Monday Poster Session
Category: Esophagus
P2801 - Long-Term Dupilumab Therapy Maintains Improvements in Esophageal Features of Eosinophilic Esophagitis (EoE) as Measured by Endoscopic Reference Score in Children With EoE: 100-Week Results From EoE KIDS
Monday, October 27, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall
- SS
Shauna Schroeder, MD, MS
Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition, Phoenix Children’s Hospital
Phoenix, AZ
Presenting Author(s)
Shauna Schroeder, MD, MS1, Mirna Chehade, MD, MPH2, Evan S. Dellon, MD, MPH3, Calies Menard-Katcher, MD4, Navneet Virk Hundal, MD5, Ruiqi Liu, PhD6, Margee Louisias, MD, MPH7, Allen Radin, MD6
1Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition, Phoenix Children’s Hospital, Phoenix, AZ; 2Mount Sinai Center for Eosinophilic Disorders, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY; 3Center for Esophageal Diseases and Swallowing, University of North Carolina School of Medicine, Chapel Hill, NC; 4Digestive Health Institute, Children’s Hospital Colorado, Aurora, CO; 5Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA; 6Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Inc., Tarrytown, NY; 7Sanofi, Cambridge, MA
Introduction: Eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) is a chronic, progressive, type 2 inflammatory disease of the esophagus. Endoscopic Reference Score (EREFS) evaluates severity of endoscopic EoE features (edema, rings, exudates, furrows, and strictures), with subscores for inflammation and fibrostenosis. Dupilumab is approved for EoE in the USA and EU in patients (pts) aged ≥1 year, weighing ≥15 kg. Dupilumab significantly improved worst observed region (WOR) EREFS scores in children aged 1–11 years with active EoE in Parts A and B of the phase 3 EoE KIDS study (NCT04394351). This post hoc analysis assessed long-term dupilumab’s effect on WOR EREFS scores to Week (W) 100 in EoE KIDS.
Methods: This analysis includes pts who received higher-exposure (HE) dupilumab or placebo (PBO) during the 16-W double-blind phase (Part A), and HE dupilumab during the 36-W extension (Part B). Pts who completed Part B were eligible for Part C, where they received the same weight-tiered, open-label dupilumab regimen. EREFS scoring was based on WOR (range 0–9), derived using the highest score for each feature from proximal/distal esophageal regions.
Results: Thirty-three of 61 pts enrolled in Part C were included. At Part A baseline, mean (95% confidence interval [CI]) EREFS total scores for PBO/dupilumab and dupilumab/dupilumab groups were 4.27 (3.34, 5.19) and 4.03 (3.44, 4.62), respectively, and proportions of pts (95% CI) who achieved EREFS total scores of ≤2 and 0 were 13.3% (1.7%, 40.5%) and 17.6% (6.8%, 34.5%), and 0.0% (0.0%, 21.8%) and 2.9% (0.1%, 15.3%), respectively. At W100, mean (95% CI) change in EREFS total score was maintained from W52 (–3.27 [–4.14, –2.39] vs –2.56 [–3.21, –1.91], respectively) (Figure). Mean (95% CI) changes at W100 were maintained from W52 in EREFS inflammation subscore (–2.87 [–3.56, –2.18] vs –2.28 [–2.81, –1.75]) and fibrostenotic subscore (–0.40 [–0.68, –0.12] vs –0.28 [–0.53, –0.03]). Greater proportions of pts (95% CI) achieved endoscopic improvement (EREFS total score ≤2) and endoscopic normalization (EREFS total score 0) at W100 relative to W52 (100.0% [81.5%, 100.0%] vs 83.9% [66.3%, 94.6%] and 38.9% [17.3%, 64.3%] vs 25.8% [11.9%, 44.6%], respectively).
Discussion: Long-term dupilumab maintained improvements in EREFS total score, and inflammation and fibrostenotic subscores at W100 relative to W52 in pediatric pts with EoE. Further improvements were also observed in proportions of pts achieving endoscopic improvement and normalization.
