Sunday Poster Session
Category: IBD
P1100 - Safety of Combination Biologic And/or Small Molecule Therapies in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Single-Center Analysis
Sunday, October 26, 2025
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Jacob K. Jamison, BA (he/him/his)
Weill Cornell Medicine
New York, NY
Presenting Author(s)
Award: ACG Presidential Poster Award
Jacob K. Jamison, BA1, Anjile An, MPH1, Caroline J. Young, MS1, Michael Mintz, MD2, Laura Sahyoun, MD2, Randy S. Longman, MD, PhD2, Vinita Jacob, MD2, Ellen J. Scherl, MD2, Dana J. Lukin, MD, PhD, FACG2
1Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, NY; 2Jill Roberts Center for Inflammatory Bowel Disease, Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, NY
Introduction: Despite an increasing variety of treatment options, many inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) patients do not achieve therapy goals. Many require hospitalization and high-risk interventions, such as steroids or surgery. This study evaluates the safety of combination regimens including newer agents in adult IBD patients.
Methods: Adult patients with Crohn’s disease (CD) or ulcerative colitis (UC) treated ≥6 weeks with two concomitant biologic and/or small molecule therapies (including TNF antagonists [TNF-a], anti-integrin agents, IL-(12/)23 inhibitors [IL-12/23i], JAK inhibitors [JAKi], or S1P receptor modulators) were identified via clinical practice and an institutional IBD patient database. Data were obtained on demographics, treatment, and safety outcomes. For patients who received >1 combination, the first combination was used for demographics. Chi-square test was used to analyze categorical variables.
Results: 125 regimens among 102 patients (64 CD, 38 UC) were analyzed with 49% female, 9% Black, and 11% Hispanic; mean age was 40 ±17 years. Average disease duration by combination start was 14 ±12 years. 92% received prior steroids and 88% prior TNF-a. 72% failed ≥2 advanced therapies, and 56% of CD patients had prior surgery.
Mean combination duration was 12.1 ±12.7 months. Of the 62 that were discontinued, 13 (21%) were due to adverse events. 11% of combinations involved IBD surgery during or ≤12 weeks post-cessation. Overall rates of infection and IBD-related hospitalization were 31% and 13%, respectively. There was one case each (1%) of herpes zoster, C. Difficile infection, and a thrombotic event. At the time of combination start, 41 regimens (33%) included baseline steroid treatment. Compared to no steroids at baseline, regimens with baseline steroid use were associated with significantly greater rates of infection (44% vs 24%, p</em>=0.02), infection requiring antibiotics (41% vs 17%, p=0.003), and infection requiring hospitalization (7% vs 0%, p=0.01), with numerically higher rates of any IBD-related hospitalization (15% vs 4.8%, p=0.056).
Discussion: In a large specialty IBD center, combination therapy was generally feasible with an acceptable safety profile among patients with severe, treatment-refractory disease. Baseline treatment with steroids at combination initiation was associated with a >2x higher rate of serious infection and >3x higher rate of IBD-related hospitalization, though the latter did not reach statistical significance.
