Sunday Poster Session
Category: Stomach and Spleen
P2132 - Outcomes of Partial Splenic Embolization for Severe Thrombocytopenia in Decompensated Cirrhosis: A Single Center Case Series
Sunday, October 26, 2025
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall
- JW
Jennifer L. Wiese, MD
Marshall University Joan C. Edwards School of Medicine
Huntington, WV
Presenting Author(s)
Jennifer L. Wiese, MD1, Yonas Fetle, MD1, Yasir Rajwana, MD2, Lauren Searls, MD2, Adamsegd Gebremedhen, MD1, Mujtaba Mohamed, MD1, Elizabeth Harris, MD1
1Marshall University Joan C. Edwards School of Medicine, Huntington, WV; 2Joan C. Edwards School of Medicine, Marshall University, Huntington, WV
Introduction: Thrombocytopenia in decompensated cirrhosis increases risk for bleeding which can delay critical procedures. Treatment options include platelet transfusion, partial splenic embolization (PSE), and splenectomy. While PSE is minimally invasive, there are complications, most commonly post-embolization syndrome. In this case series of 4 cirrhotic patients who underwent PSE, all 4 developed peritonitis and 2 developed abscesses.
Case Description/
Methods: We describe 4 decompensated cirrhotic patients with ascites who underwent PSE for thrombocytopenia at our institution between 1/1/2025 and 3/1/2025.
Case 1: A 55-year-old male with HCV cirrhosis was admitted for worsening ascites. Initial platelet count was 6,000/µL and did not improve with platelet transfusion. He underwent PSE and platelets improved to 431,000/µL. However, he developed new peritonitis post-PSE. He was treated with antibiotics and discharged after a 30-day hospital stay.
