Monday Poster Session
Category: Esophagus
P2771 - Causes of Esophageal Food Bolus Impactions
Monday, October 27, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Ammar Ahmad, MD
Wright State University Boonshoft School of Medicine
Tipp City, OH
Presenting Author(s)
Ammar Ahmad, MD1, Drew Triplett, DO2, Sangeeta Agrawal, MD2
1Wright State University Boonshoft School of Medicine, Tipp City, OH; 2Wright State University Boonshoft School of Medicine, Dayton, OH
Introduction: Food bolus impaction is a frequently encountered clinical condition that often requires endoscopic intervention for resolution. In the United States, the estimated annual incidence of esophageal food bolus impaction is approximately 13 episodes per 100,000 people, with a notably upward trend in incidence observed over time. The primary objective of our study was to explore the underlying causes of food bolus impaction.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective analysis of endoscopies completed for food bolus impaction within Premier Health System in Dayton, OH, from January 2010 to December 2020. This study included all adults aged 18 and older who presented with food bolus impaction, underwent endoscopy for resolution, and had esophageal biopsies performed during the endoscopy.
Results: In total, 261 cases of food bolus impaction were identified who required endoscopy and underwent biopsy during endoscopy. The mean age of patients who presented with esophageal food bolus impaction was 46.5 years. 186 (71%) patients were male, and 75 (29%) patients were female. The most common cause of esophageal food bolus impaction was eosinophilic esophagitis (134 patients, 51.3%). Esophageal strictures were the second most common cause of esophageal food bolus impaction (58 patients, 22.2%). No clear cause was identified in 53 patients (20.3%). 8 patients had Schatzki’s ring (3.1%), 6 patients had esophageal cancer (2.3%), and 2 patients had prior diagnosis of achalasia (0.8%).
Discussion: Our study highlights that eosinophilic esophagitis is the most common cause of food bolus impaction among adults. This highlights the importance of getting appropriate biopsies for diagnosis of Eosinophilic Esophagitis on index endoscopy as treating the underlying condition promptly is crucial for tailoring effective treatment and preventing recurrence of impactions.
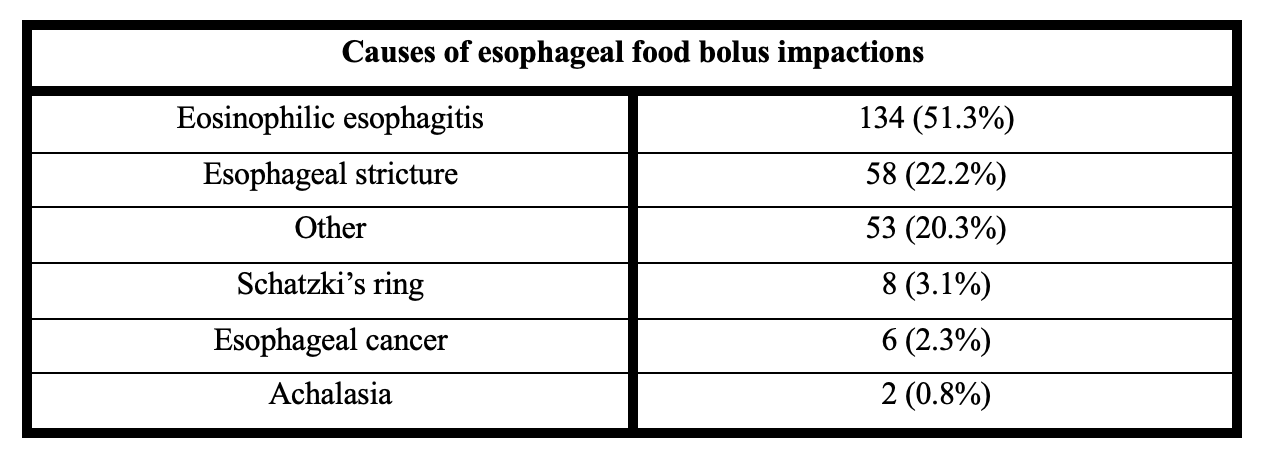
Figure: Table 1: Causes of esophageal food bolus impactions
Disclosures:
Ammar Ahmad indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Drew Triplett indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sangeeta Agrawal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ammar Ahmad, MD1, Drew Triplett, DO2, Sangeeta Agrawal, MD2. P2771 - Causes of Esophageal Food Bolus Impactions, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Wright State University Boonshoft School of Medicine, Tipp City, OH; 2Wright State University Boonshoft School of Medicine, Dayton, OH
Introduction: Food bolus impaction is a frequently encountered clinical condition that often requires endoscopic intervention for resolution. In the United States, the estimated annual incidence of esophageal food bolus impaction is approximately 13 episodes per 100,000 people, with a notably upward trend in incidence observed over time. The primary objective of our study was to explore the underlying causes of food bolus impaction.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective analysis of endoscopies completed for food bolus impaction within Premier Health System in Dayton, OH, from January 2010 to December 2020. This study included all adults aged 18 and older who presented with food bolus impaction, underwent endoscopy for resolution, and had esophageal biopsies performed during the endoscopy.
Results: In total, 261 cases of food bolus impaction were identified who required endoscopy and underwent biopsy during endoscopy. The mean age of patients who presented with esophageal food bolus impaction was 46.5 years. 186 (71%) patients were male, and 75 (29%) patients were female. The most common cause of esophageal food bolus impaction was eosinophilic esophagitis (134 patients, 51.3%). Esophageal strictures were the second most common cause of esophageal food bolus impaction (58 patients, 22.2%). No clear cause was identified in 53 patients (20.3%). 8 patients had Schatzki’s ring (3.1%), 6 patients had esophageal cancer (2.3%), and 2 patients had prior diagnosis of achalasia (0.8%).
Discussion: Our study highlights that eosinophilic esophagitis is the most common cause of food bolus impaction among adults. This highlights the importance of getting appropriate biopsies for diagnosis of Eosinophilic Esophagitis on index endoscopy as treating the underlying condition promptly is crucial for tailoring effective treatment and preventing recurrence of impactions.

Figure: Table 1: Causes of esophageal food bolus impactions
Disclosures:
Ammar Ahmad indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Drew Triplett indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sangeeta Agrawal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ammar Ahmad, MD1, Drew Triplett, DO2, Sangeeta Agrawal, MD2. P2771 - Causes of Esophageal Food Bolus Impactions, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