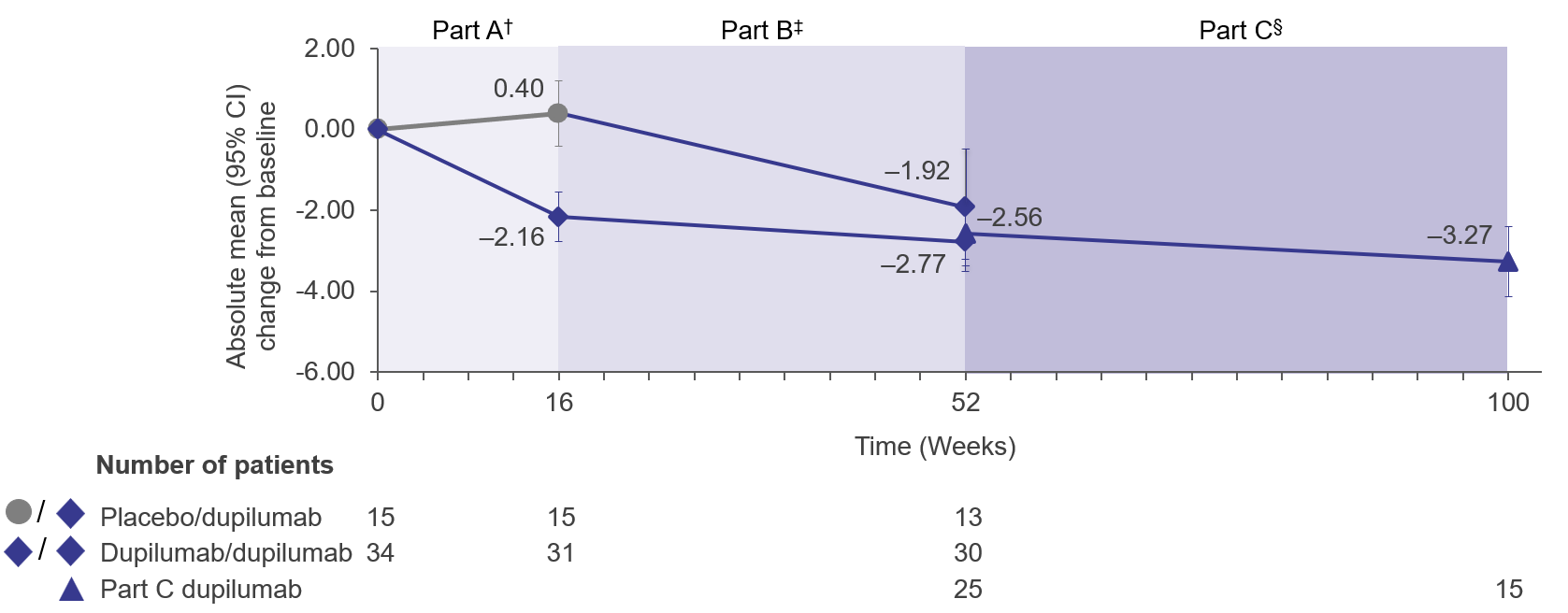
Figure: Figure. Absolute change in EREFS total score from Week 0 to Week 100.
† From Week 0 to 16, the placebo/dupilumab group received placebo and the dupilumab/dupilumab group received dupilumab higher exposure.
‡ From Week 16 to 52, the placebo/dupilumab and dupilumab/dupilumab groups received dupilumab higher exposure.
§ From Week 52 to 100, all patients received the dupilumab regimen later approved by the FDA for pediatric patients with EoE. This regimen was similar to the dupilumab higher-exposure regimen used in Parts A and B. The Part C group included patients who previously received dupilumab higher exposure at any point during Parts A and B of the study.
CI, confidence interval; EoE, eosinophilic esophagitis; EREFS, Eosinophilic Esophagitis Endoscopic Reference Score; FDA, US Food and Drug Administration.
Disclosures:
Shauna Schroeder: EvoEndo – Advisory board/consultancy fees. Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Inc. – Advisory board/consultancy fees. Sanofi – Advisory board/consultancy fees.
Mirna Chehade: Adare Pharma Solutions/Ellodi Pharmaceuticals – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Allakos – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. AstraZeneca – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Bristol Myers Squibb – Consultant. Celgene – Grant/Research Support. Danone – Grant/Research Support. Nexstone Immunology/Uniquity Bio – Consultant. Phathom Pharmaceuticals – Consultant. Recludix Pharma – Consultant. Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Inc. – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Sanofi – Consultant. Shire/Takeda – Consultant, Grant/Research Support.