Case 2: A 62-year-old male with autoimmune cirrhosis and prior TIPS was admitted with hematemesis treated with banding of esophageal varices (EV). Initial platelet count was 56,000/µL. He underwent unsuccessful traversal of TIPS due to chronic occlusion as well as PSE. Platelets improved to 315,000/µL. However, he developed new persistent peritonitis post-PSE, with enterococcus faecalis growth. Imaging showed infarcted spleen with a large fluid collection, requiring drainage. He died one day after discharge to hospice.
Case 3: A 78-year-old female with MASH cirrhosis and HCC was admitted for abdominal pain after liver lesion cryoablation and PSE. Platelet count prior to PSE was 15,000/µL, which improved to 296,000/µL. Paracenteses confirmed peritonitis, which persisted despite prolonged antibiotic treatment. She was discharged after a 22-day hospital stay.
Case 4: A 43-year-old male with HCV cirrhosis was admitted for hematemesis treated with EV banding. Initial platelet count was 55,000/µL. He underwent PSE one day prior to discharge. He then had repeat PSE for persistent thrombocytopenia and was readmitted with peritonitis. Platelets were 288,000/µL. 16S rRNA sequencing on ascitic fluid was positive for Robinsoniella peoriensis. One month later he developed large intraperitoneal abscess, requiring drainage.
Discussion: This case series demonstrates that while PSE is effective in resolving thrombocytopenia in patients with decompensated cirrhosis and ascites, peritonitis is a serious complication that may limit its use in this specific patient population.
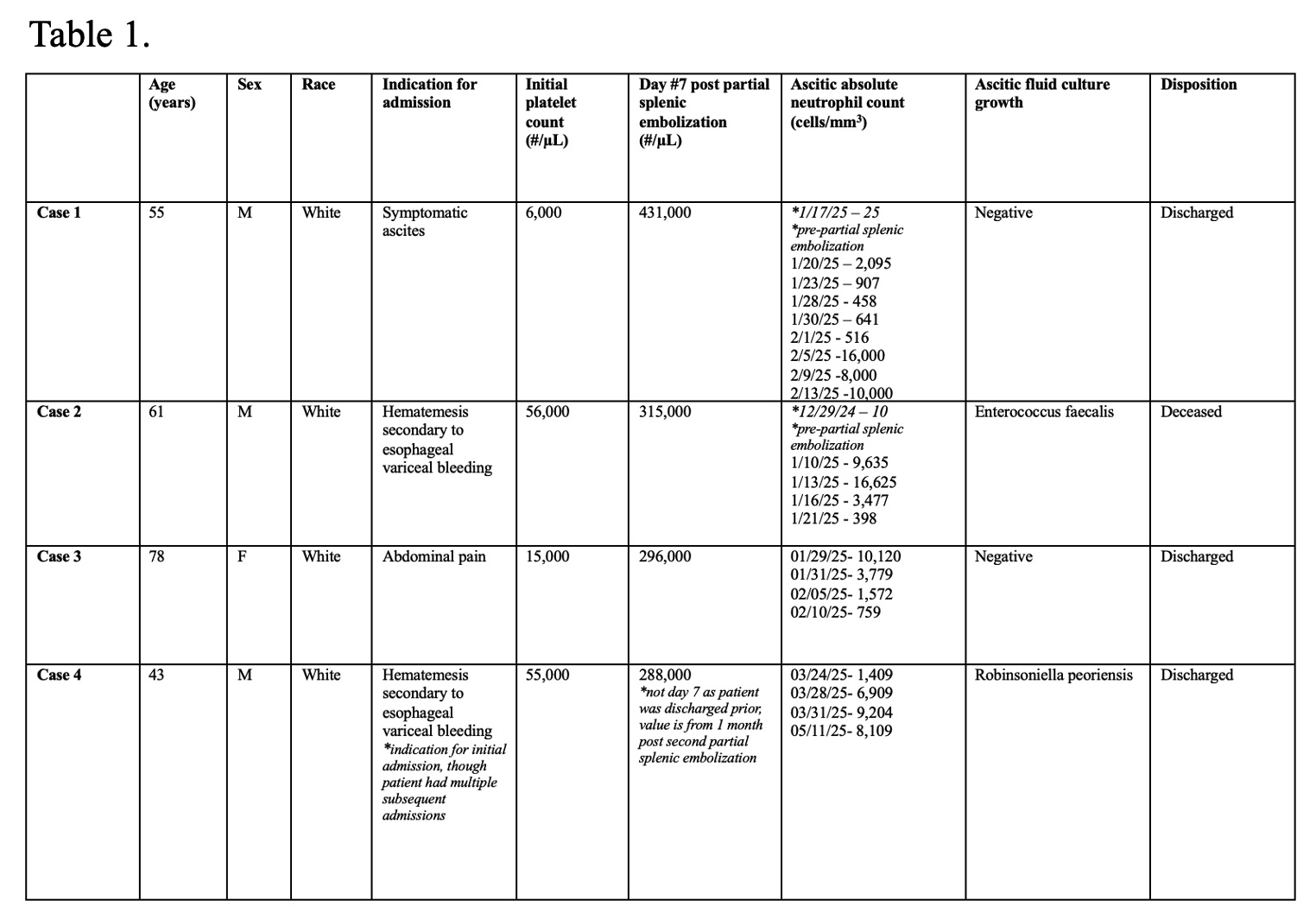
Figure: Table 1. Baseline characteristics and clinical outcomes.
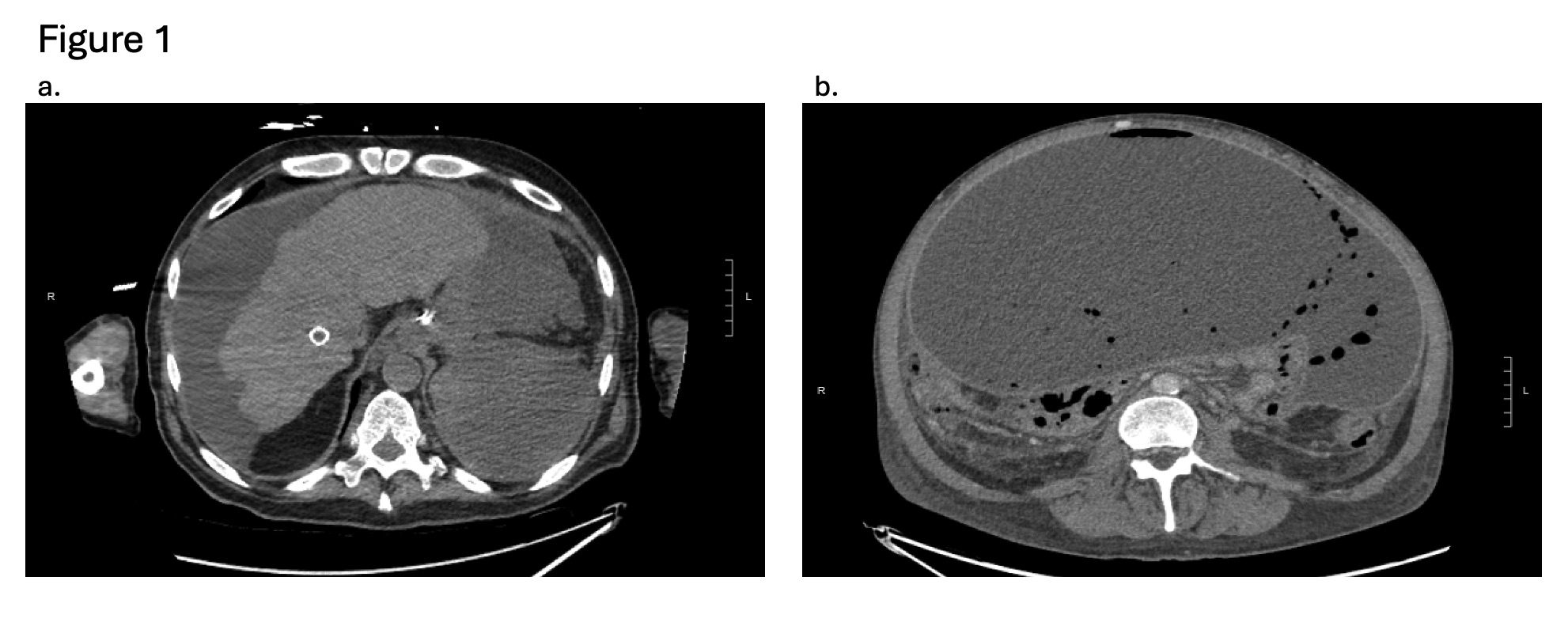
Figure: Figure 1a. Case 2 computed tomography scan post partial splenic embolization showing an occluded transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) in the liver and an infarcted spleen with a 19 x 12.8 x 9.1 cm fluid collection in the left upper quadrant.
