Monday Poster Session
Category: General Endoscopy
P3031 - Common Variable Immunodeficiency Enteropathy: A Complex Case of Gastrointestinal Involvement in Primary Immunodeficiency
Monday, October 27, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Ali Shaat, MD
Lahey Hospital and Medical Center
Burlington, MA
Presenting Author(s)
Ali Shaat, MD1, Ishan Antony, MD2, Christopher Ward, MD1, Pujitha Kudaravalli, MD1
1Lahey Hospital and Medical Center, Burlington, MA; 2Beth Israel Lahey Health, Burlington, MA
Introduction: Common Variable Immunodeficiency (CVID) is a primary immunodeficiency disorder characterized by hypogammaglobulinemia, recurrent infections, and immune dysregulation. This case highlights the diagnostic challenge and potential complications of CVID enteropathy.
Case Description/
Methods: A 39-year-old female with a history of follicular thyroid cancer, post-surgical hypothyroidism, recurrent intestinal Giardia infections, and CVID on intavenous immunoglobin infusions was referred to the gastroenterology clinic for concerns of malabsorption. Her thyroid profile showed significant variability despite strict medication adherence. The patient reported intermittent dysphagia to solid foods and 15-pound unintentional weight loss. Family history was notable for a second-degree relative of colon cancer and possible ulcerative colitis. Laboratory results were normal except for calprotectin (292 mcg/g) and vitamin D 25-OH (13 ng/ml). The patient underwent an esophagogastroduodenoscopy which demonstrated nodular polypoid mucosa throughout the duodenum and biopsies were performed (Figure 1). The antrum had mild erythema while the remaining of the stomach and esophagus were normal. Biopsy of the duodenum demonstrated extensive lymphoid follicular hyperplasia, markedly decreased plasma cells, intraepithelial lymphocytosis, villous blunting, and rare Giardia organisms confirmed through CD117 immunostaining. CD20, CD3, CD21, CD30, and Ki-67 supported reactive lymphoid proliferation. Colonoscopy demonstrated nodular mucosa in the terminal ileum and biopsies demonstrated prominent lymphoid follicles (Figure 2). A 15 mm pedunculated polyp was identified in the transverse colon and biopsy demonstrated a tubulovillous adenoma.
Discussion: CVID-enteropathy presents diagnostic challenges due to its overlap with celiac disease, autoimmune enteritis, and infections. Elevated fecal calprotectin indicated gastrointestinal inflammation, while immunohistochemical studies ruled out lymphoproliferative disorders. The presence of Giardia emphasizes the role of secondary infections in CVID. Additionally, the detection of a tubulovillous adenoma highlights the need for vigilant colorectal cancer screening. This case underscores the importance of a comprehensive approach to diagnosing CVID enteropathy. Endoscopic evaluation, coupled with histological and immunohistochemical analyses, is critical for accurate diagnosis. Regular surveillance is crucial to monitor for potential neoplastic changes in the gastrointestinal tract.
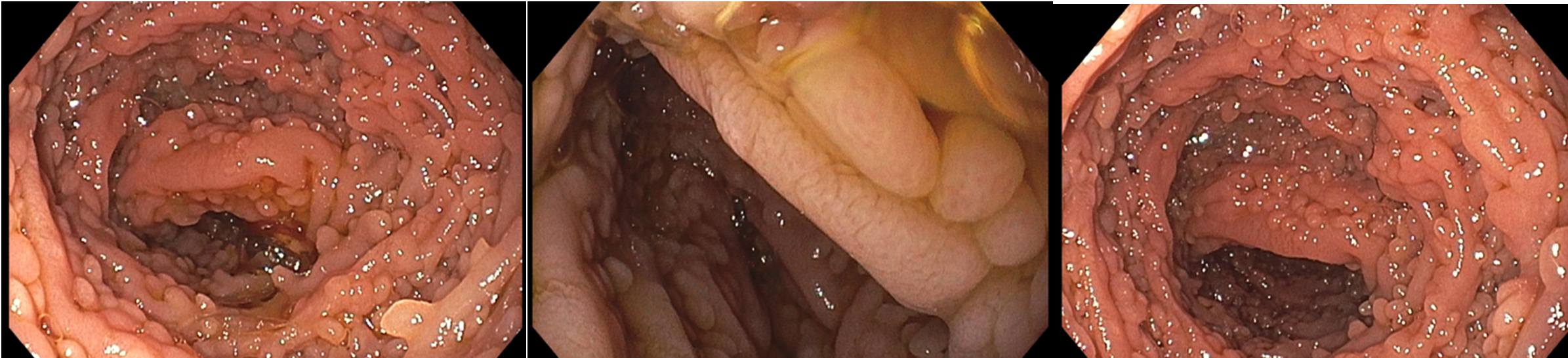
Figure: Esophagogastroduodenoscopy Visualizing The First, Second, and Third Part of The Duodenum (Left to Right).
