Monday Poster Session
Category: GI Bleeding
P3131 - Bleeding Battles on Two Fronts: Managing Severe GI and Oropharyngeal AVMs in Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia
Monday, October 27, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Wael T. Mohamed, MD (he/him/his)
University of Kansas School of Medicine
Wichita, KS
Presenting Author(s)
Wael T. Mohamed, MD, Kyle Rowe, MD
University of Kansas School of Medicine, Wichita, KS
Introduction: Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (HHT) is a rare autosomal dominant disorder marked by mucocutaneous and visceral AVMs. We present a case of an elderly patient with recurrent gastrointestinal (GI) and oropharyngeal bleeding due to HHT.
Case Description/
Methods: An 85-year-old male with a history of HHT, chronic anemia, cardiac arrhythmia, fatty liver, prostate cancer status post-prostatectomy, and peptic ulcer disease presented with hematemesis and anemia. He had recently undergone argon plasma coagulation (APC) treatment for 11 AVMs located in the stomach and duodenum. Within days of discharge, he returned to the emergency department with episodes of epistaxis and hemoptysis. Bilateral nasal cauterization was performed, and a bleeding tongue lesion was managed with sutures.
The patient later reported recurrent melena and oropharyngeal bleeding. Laboratory workup revealed hemoglobin of 5.8 g/dL, ESR 54, and CRP 114. He was admitted for anemia management and evaluation of left shoulder pain, with concern for possible septic arthritis. ENT consultation confirmed mild oral bleeding and provided supportive recommendations. A combined endoscopy and ENT procedure under general anesthesia identified two actively bleeding tongue AVMs, which were successfully cauterized, with one requiring suture placement.
Upper endoscopy revealed clotted blood in the oropharynx, a normal esophagus, seven gastric AVMs (some with active bleeding or stigmata of prior treatment), and three duodenal AVMs. APC was re-applied to several gastric lesions and all three duodenal lesions. Clips were also placed for hemostasis.
Discussion: HHT-associated bleeding is often multifocal and recurrent, posing significant clinical challenges. This case illustrates the importance of multidisciplinary coordination between gastroenterology, ENT, and hematology. Despite recent endoscopic and surgical interventions, the patient continued to experience severe bleeding. Systemic antiangiogenic therapy such as bevacizumab was considered given the transfusion-dependent anemia and refractory nature of his disease.
Conclusion: Recurrent bleeding in HHT requires coordinated, multidisciplinary care. For patients unresponsive to local therapies, systemic treatments may be warranted.
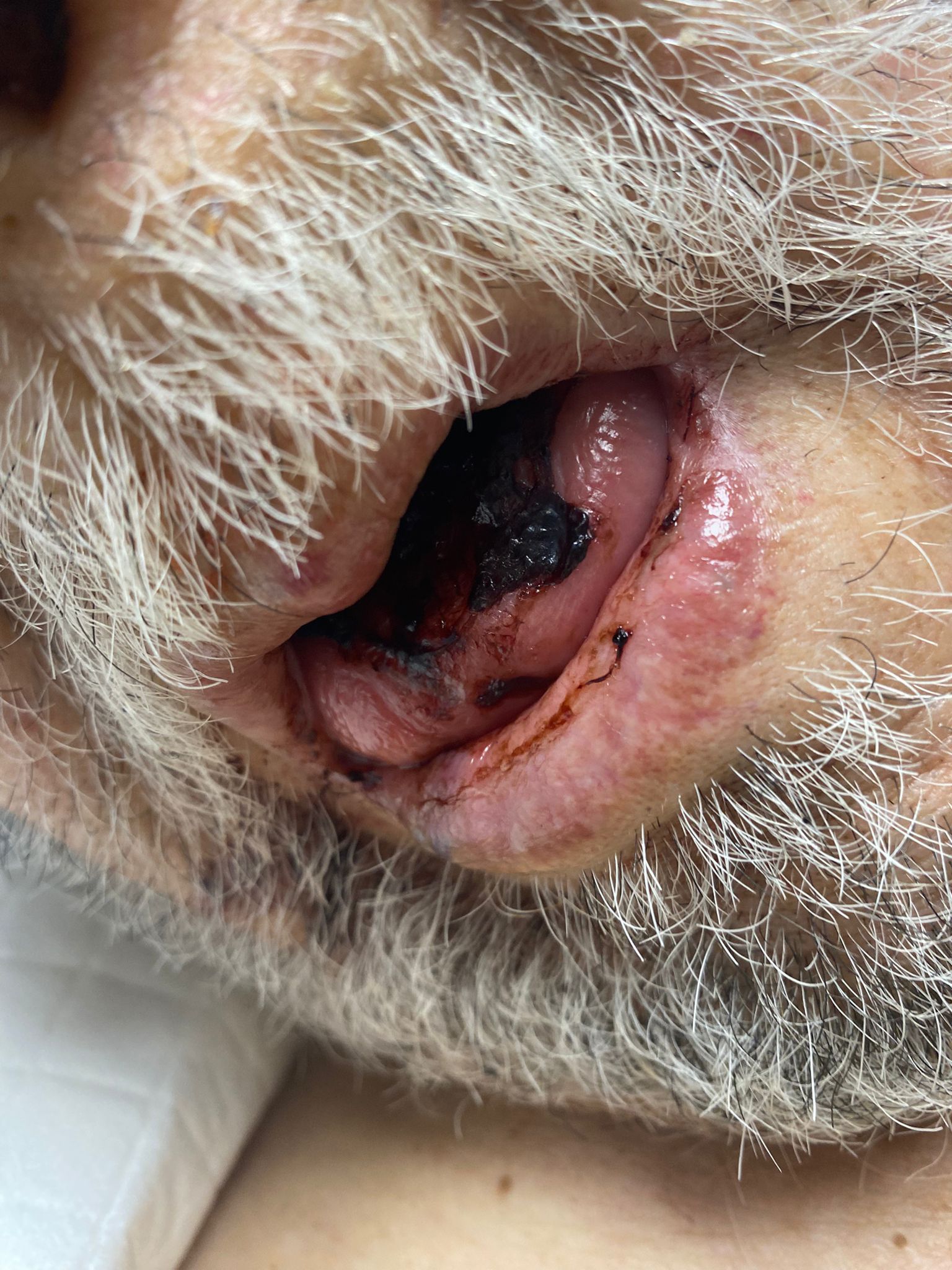
Figure: HHT
Disclosures:
Wael Mohamed indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kyle Rowe indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Wael T. Mohamed, MD, Kyle Rowe, MD. P3131 - Bleeding Battles on Two Fronts: Managing Severe GI and Oropharyngeal AVMs in Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
University of Kansas School of Medicine, Wichita, KS
Introduction: Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (HHT) is a rare autosomal dominant disorder marked by mucocutaneous and visceral AVMs. We present a case of an elderly patient with recurrent gastrointestinal (GI) and oropharyngeal bleeding due to HHT.
Case Description/
Methods: An 85-year-old male with a history of HHT, chronic anemia, cardiac arrhythmia, fatty liver, prostate cancer status post-prostatectomy, and peptic ulcer disease presented with hematemesis and anemia. He had recently undergone argon plasma coagulation (APC) treatment for 11 AVMs located in the stomach and duodenum. Within days of discharge, he returned to the emergency department with episodes of epistaxis and hemoptysis. Bilateral nasal cauterization was performed, and a bleeding tongue lesion was managed with sutures.
The patient later reported recurrent melena and oropharyngeal bleeding. Laboratory workup revealed hemoglobin of 5.8 g/dL, ESR 54, and CRP 114. He was admitted for anemia management and evaluation of left shoulder pain, with concern for possible septic arthritis. ENT consultation confirmed mild oral bleeding and provided supportive recommendations. A combined endoscopy and ENT procedure under general anesthesia identified two actively bleeding tongue AVMs, which were successfully cauterized, with one requiring suture placement.
Upper endoscopy revealed clotted blood in the oropharynx, a normal esophagus, seven gastric AVMs (some with active bleeding or stigmata of prior treatment), and three duodenal AVMs. APC was re-applied to several gastric lesions and all three duodenal lesions. Clips were also placed for hemostasis.
Discussion: HHT-associated bleeding is often multifocal and recurrent, posing significant clinical challenges. This case illustrates the importance of multidisciplinary coordination between gastroenterology, ENT, and hematology. Despite recent endoscopic and surgical interventions, the patient continued to experience severe bleeding. Systemic antiangiogenic therapy such as bevacizumab was considered given the transfusion-dependent anemia and refractory nature of his disease.
Conclusion: Recurrent bleeding in HHT requires coordinated, multidisciplinary care. For patients unresponsive to local therapies, systemic treatments may be warranted.

Figure: HHT
Disclosures:
Wael Mohamed indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kyle Rowe indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Wael T. Mohamed, MD, Kyle Rowe, MD. P3131 - Bleeding Battles on Two Fronts: Managing Severe GI and Oropharyngeal AVMs in Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