Figure 1b. Case 4 computed tomography scan post partial splenic embolization showing a 26.0 x 16.6 x 28.2 cm intraperitoneal fluid collection with intralesional gas and associated peritoneal thickening.
Disclosures:
Jennifer Wiese indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Yonas Fetle indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Yasir Rajwana indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Lauren Searls indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Adamsegd Gebremedhen indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mujtaba Mohamed indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Elizabeth Harris indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jennifer L. Wiese, MD1, Yonas Fetle, MD1, Yasir Rajwana, MD2, Lauren Searls, MD2, Adamsegd Gebremedhen, MD1, Mujtaba Mohamed, MD1, Elizabeth Harris, MD1. P2132 - Outcomes of Partial Splenic Embolization for Severe Thrombocytopenia in Decompensated Cirrhosis: A Single Center Case Series, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Marshall University Joan C. Edwards School of Medicine, Huntington, WV; 2Joan C. Edwards School of Medicine, Marshall University, Huntington, WV
Introduction: Thrombocytopenia in decompensated cirrhosis increases risk for bleeding which can delay critical procedures. Treatment options include platelet transfusion, partial splenic embolization (PSE), and splenectomy. While PSE is minimally invasive, there are complications, most commonly post-embolization syndrome. In this case series of 4 cirrhotic patients who underwent PSE, all 4 developed peritonitis and 2 developed abscesses.
Case Description/
Methods: We describe 4 decompensated cirrhotic patients with ascites who underwent PSE for thrombocytopenia at our institution between 1/1/2025 and 3/1/2025.
Case 1: A 55-year-old male with HCV cirrhosis was admitted for worsening ascites. Initial platelet count was 6,000/µL and did not improve with platelet transfusion. He underwent PSE and platelets improved to 431,000/µL. However, he developed new peritonitis post-PSE. He was treated with antibiotics and discharged after a 30-day hospital stay.
Case 2: A 62-year-old male with autoimmune cirrhosis and prior TIPS was admitted with hematemesis treated with banding of esophageal varices (EV). Initial platelet count was 56,000/µL. He underwent unsuccessful traversal of TIPS due to chronic occlusion as well as PSE. Platelets improved to 315,000/µL. However, he developed new persistent peritonitis post-PSE, with enterococcus faecalis growth. Imaging showed infarcted spleen with a large fluid collection, requiring drainage. He died one day after discharge to hospice.
Case 3: A 78-year-old female with MASH cirrhosis and HCC was admitted for abdominal pain after liver lesion cryoablation and PSE. Platelet count prior to PSE was 15,000/µL, which improved to 296,000/µL. Paracenteses confirmed peritonitis, which persisted despite prolonged antibiotic treatment. She was discharged after a 22-day hospital stay.
Case 4: A 43-year-old male with HCV cirrhosis was admitted for hematemesis treated with EV banding. Initial platelet count was 55,000/µL. He underwent PSE one day prior to discharge. He then had repeat PSE for persistent thrombocytopenia and was readmitted with peritonitis. Platelets were 288,000/µL. 16S rRNA sequencing on ascitic fluid was positive for Robinsoniella peoriensis. One month later he developed large intraperitoneal abscess, requiring drainage.
Discussion: This case series demonstrates that while PSE is effective in resolving thrombocytopenia in patients with decompensated cirrhosis and ascites, peritonitis is a serious complication that may limit its use in this specific patient population.

Figure: Table 1. Baseline characteristics and clinical outcomes.

Figure: Figure 1a. Case 2 computed tomography scan post partial splenic embolization showing an occluded transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) in the liver and an infarcted spleen with a 19 x 12.8 x 9.1 cm fluid collection in the left upper quadrant.
Figure 1b. Case 4 computed tomography scan post partial splenic embolization showing a 26.0 x 16.6 x 28.2 cm intraperitoneal fluid collection with intralesional gas and associated peritoneal thickening.
Disclosures:
Jennifer Wiese indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Yonas Fetle indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Yasir Rajwana indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Lauren Searls indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Adamsegd Gebremedhen indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mujtaba Mohamed indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Elizabeth Harris indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jennifer L. Wiese, MD1, Yonas Fetle, MD1, Yasir Rajwana, MD2, Lauren Searls, MD2, Adamsegd Gebremedhen, MD1, Mujtaba Mohamed, MD1, Elizabeth Harris, MD1. P2132 - Outcomes of Partial Splenic Embolization for Severe Thrombocytopenia in Decompensated Cirrhosis: A Single Center Case Series, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.

