Monday Poster Session
Category: Biliary/Pancreas
P2247 - Role of Cholangioscopy in the Work-up of Bile Duct Lesions With Elevated CA 19-9 and AFP
Monday, October 27, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall
- IG
Ismail Ghafary, MD
University of Connecticut Health Center
Farmington, CT
Presenting Author(s)
Ismail Ghafary, MD1, Neil Khoury, MD1, Karthik Mathialagan, MD2, Mesut Toprak, MD1, Murali Dharan, 3
1University of Connecticut Health Center, Farmington, CT; 2University of Connecticut, Farmington, CT; 3Employed, Farmington, CT
Introduction: ERCP with per-oral single-operator cholangioscopy (PSOC) is invaluable in evaluating pancreatic and biliary diseases. This study explores a unique application of PSOC.
Case Description/
Methods: A 67-year-old male with compensated cirrhosis and HCV-HIV co-infection presented with abdominal pain and jaundice. MRI showed cirrhosis, capsular retraction of the right lateral lobe, right intrahepatic biliary dilation, and non-dilated extrahepatic bile duct. There was enhancement in segment 5 extending to segment 4B, with nodularity near the main portal vein. AFP and CA 19-9 levels were elevated. ERCP with PSOC revealed a stricture and nodular mass at the hilar confluence.
Biopsies revealed atypical cells with hepatoid differentiation. Immunohistochemical stains were Hep-par positive and CK7 negative consistent with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
Discussion: Biliary strictures are common in cholangiocarcinoma (CCA) but are rare with HCC (1). Bile duct invasion (BDI) by HCC can be misdiagnosed as cholecystitis, cholangitis, choledocholithiasis, or CCA (2). Cirrhosis is often present in HCC with BDI, and on PSOC, a non-circumferential stricture and a friable luminal mass with villiform surface and increased vascularity is usually seen. The lesion is often located at the hilar confluence and can be covered with tumor capsule (3), so scraping the lesion improves tissue diagnosis (4). Literature on PSOC diagnosis of HCC has mainly commented on AFP levels. At least one case of combined HCC-CCA on PSOC-directed biopsies has been reported. In our patient, elevation of both CA 19-9 and AFP levels with abnormal biliary imaging presented a conundrum. PSOC-directed biopsies established the correct diagnosis. To the best of our knowledge, this entity has not been previously recognized. CA 19-9 levels could have been elevated due to biliary obstruction or HCC (5).
1. Lin Z, Han M, Zhou Z. Biosci Trends. 2019;13:77–85.
2. Nagaria TS, Raijman I, Othman MO, et al. iGIE. 2022;1(1):62–76.
3. Hiba M, Aokawa M, Goto T, et al. J Rural Med. 2024;19(1):44–48.
4. Ito R, Kobayashi M, Ohtsuka K, et al. VideoGIE. 2021;6(8):354–357.
5. Alhadi MI, Chutturghoon VK, Kwabena G, et al. Iran J Public Health. 2019;48(2):314–322.
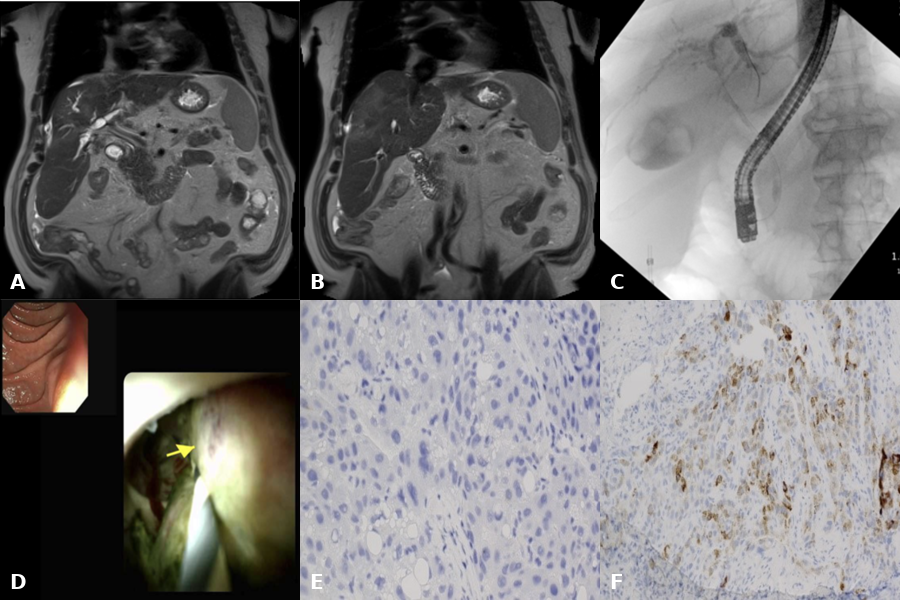
Figure: A & B: MRI with biliary obstruction & hepatic lesion in segments 5 & 4
C: Cholangiogram with biliary stricture at the confluence
D: PSOC with mass at the confluence
E: Biopsy of mass showing tumor cells with hepatocytic differentiation on H&E stain
F: IHC revealing Hep-par-positive cells
Disclosures:
Ismail Ghafary indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Neil Khoury indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Karthik Mathialagan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mesut Toprak indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Murali Dharan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ismail Ghafary, MD1, Neil Khoury, MD1, Karthik Mathialagan, MD2, Mesut Toprak, MD1, Murali Dharan, 3. P2247 - Role of Cholangioscopy in the Work-up of Bile Duct Lesions With Elevated CA 19-9 and AFP, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1University of Connecticut Health Center, Farmington, CT; 2University of Connecticut, Farmington, CT; 3Employed, Farmington, CT
