Monday Poster Session
Category: Diet, Nutrition, and Obesity
P2696 - The Effect of Gut Microbiome-Modulating Therapies on Lipid Profile in Metabolic Syndrome: A Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis, and Meta-Regression
Monday, October 27, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall
- PP
Pradipta Paul, MD (he/him/his)
Rochester General Hospital
Rochester, NY
Presenting Author(s)
Pradipta Paul, MD1, Ridhima Kaul, MD2, Muhammad Ayyan, 3, Manale Harfouche, BSc, MPH3, Sa'ad Laws, MA, MLIS, BA3, Ali Chaari, PhD3
1Rochester General Hospital, Rochester, NY; 2Cleveland Clinic Foundation, Cleveland, OH; 3Weill Cornell Medicine - Qatar, Qatar Foundation, Ar Rayyan, Qatar
Introduction: Dyslipidemia, characterized by elevated triglycerides (TG; >150 mg/dL) and reduced high-density lipoprotein (HDL; < 50 mg/dL), is a key component of metabolic syndrome (MetS). The human gut microbiome plays a crucial role in physiological homeostasis and is both affected in and by pathological states, including MetS. We aimed to evaluate the impact of gut microbiome-modulating therapies—including probiotics, prebiotics, synbiotics, and fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT)—on lipid profile parameters in individuals with MetS.
Methods: We performed a systematic review, random-effects meta-analysis and univariate meta-regression of clinical trials indexed in PubMed, Web of Science, and Scopus published through April 2023, to evaluate the influence of gut microbiome therapies on biomarkers of lipidemia (total cholesterol, LDL, HDL, or triglycerides) in adult patients diagnosed with MetS using ATP III, IDF or WHO criteria. Results were depicted as mean differences (MDs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs), and hetergenity was quantified using I² statistics, whereas univariate linear meta-regressions were conducted using age, BMI, dosage, intervention duration, and region. Risk of bias was assessed using Cochrane RoB 2 tool.
Results: Nineteen studies (21 trial comparisons; n = 897) were included. Gut microbiome interventions significantly reduced total cholesterol (MD: -8.97 mg/dL; 95% CI: -12.55 to -5.38; I² = 43.2%), triglycerides (MD: -11.33 mg/dL; 95% CI: -19.25 to -3.40; I² = 55.9%), and LDL (MD: -5.05 mg/dL; 95% CI: -9.57 to -0.53; I² = 73.8%). HDL levels showed no significant change. Subgroup analyses suggested enhanced effects with higher probiotic doses (≥10¹⁰ CFU/day), ≥12-week interventions, and studies from Europe and the Eastern Mediterranean. Participant age and baseline BMI significantly moderated lipid outcomes.
Discussion: These findings suggest that microbiome-modulating therapies improve key lipid biomarkers in MetS, supporting their potential as adjunct treatments. The lack of significant impact on HDL highlights the complexity of lipid metabolism modulation through microbiome interventions. Further investigations, including well-designed large-scale clinical trials and meta-regression analyses, are warranted to elucidate the specific mechanisms underlying these effects, determine optimal formulations and target populations, and to further explore sources of heterogeneity.