Evan Dellon: AbbVie – Consultant. Adare/Ellodi – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Akesobio – Consultant. Alfasigma – Consultant. ALK – Consultant. Allakos – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Amgen – Consultant. Apogee – Consultant. Apollo – Consultant. Aqilion – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Arena/Pfizer – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Aslan – Consultant. AstraZeneca – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Avir – Consultant. Biocryst – Consultant. Bryn – Consultant. Calypso – Consultant. Celgene/Receptos/Bristol Myers Squibb – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Celldex – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Dr. Falk Pharma – Consultant. EsoCap – Consultant. Eupraxia – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Ferring – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. GI Reviewers – Consultant. GSK – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Holoclara – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Invea – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Knightpoint – Consultant. LucidDx – Consultant. Meritage – Grant/Research Support. Miraca – Grant/Research Support. Morphic – Consultant. Nexstone Immunology/Uniquity – Consultant. Nutricia – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Parexel/Calyx – Consultant. Phathom – Consultant. Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Inc. – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Revolo – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Robarts/Alimentiv – Consultant. Sanofi – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Shire/Takeda – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Target RWE – Consultant. Third Harmonic Bio – Consultant. Uniquity – Grant/Research Support. Upstream Bio – Consultant.
Calies Menard-Katcher: Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Inc. – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Sanofi – Advisory Committee/Board Member.
Navneet Virk Hundal: Aché – Advisory board/consulting fees. Danone – Advisory board/consulting fees. Nestlé – Advisory board/consulting fees. Sanofi – Advisory board/consulting fees.
Ruiqi Liu: Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Inc. – Employee and shareholder.
Margee Louisias: Sanofi – Employee, may hold stock and/or stock options in the company.
Allen Radin: Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Inc. – Employee and shareholder.
Shauna Schroeder, MD, MS1, Mirna Chehade, MD, MPH2, Evan S. Dellon, MD, MPH3, Calies Menard-Katcher, MD4, Navneet Virk Hundal, MD5, Ruiqi Liu, PhD6, Margee Louisias, MD, MPH7, Allen Radin, MD6. P2801 - Long-Term Dupilumab Therapy Maintains Improvements in Esophageal Features of Eosinophilic Esophagitis (EoE) as Measured by Endoscopic Reference Score in Children With EoE: 100-Week Results From EoE KIDS, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition, Phoenix Children’s Hospital, Phoenix, AZ; 2Mount Sinai Center for Eosinophilic Disorders, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY; 3Center for Esophageal Diseases and Swallowing, University of North Carolina School of Medicine, Chapel Hill, NC; 4Digestive Health Institute, Children’s Hospital Colorado, Aurora, CO; 5Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA; 6Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Inc., Tarrytown, NY; 7Sanofi, Cambridge, MA
Introduction: Eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) is a chronic, progressive, type 2 inflammatory disease of the esophagus. Endoscopic Reference Score (EREFS) evaluates severity of endoscopic EoE features (edema, rings, exudates, furrows, and strictures), with subscores for inflammation and fibrostenosis. Dupilumab is approved for EoE in the USA and EU in patients (pts) aged ≥1 year, weighing ≥15 kg. Dupilumab significantly improved worst observed region (WOR) EREFS scores in children aged 1–11 years with active EoE in Parts A and B of the phase 3 EoE KIDS study (NCT04394351). This post hoc analysis assessed long-term dupilumab’s effect on WOR EREFS scores to Week (W) 100 in EoE KIDS.
Methods: This analysis includes pts who received higher-exposure (HE) dupilumab or placebo (PBO) during the 16-W double-blind phase (Part A), and HE dupilumab during the 36-W extension (Part B). Pts who completed Part B were eligible for Part C, where they received the same weight-tiered, open-label dupilumab regimen. EREFS scoring was based on WOR (range 0–9), derived using the highest score for each feature from proximal/distal esophageal regions.
Results: Thirty-three of 61 pts enrolled in Part C were included. At Part A baseline, mean (95% confidence interval [CI]) EREFS total scores for PBO/dupilumab and dupilumab/dupilumab groups were 4.27 (3.34, 5.19) and 4.03 (3.44, 4.62), respectively, and proportions of pts (95% CI) who achieved EREFS total scores of ≤2 and 0 were 13.3% (1.7%, 40.5%) and 17.6% (6.8%, 34.5%), and 0.0% (0.0%, 21.8%) and 2.9% (0.1%, 15.3%), respectively. At W100, mean (95% CI) change in EREFS total score was maintained from W52 (–3.27 [–4.14, –2.39] vs –2.56 [–3.21, –1.91], respectively) (Figure). Mean (95% CI) changes at W100 were maintained from W52 in EREFS inflammation subscore (–2.87 [–3.56, –2.18] vs –2.28 [–2.81, –1.75]) and fibrostenotic subscore (–0.40 [–0.68, –0.12] vs –0.28 [–0.53, –0.03]). Greater proportions of pts (95% CI) achieved endoscopic improvement (EREFS total score ≤2) and endoscopic normalization (EREFS total score 0) at W100 relative to W52 (100.0% [81.5%, 100.0%] vs 83.9% [66.3%, 94.6%] and 38.9% [17.3%, 64.3%] vs 25.8% [11.9%, 44.6%], respectively).
