Sunday Poster Session
Category: Liver
P1554 - Risk of Non-Gastrointestinal Solid Organ Malignancy in Patients With Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease: A US-based Propensity Matched Cohort Study
Sunday, October 26, 2025
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Rishi Chowdhary, MD (he/him/his)
Case Western Reserve University / MetroHealth
Cleveland, OH
Presenting Author(s)
Rishi Chowdhary, MD1, Harsh Vadnagara, MBBS2, Thai Hau Koo, MD3, Kirti Arora, 4, Dhruvi A. Shah, MD5, Rohit Goyal, MD6, Arshia Sethi, 7, Shivam Kalra, MBBS, MHA8, Samiksha Jain, MBBS9
1Case Western Reserve University / MetroHealth, Cleveland, OH; 2BJ Medical College, Cleveland, OH; 3University of Sciences Malaysia Specialist Hospital, Kelantan, Kelantan, Malaysia; 4Cleveland Clinic Akron General, Akron, OH; 5University of Maryland Medical Center, Mahwah, NJ; 6Louisiana State University, Shreveport, LA; 7Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY; 8Trident Medical Center, North Charleston, SC; 9Guntur Medical College, India, Guntur, Andhra Pradesh, India
Introduction: Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD), affecting over one-third of the global population by 2030, represents the most prevalent chronic liver condition worldwide. While MASLD's association with hepatocellular carcinoma is established, its relationship with extrahepatic malignancies remains poorly defined. We investigated the risk of overall and site-specific non-gastrointestinal cancers in MASLD patients using comprehensive real-world data.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective cohort study using TriNetX, a federated electronic health record (EHR) network comprising 69 U.S. healthcare organizations. Adults (≥18 years) with MASLD were identified using ICD-10 codes (K75.81, K76.0) between 2010–2020, with radiologic confirmation. Patients with alcohol-related liver disease, viral hepatitis, autoimmune liver disease, organ transplant, HIV, or prior malignancy were excluded. Propensity score matching (1:1) was performed for demographics, comorbidities, and smoking history, yielding matched cohorts (n=360,650 each). Outcomes included overall and site-specific cancers (thyroid, breast, kidney, prostate, lung). Odds ratios (ORs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) and Kaplan-Meier analyses were performed.
Results: MASLD patients demonstrated a significantly elevated malignancy risk compared to matched controls (OR 1.35; 95% CI: 1.33–1.36; p< 0.001). Site-specific analysis revealed increased risks for thyroid cancer (OR 1.32; 95% CI: 1.20–1.46), breast cancer (OR 1.17; 95% CI: 1.11–1.23), kidney cancer (OR 1.34; 95% CI: 1.24–1.46), and prostate cancer (OR 1.13; 95% CI: 1.07–1.20). Notably, lung cancer risk remained unchanged (OR 1.03; 95% CI: 0.97–1.09). Sex-stratified analysis revealed females experienced higher overall malignancy burden than males (24.5% vs. 20.1%; OR 1.29; 95% CI: 1.27–1.32), with males showing predominant risks for prostate and kidney cancers.
Discussion: This large-scale analysis establishes MASLD as an independent risk factor for multiple extrahepatic malignancies, with a 35% increased overall cancer risk. The pronounced associations with hormone-sensitive cancers (thyroid, breast, prostate) and kidney cancer suggest shared metabolic pathways linking hepatic steatosis to carcinogenesis. These findings mandate comprehensive cancer surveillance strategies in MASLD patients, particularly women, and highlight the systemic nature of metabolic dysfunction beyond hepatic manifestations.