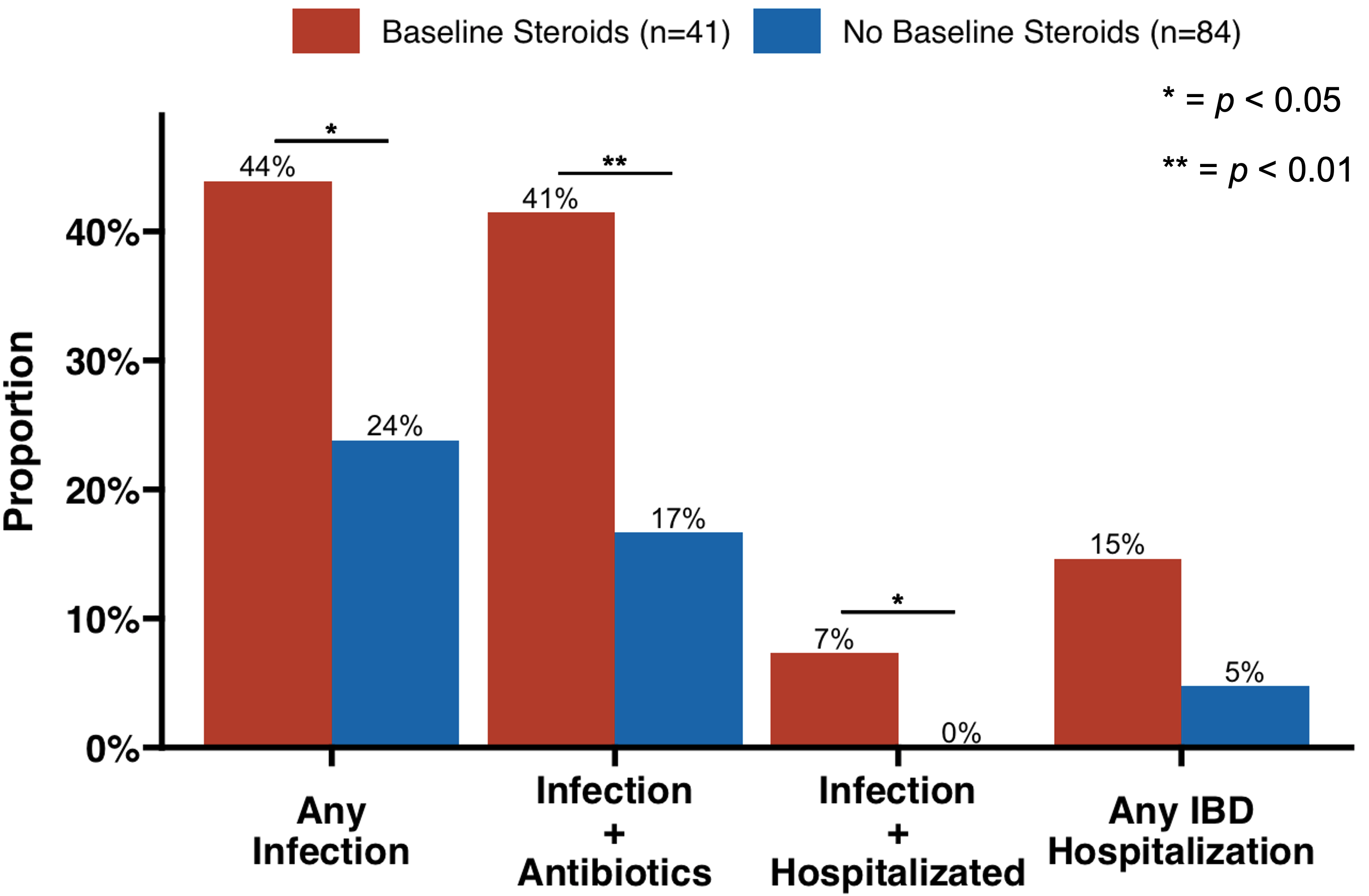
Figure: Figure 1. Adverse event rates by steroid use at baseline.
