Sunday Poster Session
Category: IBD
P1179 - Early Results of a New Intestinal Ultrasound Program as a Real-Time Disease Monitoring Tool in Patients With Crohn’s Disease: A Retrospective Case Series
Sunday, October 26, 2025
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall
- NE
Nabil El Hage Chehade, MD
Scripps Clinic
San Diego, CA
Presenting Author(s)
Nabil El Hage Chehade, MD1, Tara Alleyasin, MD2, Mazer Ally, MD3, Rebecca Matro, MD4, Gauree Konijeti, MD, MPH, FACG5
1Scripps Clinic, San Diego, CA; 2Scripps Green Hospital, San Diego, CA; 3Scripps Clinic Medical Group, San Diego, CA; 4Scripps Health, San Diego, CA; 5Scripps Clinic Medical Group, La Jolla, CA
Introduction: Intestinal ultrasound (IUS) is a non-invasive and inexpensive point-of-care disease monitoring tool that has been slowly getting incorporated into clinical practice in the US. The aim of our retrospective case series was to assess the accuracy of IUS in the management of Crohn’s disease (CD) patients within our institution’s new IUS program.
Methods: Adult patients ≥ 18 years old with CD who underwent IUS between July and November 2024 at Scripps Clinic were included. Indications for IUS were to assess disease activity or response to therapy. Data on clinical disease activity scores, recent endoscopic/radiographic findings, and fecal calprotectin (FC) were collected. The primary endpoint of the study was to assess the correlation between IUS findings and clinical, biochemical, endoscopic, and radiographic (CT or MR enterography) disease state within six months of IUS.
Results: A total of 69 adult patients (mean age=50.7 years, male gender= 30) with CD (ileal=26, ileocolonic=33, colonic=10) underwent IUS over the designated study period. Of those, 21 (30.4%) had prior abdominal surgeries (small bowel resection=4, ileocecectomy=12, right hemicolectomy=4, colectomy=1). 35% (24/69) of patients failed at least one prior biologic therapy. 47 patients (68%) were on biologic therapy when IUS was performed. IUS was not completed in 2 patients due to limited views and patient discomfort. 43% (29/67) of patients had IUS findings consistent with radiographic remission. IUS findings were concordant with clinical symptoms in 91% (61/67) of patients. IUS findings were also concordant with luminal disease extent/severity, radiographic findings, and FC in 96.8% (30/31), 93.1% (27/29), and 88.5% (46/52) of cases, respectively. The use of IUS helped guide escalating and de-escalating therapy in 28 (41%) and 5 (7%) patients, respectively. 3 patients (4%) were referred to surgery when IUS findings were taken along with clinical context. In the remaining 52% of patients, IUS was helpful to confirm radiographic remission and response, which led to the continuation of the same therapy.
Discussion: Our retrospective study demonstrates that IUS is a promising disease monitoring tool in CD patients as findings accurately correlate with clinical symptoms as well as biochemical, endoscopic, and radiographic disease state. It helped provide valuable real-time data, which led to therapy modification in almost 50% of included patients.
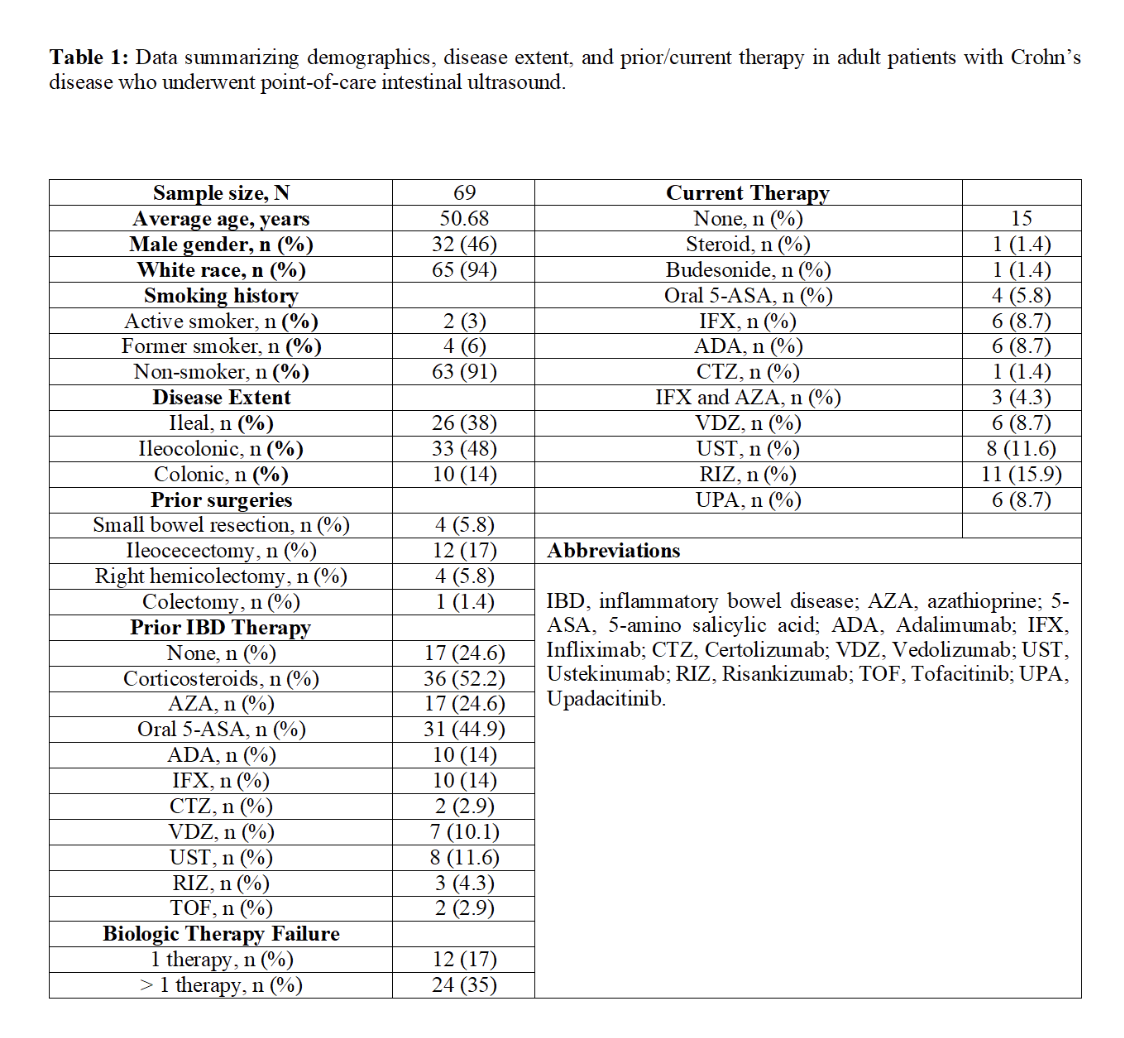
Figure: Table 1: Data summarizing demographics, disease extent, and prior/current therapy in adult patients with Crohn’s disease who underwent point-of-care intestinal ultrasound.