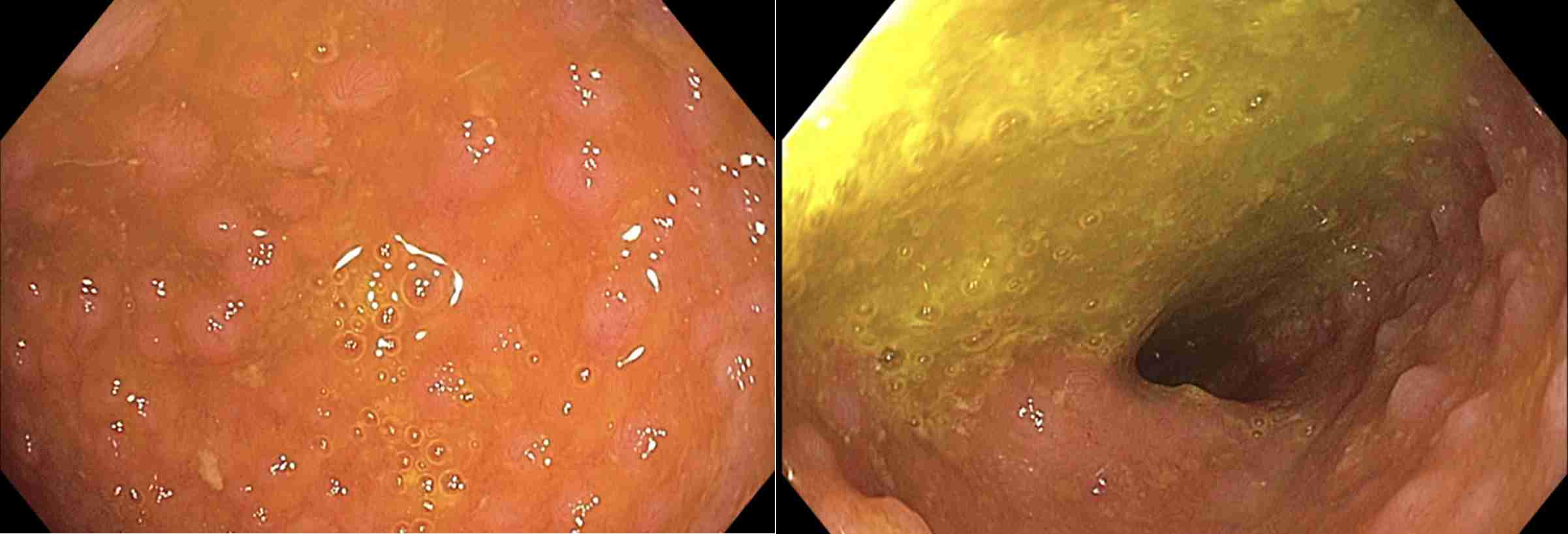
Figure: Colonoscopy Visualizing the Terminal Ileum.
Disclosures:
Ali Shaat indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ishan Antony indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Christopher Ward indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Pujitha Kudaravalli indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ali Shaat, MD1, Ishan Antony, MD2, Christopher Ward, MD1, Pujitha Kudaravalli, MD1. P3031 - Common Variable Immunodeficiency Enteropathy: A Complex Case of Gastrointestinal Involvement in Primary Immunodeficiency, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Lahey Hospital and Medical Center, Burlington, MA; 2Beth Israel Lahey Health, Burlington, MA
Introduction: Common Variable Immunodeficiency (CVID) is a primary immunodeficiency disorder characterized by hypogammaglobulinemia, recurrent infections, and immune dysregulation. This case highlights the diagnostic challenge and potential complications of CVID enteropathy.
Case Description/
Methods: A 39-year-old female with a history of follicular thyroid cancer, post-surgical hypothyroidism, recurrent intestinal Giardia infections, and CVID on intavenous immunoglobin infusions was referred to the gastroenterology clinic for concerns of malabsorption. Her thyroid profile showed significant variability despite strict medication adherence. The patient reported intermittent dysphagia to solid foods and 15-pound unintentional weight loss. Family history was notable for a second-degree relative of colon cancer and possible ulcerative colitis. Laboratory results were normal except for calprotectin (292 mcg/g) and vitamin D 25-OH (13 ng/ml). The patient underwent an esophagogastroduodenoscopy which demonstrated nodular polypoid mucosa throughout the duodenum and biopsies were performed (Figure 1). The antrum had mild erythema while the remaining of the stomach and esophagus were normal. Biopsy of the duodenum demonstrated extensive lymphoid follicular hyperplasia, markedly decreased plasma cells, intraepithelial lymphocytosis, villous blunting, and rare Giardia organisms confirmed through CD117 immunostaining. CD20, CD3, CD21, CD30, and Ki-67 supported reactive lymphoid proliferation. Colonoscopy demonstrated nodular mucosa in the terminal ileum and biopsies demonstrated prominent lymphoid follicles (Figure 2). A 15 mm pedunculated polyp was identified in the transverse colon and biopsy demonstrated a tubulovillous adenoma.
Discussion: CVID-enteropathy presents diagnostic challenges due to its overlap with celiac disease, autoimmune enteritis, and infections. Elevated fecal calprotectin indicated gastrointestinal inflammation, while immunohistochemical studies ruled out lymphoproliferative disorders. The presence of Giardia emphasizes the role of secondary infections in CVID. Additionally, the detection of a tubulovillous adenoma highlights the need for vigilant colorectal cancer screening. This case underscores the importance of a comprehensive approach to diagnosing CVID enteropathy. Endoscopic evaluation, coupled with histological and immunohistochemical analyses, is critical for accurate diagnosis. Regular surveillance is crucial to monitor for potential neoplastic changes in the gastrointestinal tract.

Figure: Esophagogastroduodenoscopy Visualizing The First, Second, and Third Part of The Duodenum (Left to Right).

Figure: Colonoscopy Visualizing the Terminal Ileum.
Disclosures:
Ali Shaat indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ishan Antony indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Christopher Ward indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Pujitha Kudaravalli indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ali Shaat, MD1, Ishan Antony, MD2, Christopher Ward, MD1, Pujitha Kudaravalli, MD1. P3031 - Common Variable Immunodeficiency Enteropathy: A Complex Case of Gastrointestinal Involvement in Primary Immunodeficiency, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