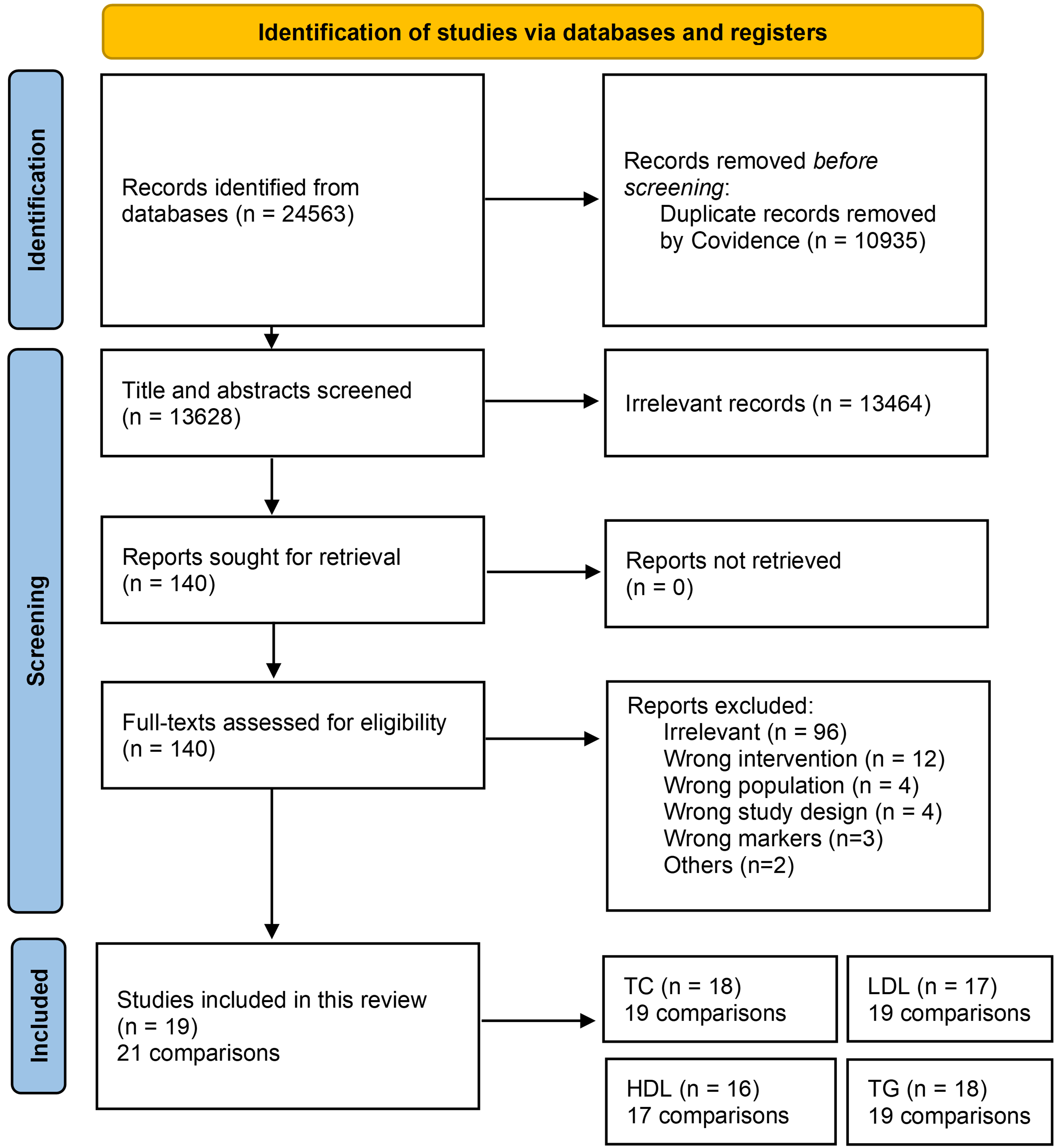
Figure: PRISMA flowchart of search strategy and included studies and trial comparisons, sorted by biomarker.