Disclosures:
Nabil El Hage Chehade indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Tara Alleyasin indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mazer Ally: Abbvie – Speakers Bureau. Lilly – Advisory Committee/Board Member.
Rebecca Matro indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Gauree Konijeti: Abbvie – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Johnson and Johnson – Consultant. Lilly – Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Pfizer – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Takeda – Speakers Bureau. WellTheory – Consultant, Stock Options.
Nabil El Hage Chehade, MD1, Tara Alleyasin, MD2, Mazer Ally, MD3, Rebecca Matro, MD4, Gauree Konijeti, MD, MPH, FACG5. P1179 - Early Results of a New Intestinal Ultrasound Program as a Real-Time Disease Monitoring Tool in Patients With Crohn’s Disease: A Retrospective Case Series, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Scripps Clinic, San Diego, CA; 2Scripps Green Hospital, San Diego, CA; 3Scripps Clinic Medical Group, San Diego, CA; 4Scripps Health, San Diego, CA; 5Scripps Clinic Medical Group, La Jolla, CA
Introduction: Intestinal ultrasound (IUS) is a non-invasive and inexpensive point-of-care disease monitoring tool that has been slowly getting incorporated into clinical practice in the US. The aim of our retrospective case series was to assess the accuracy of IUS in the management of Crohn’s disease (CD) patients within our institution’s new IUS program.
Methods: Adult patients ≥ 18 years old with CD who underwent IUS between July and November 2024 at Scripps Clinic were included. Indications for IUS were to assess disease activity or response to therapy. Data on clinical disease activity scores, recent endoscopic/radiographic findings, and fecal calprotectin (FC) were collected. The primary endpoint of the study was to assess the correlation between IUS findings and clinical, biochemical, endoscopic, and radiographic (CT or MR enterography) disease state within six months of IUS.
Results: A total of 69 adult patients (mean age=50.7 years, male gender= 30) with CD (ileal=26, ileocolonic=33, colonic=10) underwent IUS over the designated study period. Of those, 21 (30.4%) had prior abdominal surgeries (small bowel resection=4, ileocecectomy=12, right hemicolectomy=4, colectomy=1). 35% (24/69) of patients failed at least one prior biologic therapy. 47 patients (68%) were on biologic therapy when IUS was performed. IUS was not completed in 2 patients due to limited views and patient discomfort. 43% (29/67) of patients had IUS findings consistent with radiographic remission. IUS findings were concordant with clinical symptoms in 91% (61/67) of patients. IUS findings were also concordant with luminal disease extent/severity, radiographic findings, and FC in 96.8% (30/31), 93.1% (27/29), and 88.5% (46/52) of cases, respectively. The use of IUS helped guide escalating and de-escalating therapy in 28 (41%) and 5 (7%) patients, respectively. 3 patients (4%) were referred to surgery when IUS findings were taken along with clinical context. In the remaining 52% of patients, IUS was helpful to confirm radiographic remission and response, which led to the continuation of the same therapy.
Discussion: Our retrospective study demonstrates that IUS is a promising disease monitoring tool in CD patients as findings accurately correlate with clinical symptoms as well as biochemical, endoscopic, and radiographic disease state. It helped provide valuable real-time data, which led to therapy modification in almost 50% of included patients.

Figure: Table 1: Data summarizing demographics, disease extent, and prior/current therapy in adult patients with Crohn’s disease who underwent point-of-care intestinal ultrasound.
Disclosures:
Nabil El Hage Chehade indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Tara Alleyasin indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mazer Ally: Abbvie – Speakers Bureau. Lilly – Advisory Committee/Board Member.
Rebecca Matro indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Gauree Konijeti: Abbvie – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Johnson and Johnson – Consultant. Lilly – Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Pfizer – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Takeda – Speakers Bureau. WellTheory – Consultant, Stock Options.
Nabil El Hage Chehade, MD1, Tara Alleyasin, MD2, Mazer Ally, MD3, Rebecca Matro, MD4, Gauree Konijeti, MD, MPH, FACG5. P1179 - Early Results of a New Intestinal Ultrasound Program as a Real-Time Disease Monitoring Tool in Patients With Crohn’s Disease: A Retrospective Case Series, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