Discussion: Long-term dupilumab maintained improvements in EREFS total score, and inflammation and fibrostenotic subscores at W100 relative to W52 in pediatric pts with EoE. Further improvements were also observed in proportions of pts achieving endoscopic improvement and normalization.

Figure: Figure. Absolute change in EREFS total score from Week 0 to Week 100.
† From Week 0 to 16, the placebo/dupilumab group received placebo and the dupilumab/dupilumab group received dupilumab higher exposure.
‡ From Week 16 to 52, the placebo/dupilumab and dupilumab/dupilumab groups received dupilumab higher exposure.
§ From Week 52 to 100, all patients received the dupilumab regimen later approved by the FDA for pediatric patients with EoE. This regimen was similar to the dupilumab higher-exposure regimen used in Parts A and B. The Part C group included patients who previously received dupilumab higher exposure at any point during Parts A and B of the study.
CI, confidence interval; EoE, eosinophilic esophagitis; EREFS, Eosinophilic Esophagitis Endoscopic Reference Score; FDA, US Food and Drug Administration.
Disclosures:
Shauna Schroeder: EvoEndo – Advisory board/consultancy fees. Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Inc. – Advisory board/consultancy fees. Sanofi – Advisory board/consultancy fees.
Mirna Chehade: Adare Pharma Solutions/Ellodi Pharmaceuticals – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Allakos – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. AstraZeneca – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Bristol Myers Squibb – Consultant. Celgene – Grant/Research Support. Danone – Grant/Research Support. Nexstone Immunology/Uniquity Bio – Consultant. Phathom Pharmaceuticals – Consultant. Recludix Pharma – Consultant. Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Inc. – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Sanofi – Consultant. Shire/Takeda – Consultant, Grant/Research Support.
Evan Dellon: AbbVie – Consultant. Adare/Ellodi – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Akesobio – Consultant. Alfasigma – Consultant. ALK – Consultant. Allakos – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Amgen – Consultant. Apogee – Consultant. Apollo – Consultant. Aqilion – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Arena/Pfizer – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Aslan – Consultant. AstraZeneca – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Avir – Consultant. Biocryst – Consultant. Bryn – Consultant. Calypso – Consultant. Celgene/Receptos/Bristol Myers Squibb – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Celldex – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Dr. Falk Pharma – Consultant. EsoCap – Consultant. Eupraxia – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Ferring – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. GI Reviewers – Consultant. GSK – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Holoclara – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Invea – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Knightpoint – Consultant. LucidDx – Consultant. Meritage – Grant/Research Support. Miraca – Grant/Research Support. Morphic – Consultant. Nexstone Immunology/Uniquity – Consultant. Nutricia – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Parexel/Calyx – Consultant. Phathom – Consultant. Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Inc. – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Revolo – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Robarts/Alimentiv – Consultant. Sanofi – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Shire/Takeda – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Target RWE – Consultant. Third Harmonic Bio – Consultant. Uniquity – Grant/Research Support. Upstream Bio – Consultant.
Calies Menard-Katcher: Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Inc. – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Sanofi – Advisory Committee/Board Member.
Navneet Virk Hundal: Aché – Advisory board/consulting fees. Danone – Advisory board/consulting fees. Nestlé – Advisory board/consulting fees. Sanofi – Advisory board/consulting fees.
Ruiqi Liu: Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Inc. – Employee and shareholder.
Margee Louisias: Sanofi – Employee, may hold stock and/or stock options in the company.
Allen Radin: Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Inc. – Employee and shareholder.
Shauna Schroeder, MD, MS1, Mirna Chehade, MD, MPH2, Evan S. Dellon, MD, MPH3, Calies Menard-Katcher, MD4, Navneet Virk Hundal, MD5, Ruiqi Liu, PhD6, Margee Louisias, MD, MPH7, Allen Radin, MD6. P2801 - Long-Term Dupilumab Therapy Maintains Improvements in Esophageal Features of Eosinophilic Esophagitis (EoE) as Measured by Endoscopic Reference Score in Children With EoE: 100-Week Results From EoE KIDS, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
