreased (p=0.014) from 5.3 (5.0) at baseline to 4.2 (4.3) at 6 months and more patients were in remission (HBI < 5) at 6 months (67.0%, 61/91) than at baseline (56.0%, 51/91) (Figure 1). Specifically, patients reporting general well-being as very well and no abdominal pain increased from 32.0% (40/125) to 49.6% (62/125; p< 0.001) and 44.0% (55/125) to 61.6% (77/125; p=0.009), respectively. At 6 months, mean (SD) fatigue (N=123) and pain interference (N=124) scores decreased from 54.6 (11.9) to 51.6 (12.2; p< 0.001) and 53.0 (11.1) to 50.4 (10.7; p=0.004), respectively. At baseline, 56.9% (n=70) and 48.4% (n=60) of patients had above normal (≥55) fatigue and pain levels, which decreased to 45.5% (n=56, p=0.011) and 33.9% (n=42, p=0.002) at 6 months, respectively (Figure 2). Among RZB initiators, 65.1% were employed (82/126); reductions in WPAI impairment while working (81.5% [53/65] to 63.1% [41/65]; p=0.003), WPAI absenteeism (28.8% [19/66] to 15.2% [10/66]; p=0.052) and WPAI activity impairment (76.6% [95/124] to 64.5% [80/124]; p=0.009) were observed from baseline to 6 months.
Discussion: This real-world analysis found RZB significantly reduced disease activity and improved PROs 6 months after initiation, indicating that RZB is an effective treatment in patients with CD who were predominantly advanced-therapy experienced.

Figure: Figure 1

Figure: Figure 2
Disclosures:
Raymond K. Cross: Abbvie – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Consultant, Speakers Bureau. BMS – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Consultant, Speakers Bureau. CorEvitas – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Fresenius Kabi – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Genetech – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Gilead – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. IBD Education Group – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Janssen – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Magellan Health – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Option Care – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Pfizer – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Pharmacosmos – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Samsung Bioepis – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Sandoz – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Takeda – Grant/Research Support.
Jenny M. Griffith: AbbVie – Employee, Stock Options.
Alicia Beeghly: Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc – Employee, Stock-publicly held company(excluding mutual/index funds).
Margaux Crabtree: Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc – Employee, Stock-publicly held company(excluding mutual/index funds).
Jae Rok Kim: AbbVie – Employee, Stock Options.
Marie Gurrola: Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc – Employee.
Raymond K. Cross, MD, MS, FACG1, Jenny M. Griffith, PharmD2, Alicia Beeghly, MPH, PhD3, Margaux Crabtree, MPH3, Jae Rok Kim, PharmD, MS4, Marie Gurrola, MPH3. P1104 - Real-World Effectiveness of Risankizumab on Clinical and Patient-Reported Outcomes in Patients With Moderate-to-Severe Crohn’s Disease in the PPD CorEvitas Inflammatory Bowel Disease Registry, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.