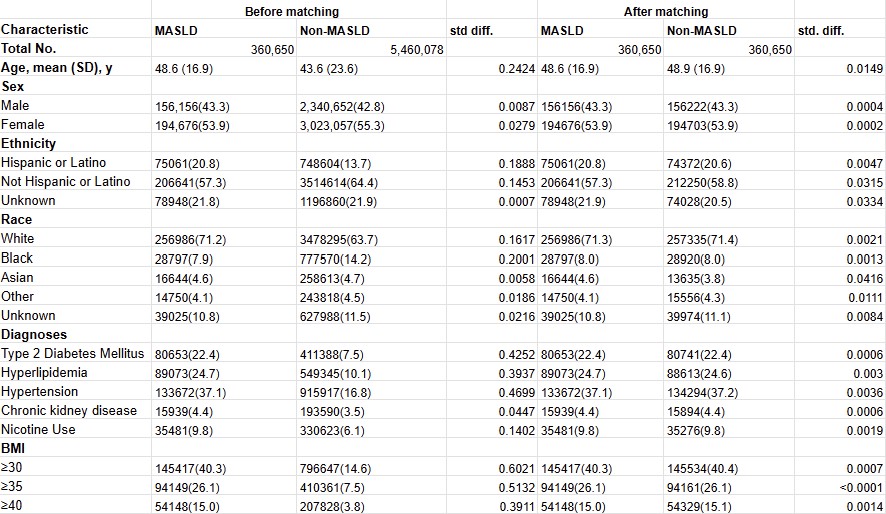
Figure: Forest plots showing the risk of site-specific malignancies in MASLD versus non-MASLD populations (left) and sex-stratified cancer risk among MASLD patients (right), expressed as odds ratios (OR) with 95% confidence intervals.
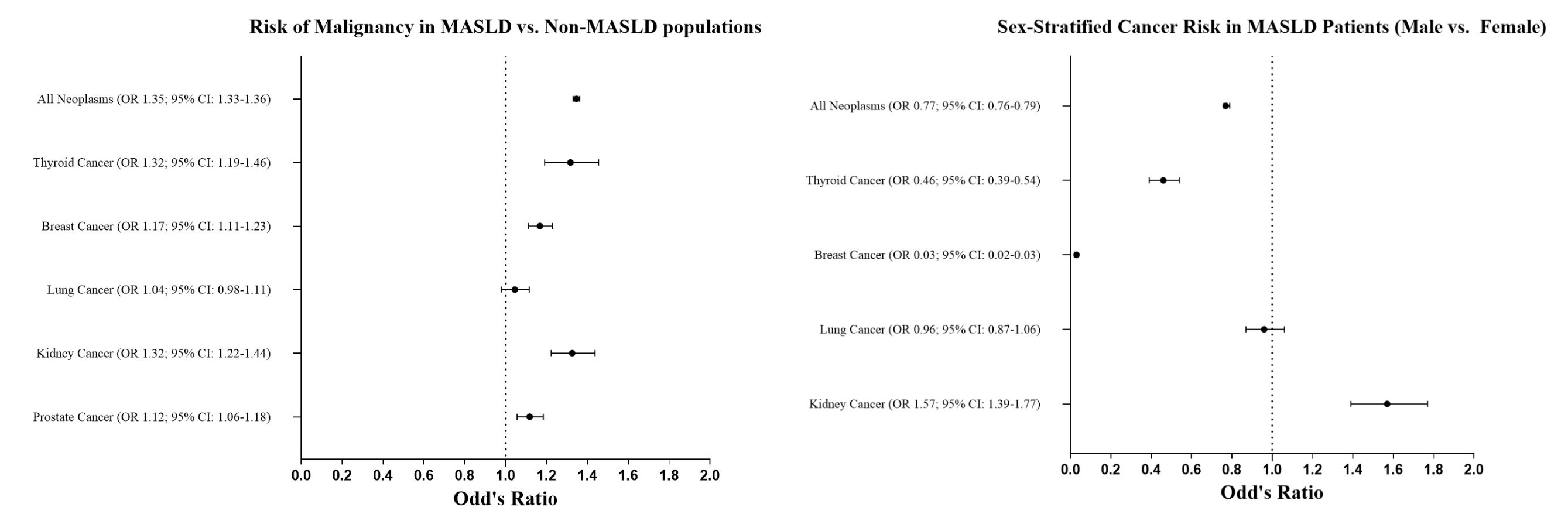
Figure: Baseline Demographics, Metabolic Comorbidities, and BMI in MASLD and Non-MASLD Cohorts Before and After Propensity Score Matching.