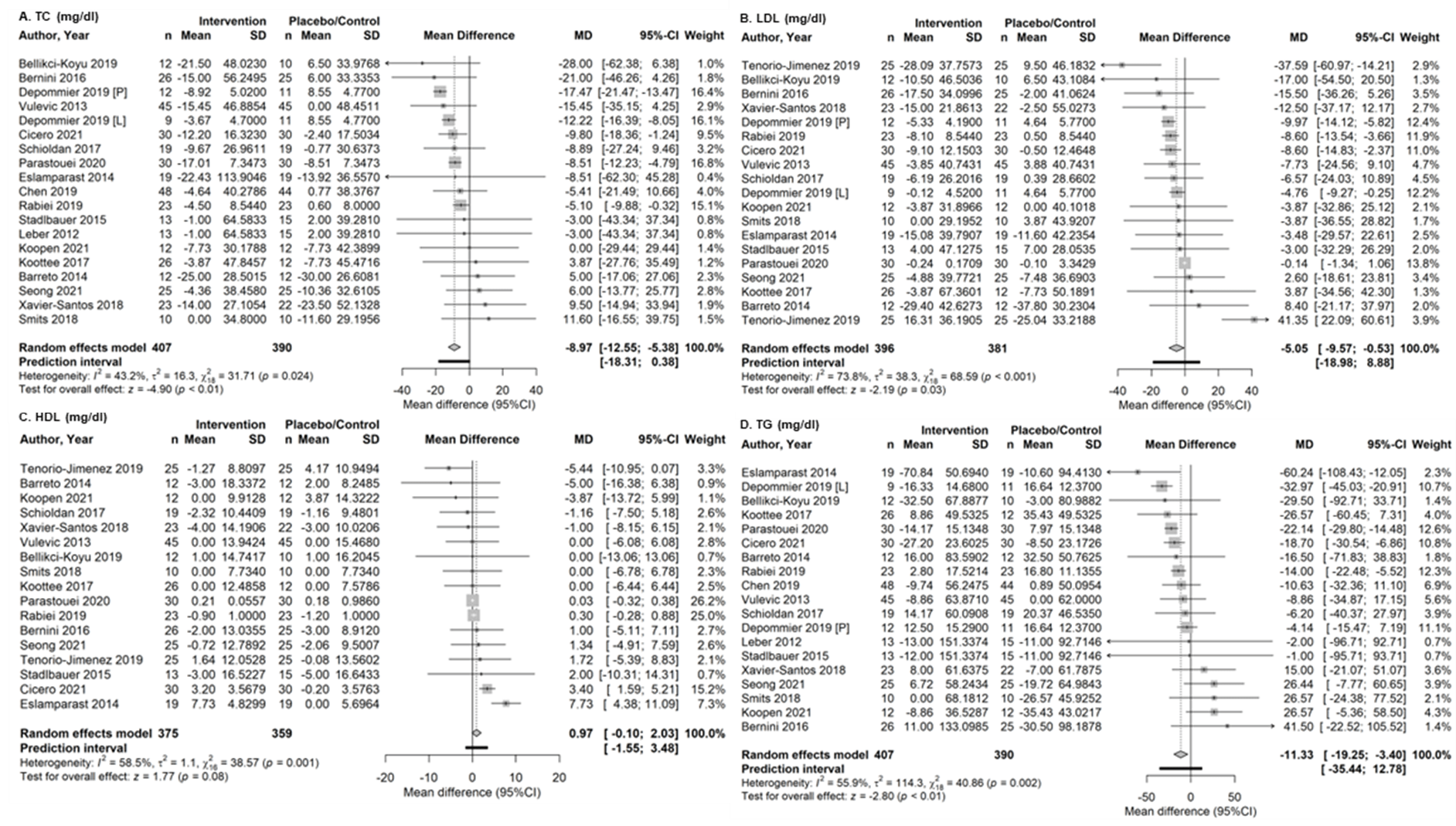
Figure: Forest plot following meta-analysis (random effects model, inverse-variance weights) of the absolute changes in (A) total cholesterol (TC; mg/dl), (B) low-density lipoprotein (LDL; mg/dl), (C) high-density lipoprotein (HDL; mg/dl), and (D) triglycerides (TG; md/dl) from trials reporting the effects of microbiome-modulating therapies on patients with metabolic syndrome. Pooled overall effect estimate is represented by grey diamond and quantified by pooled mean difference and 95% CI and statistical significance is represented by z-score and p-value; interstudy heterogeneity is quantified via I2, τ2, χ2 and p-value.