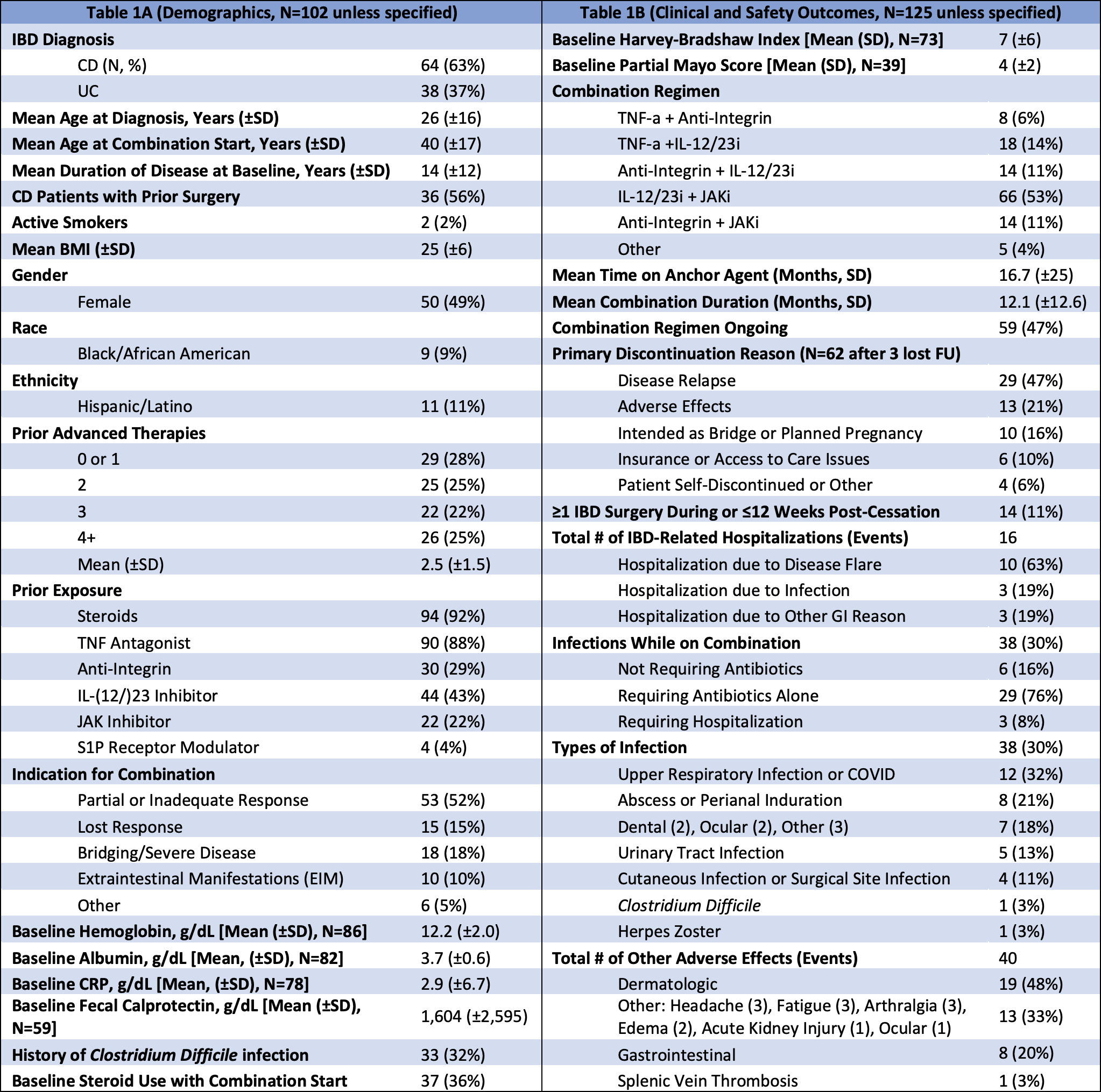
Figure: Table 1. (A) Demographics and (B) clinical and safety outcomes.
Disclosures:
Jacob Jamison indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Anjile An indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Caroline Young indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Michael Mintz indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Laura Sahyoun indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Randy Longman: Ancilia – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Boehringer Ingelheim – Grant/Research Support. CJ Biosciences – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Sanofi – Consultant. Xencor – Consultant.
Vinita Jacob indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ellen Scherl indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Dana Lukin: AbbVie – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Altrubio – Consultant. Boehringer Ingelheim – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Bristol Myers Squibb – Consultant. Johnson & Johnson – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Palatin Technologies – Consultant. Pfizer – Consultant. Prime – Consultant. PSI – Consultant. Takeda – Consultant. Vedanta – Consultant.