MASLD = Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease; SD = Standard deviation; BMI = Body mass index
Disclosures:
Rishi Chowdhary indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Harsh Vadnagara indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Thai Hau Koo indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kirti Arora indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Dhruvi Shah indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rohit Goyal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Arshia Sethi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Shivam Kalra indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Samiksha Jain indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rishi Chowdhary, MD1, Harsh Vadnagara, MBBS2, Thai Hau Koo, MD3, Kirti Arora, 4, Dhruvi A. Shah, MD5, Rohit Goyal, MD6, Arshia Sethi, 7, Shivam Kalra, MBBS, MHA8, Samiksha Jain, MBBS9. P1554 - Risk of Non-Gastrointestinal Solid Organ Malignancy in Patients With Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease: A US-based Propensity Matched Cohort Study, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Case Western Reserve University / MetroHealth, Cleveland, OH; 2BJ Medical College, Cleveland, OH; 3University of Sciences Malaysia Specialist Hospital, Kelantan, Kelantan, Malaysia; 4Cleveland Clinic Akron General, Akron, OH; 5University of Maryland Medical Center, Mahwah, NJ; 6Louisiana State University, Shreveport, LA; 7Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY; 8Trident Medical Center, North Charleston, SC; 9Guntur Medical College, India, Guntur, Andhra Pradesh, India
Introduction: Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD), affecting over one-third of the global population by 2030, represents the most prevalent chronic liver condition worldwide. While MASLD's association with hepatocellular carcinoma is established, its relationship with extrahepatic malignancies remains poorly defined. We investigated the risk of overall and site-specific non-gastrointestinal cancers in MASLD patients using comprehensive real-world data.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective cohort study using TriNetX, a federated electronic health record (EHR) network comprising 69 U.S. healthcare organizations. Adults (≥18 years) with MASLD were identified using ICD-10 codes (K75.81, K76.0) between 2010–2020, with radiologic confirmation. Patients with alcohol-related liver disease, viral hepatitis, autoimmune liver disease, organ transplant, HIV, or prior malignancy were excluded. Propensity score matching (1:1) was performed for demographics, comorbidities, and smoking history, yielding matched cohorts (n=360,650 each). Outcomes included overall and site-specific cancers (thyroid, breast, kidney, prostate, lung). Odds ratios (ORs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) and Kaplan-Meier analyses were performed.
Results: MASLD patients demonstrated a significantly elevated malignancy risk compared to matched controls (OR 1.35; 95% CI: 1.33–1.36; p< 0.001). Site-specific analysis revealed increased risks for thyroid cancer (OR 1.32; 95% CI: 1.20–1.46), breast cancer (OR 1.17; 95% CI: 1.11–1.23), kidney cancer (OR 1.34; 95% CI: 1.24–1.46), and prostate cancer (OR 1.13; 95% CI: 1.07–1.20). Notably, lung cancer risk remained unchanged (OR 1.03; 95% CI: 0.97–1.09). Sex-stratified analysis revealed females experienced higher overall malignancy burden than males (24.5% vs. 20.1%; OR 1.29; 95% CI: 1.27–1.32), with males showing predominant risks for prostate and kidney cancers.
Discussion: This large-scale analysis establishes MASLD as an independent risk factor for multiple extrahepatic malignancies, with a 35% increased overall cancer risk. The pronounced associations with hormone-sensitive cancers (thyroid, breast, prostate) and kidney cancer suggest shared metabolic pathways linking hepatic steatosis to carcinogenesis. These findings mandate comprehensive cancer surveillance strategies in MASLD patients, particularly women, and highlight the systemic nature of metabolic dysfunction beyond hepatic manifestations.

Figure: Forest plots showing the risk of site-specific malignancies in MASLD versus non-MASLD populations (left) and sex-stratified cancer risk among MASLD patients (right), expressed as odds ratios (OR) with 95% confidence intervals.

Figure: Baseline Demographics, Metabolic Comorbidities, and BMI in MASLD and Non-MASLD Cohorts Before and After Propensity Score Matching.
MASLD = Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease; SD = Standard deviation; BMI = Body mass index
Disclosures:
Rishi Chowdhary indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Harsh Vadnagara indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Thai Hau Koo indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kirti Arora indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Dhruvi Shah indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rohit Goyal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Arshia Sethi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Shivam Kalra indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Samiksha Jain indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rishi Chowdhary, MD1, Harsh Vadnagara, MBBS2, Thai Hau Koo, MD3, Kirti Arora, 4, Dhruvi A. Shah, MD5, Rohit Goyal, MD6, Arshia Sethi, 7, Shivam Kalra, MBBS, MHA8, Samiksha Jain, MBBS9. P1554 - Risk of Non-Gastrointestinal Solid Organ Malignancy in Patients With Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease: A US-based Propensity Matched Cohort Study, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.