Introduction: ERCP with per-oral single-operator cholangioscopy (PSOC) is invaluable in evaluating pancreatic and biliary diseases. This study explores a unique application of PSOC.
Case Description/
Methods: A 67-year-old male with compensated cirrhosis and HCV-HIV co-infection presented with abdominal pain and jaundice. MRI showed cirrhosis, capsular retraction of the right lateral lobe, right intrahepatic biliary dilation, and non-dilated extrahepatic bile duct. There was enhancement in segment 5 extending to segment 4B, with nodularity near the main portal vein. AFP and CA 19-9 levels were elevated. ERCP with PSOC revealed a stricture and nodular mass at the hilar confluence.
Biopsies revealed atypical cells with hepatoid differentiation. Immunohistochemical stains were Hep-par positive and CK7 negative consistent with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
Discussion: Biliary strictures are common in cholangiocarcinoma (CCA) but are rare with HCC (1). Bile duct invasion (BDI) by HCC can be misdiagnosed as cholecystitis, cholangitis, choledocholithiasis, or CCA (2). Cirrhosis is often present in HCC with BDI, and on PSOC, a non-circumferential stricture and a friable luminal mass with villiform surface and increased vascularity is usually seen. The lesion is often located at the hilar confluence and can be covered with tumor capsule (3), so scraping the lesion improves tissue diagnosis (4). Literature on PSOC diagnosis of HCC has mainly commented on AFP levels. At least one case of combined HCC-CCA on PSOC-directed biopsies has been reported. In our patient, elevation of both CA 19-9 and AFP levels with abnormal biliary imaging presented a conundrum. PSOC-directed biopsies established the correct diagnosis. To the best of our knowledge, this entity has not been previously recognized. CA 19-9 levels could have been elevated due to biliary obstruction or HCC (5).
1. Lin Z, Han M, Zhou Z. Biosci Trends. 2019;13:77–85.
2. Nagaria TS, Raijman I, Othman MO, et al. iGIE. 2022;1(1):62–76.
3. Hiba M, Aokawa M, Goto T, et al. J Rural Med. 2024;19(1):44–48.
4. Ito R, Kobayashi M, Ohtsuka K, et al. VideoGIE. 2021;6(8):354–357.
5. Alhadi MI, Chutturghoon VK, Kwabena G, et al. Iran J Public Health. 2019;48(2):314–322.

Figure: A & B: MRI with biliary obstruction & hepatic lesion in segments 5 & 4
C: Cholangiogram with biliary stricture at the confluence
D: PSOC with mass at the confluence
E: Biopsy of mass showing tumor cells with hepatocytic differentiation on H&E stain
F: IHC revealing Hep-par-positive cells
Disclosures:
Ismail Ghafary indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Neil Khoury indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Karthik Mathialagan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mesut Toprak indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Murali Dharan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ismail Ghafary, MD1, Neil Khoury, MD1, Karthik Mathialagan, MD2, Mesut Toprak, MD1, Murali Dharan, 3. P2247 - Role of Cholangioscopy in the Work-up of Bile Duct Lesions With Elevated CA 19-9 and AFP, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