Disclosures:
Pradipta Paul indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ridhima Kaul indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Ayyan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Manale Harfouche indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sa'ad Laws indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ali Chaari indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Pradipta Paul, MD1, Ridhima Kaul, MD2, Muhammad Ayyan, 3, Manale Harfouche, BSc, MPH3, Sa'ad Laws, MA, MLIS, BA3, Ali Chaari, PhD3. P2696 - The Effect of Gut Microbiome-Modulating Therapies on Lipid Profile in Metabolic Syndrome: A Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis, and Meta-Regression, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Rochester General Hospital, Rochester, NY; 2Cleveland Clinic Foundation, Cleveland, OH; 3Weill Cornell Medicine - Qatar, Qatar Foundation, Ar Rayyan, Qatar
Introduction: Dyslipidemia, characterized by elevated triglycerides (TG; >150 mg/dL) and reduced high-density lipoprotein (HDL; < 50 mg/dL), is a key component of metabolic syndrome (MetS). The human gut microbiome plays a crucial role in physiological homeostasis and is both affected in and by pathological states, including MetS. We aimed to evaluate the impact of gut microbiome-modulating therapies—including probiotics, prebiotics, synbiotics, and fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT)—on lipid profile parameters in individuals with MetS.
Methods: We performed a systematic review, random-effects meta-analysis and univariate meta-regression of clinical trials indexed in PubMed, Web of Science, and Scopus published through April 2023, to evaluate the influence of gut microbiome therapies on biomarkers of lipidemia (total cholesterol, LDL, HDL, or triglycerides) in adult patients diagnosed with MetS using ATP III, IDF or WHO criteria. Results were depicted as mean differences (MDs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs), and hetergenity was quantified using I² statistics, whereas univariate linear meta-regressions were conducted using age, BMI, dosage, intervention duration, and region. Risk of bias was assessed using Cochrane RoB 2 tool.
Results: Nineteen studies (21 trial comparisons; n = 897) were included. Gut microbiome interventions significantly reduced total cholesterol (MD: -8.97 mg/dL; 95% CI: -12.55 to -5.38; I² = 43.2%), triglycerides (MD: -11.33 mg/dL; 95% CI: -19.25 to -3.40; I² = 55.9%), and LDL (MD: -5.05 mg/dL; 95% CI: -9.57 to -0.53; I² = 73.8%). HDL levels showed no significant change. Subgroup analyses suggested enhanced effects with higher probiotic doses (≥10¹⁰ CFU/day), ≥12-week interventions, and studies from Europe and the Eastern Mediterranean. Participant age and baseline BMI significantly moderated lipid outcomes.
Discussion: These findings suggest that microbiome-modulating therapies improve key lipid biomarkers in MetS, supporting their potential as adjunct treatments. The lack of significant impact on HDL highlights the complexity of lipid metabolism modulation through microbiome interventions. Further investigations, including well-designed large-scale clinical trials and meta-regression analyses, are warranted to elucidate the specific mechanisms underlying these effects, determine optimal formulations and target populations, and to further explore sources of heterogeneity.

Figure: PRISMA flowchart of search strategy and included studies and trial comparisons, sorted by biomarker.

Figure: Forest plot following meta-analysis (random effects model, inverse-variance weights) of the absolute changes in (A) total cholesterol (TC; mg/dl), (B) low-density lipoprotein (LDL; mg/dl), (C) high-density lipoprotein (HDL; mg/dl), and (D) triglycerides (TG; md/dl) from trials reporting the effects of microbiome-modulating therapies on patients with metabolic syndrome. Pooled overall effect estimate is represented by grey diamond and quantified by pooled mean difference and 95% CI and statistical significance is represented by z-score and p-value; interstudy heterogeneity is quantified via I2, τ2, χ2 and p-value.
Disclosures:
Pradipta Paul indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ridhima Kaul indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Ayyan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Manale Harfouche indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sa'ad Laws indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ali Chaari indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Pradipta Paul, MD1, Ridhima Kaul, MD2, Muhammad Ayyan, 3, Manale Harfouche, BSc, MPH3, Sa'ad Laws, MA, MLIS, BA3, Ali Chaari, PhD3. P2696 - The Effect of Gut Microbiome-Modulating Therapies on Lipid Profile in Metabolic Syndrome: A Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis, and Meta-Regression, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