Jacob K. Jamison, BA1, Anjile An, MPH1, Caroline J. Young, MS1, Michael Mintz, MD2, Laura Sahyoun, MD2, Randy S. Longman, MD, PhD2, Vinita Jacob, MD2, Ellen J. Scherl, MD2, Dana J. Lukin, MD, PhD, FACG2. P1100 - Safety of Combination Biologic And/or Small Molecule Therapies in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Single-Center Analysis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
Jacob K. Jamison, BA1, Anjile An, MPH1, Caroline J. Young, MS1, Michael Mintz, MD2, Laura Sahyoun, MD2, Randy S. Longman, MD, PhD2, Vinita Jacob, MD2, Ellen J. Scherl, MD2, Dana J. Lukin, MD, PhD, FACG2
1Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, NY; 2Jill Roberts Center for Inflammatory Bowel Disease, Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, NY
Introduction: Despite an increasing variety of treatment options, many inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) patients do not achieve therapy goals. Many require hospitalization and high-risk interventions, such as steroids or surgery. This study evaluates the safety of combination regimens including newer agents in adult IBD patients.
Methods: Adult patients with Crohn’s disease (CD) or ulcerative colitis (UC) treated ≥6 weeks with two concomitant biologic and/or small molecule therapies (including TNF antagonists [TNF-a], anti-integrin agents, IL-(12/)23 inhibitors [IL-12/23i], JAK inhibitors [JAKi], or S1P receptor modulators) were identified via clinical practice and an institutional IBD patient database. Data were obtained on demographics, treatment, and safety outcomes. For patients who received >1 combination, the first combination was used for demographics. Chi-square test was used to analyze categorical variables.
Results: 125 regimens among 102 patients (64 CD, 38 UC) were analyzed with 49% female, 9% Black, and 11% Hispanic; mean age was 40 ±17 years. Average disease duration by combination start was 14 ±12 years. 92% received prior steroids and 88% prior TNF-a. 72% failed ≥2 advanced therapies, and 56% of CD patients had prior surgery.
Mean combination duration was 12.1 ±12.7 months. Of the 62 that were discontinued, 13 (21%) were due to adverse events. 11% of combinations involved IBD surgery during or ≤12 weeks post-cessation. Overall rates of infection and IBD-related hospitalization were 31% and 13%, respectively. There was one case each (1%) of herpes zoster, C. Difficile infection, and a thrombotic event. At the time of combination start, 41 regimens (33%) included baseline steroid treatment. Compared to no steroids at baseline, regimens with baseline steroid use were associated with significantly greater rates of infection (44% vs 24%, p</em>=0.02), infection requiring antibiotics (41% vs 17%, p=0.003), and infection requiring hospitalization (7% vs 0%, p=0.01), with numerically higher rates of any IBD-related hospitalization (15% vs 4.8%, p=0.056).
Discussion: In a large specialty IBD center, combination therapy was generally feasible with an acceptable safety profile among patients with severe, treatment-refractory disease. Baseline treatment with steroids at combination initiation was associated with a >2x higher rate of serious infection and >3x higher rate of IBD-related hospitalization, though the latter did not reach statistical significance.

Figure: Figure 1. Adverse event rates by steroid use at baseline.

Figure: Table 1. (A) Demographics and (B) clinical and safety outcomes.
Disclosures:
Jacob Jamison indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Anjile An indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Caroline Young indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Michael Mintz indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Laura Sahyoun indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Randy Longman: Ancilia – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Boehringer Ingelheim – Grant/Research Support. CJ Biosciences – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Sanofi – Consultant. Xencor – Consultant.
Vinita Jacob indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ellen Scherl indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Dana Lukin: AbbVie – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Altrubio – Consultant. Boehringer Ingelheim – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Bristol Myers Squibb – Consultant. Johnson & Johnson – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Palatin Technologies – Consultant. Pfizer – Consultant. Prime – Consultant. PSI – Consultant. Takeda – Consultant. Vedanta – Consultant.
Jacob K. Jamison, BA1, Anjile An, MPH1, Caroline J. Young, MS1, Michael Mintz, MD2, Laura Sahyoun, MD2, Randy S. Longman, MD, PhD2, Vinita Jacob, MD2, Ellen J. Scherl, MD2, Dana J. Lukin, MD, PhD, FACG2. P1100 - Safety of Combination Biologic And/or Small Molecule Therapies in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Single-Center Analysis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.

