Monday Poster Session
Category: IBD
P3217 - Proteasome Inhibitors and Colitis: A Comparative Look at Gastrointestinal Complications in Lymphoid and Hematopoietic Malignancies
Monday, October 27, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Chidera Onwuzo, MBBS (he/him/his)
SUNY Upstate Medical University Hospital
Syracuse, NY
Presenting Author(s)
Chidera Onwuzo, MBBS1, Somtochukwu Onwuzo, MD2, Kojo-Frimpong B. Awuah, MD3, Rashid Abdel-Razeq, MD4, Areeb Khan, MD1, Eloho Olojakpoke, MBBS1, Solomon Anighoro, MBBS5, Antoine Boustany, MD6, Laith Alomari, MD7, Al-Aman Shaukat, MBBS1
1SUNY Upstate Medical University Hospital, Syracuse, NY; 2Allegheny Center for Digestive Health, Pittsburgh, PA; 3Allegheny Health Network, Pittsburgh, PA; 4Cleveland Clinic Foundation, Cleveland, OH; 5Guthrie Robert Packer Hospital, Sayre, PA; 6University of Florida College of Medicine, Jacksonville, FL; 7Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, PA
Introduction: Gastrointestinal complications, particularly various forms of colitis, are a major concern in patients with lymphoid and hematopoietic malignancies. Proteasome inhibitors are increasingly utilized in treatment, but their impact on specific colitis-related conditions, such as CMV colitis, Ischemic colitis, diverticulitis, remains underexplored. Given the potential severity of these complications, it is crucial to assess whether proteasome inhibitors increase the risk of colitis and other GI disorders in this vulnerable population. This study aims to provide a comparative analysis of colitis-related complications in patients treated with proteasome inhibitors to inform therapeutic decisions and patient management.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective cohort analysis using data from 32,589 patients with malignant lymphoid and hematopoietic neoplasms from the TriNetX research network. Two cohorts were identified: patients treated with proteasome inhibitors (Cohort 1) and those without (Cohort 2). Inclusion criteria were age ≥18 years, and patients with a diagnosis of ulcerative colitis or Crohn’s disease were excluded. Propensity score matching was performed to adjust for confounding variables, including age, sex, race, and comorbidities such as type 2 diabetes mellitus, essential hypertension, overweight/obesity, cerebrovascular disease, ischemic heart disease, chronic kidney disease, nicotine dependence, and alcohol abuse. Primary outcomes included colitis-related complications, such as microscopic colitis, CMV colitis, diverticulitis, and ischemic colitis. Hazard ratios (HR) and 95% confidence intervals (CI) were calculated using Cox proportional hazards regression.
Results: Proteasome inhibitor use was associated with increased risk of CMV colitis (HR 1.595, 95% CI 1.406–1.808), diverticulitis (HR 1.325, 95% CI 1.152–1.524), and ischemic colitis (HR 1.674, 95% CI 0.817–3.432), though the latter was not statistically significant. Microscopic colitis showed a lower, non-significant risk (HR 0.95, 95% CI 0.597–1.518).
Discussion: Proteasome inhibitor use in patients with lymphoid and hematopoietic malignancies was associated with a significantly higher risk of CMV colitis and diverticulitis, as well as an elevated risk of ischemic colitis. In contrast, the risk of microscopic colitis appeared lower. These findings suggest a potential for serious gastrointestinal complications, emphasizing the need for monitoring and a careful approach to proteasome inhibitor therapy.
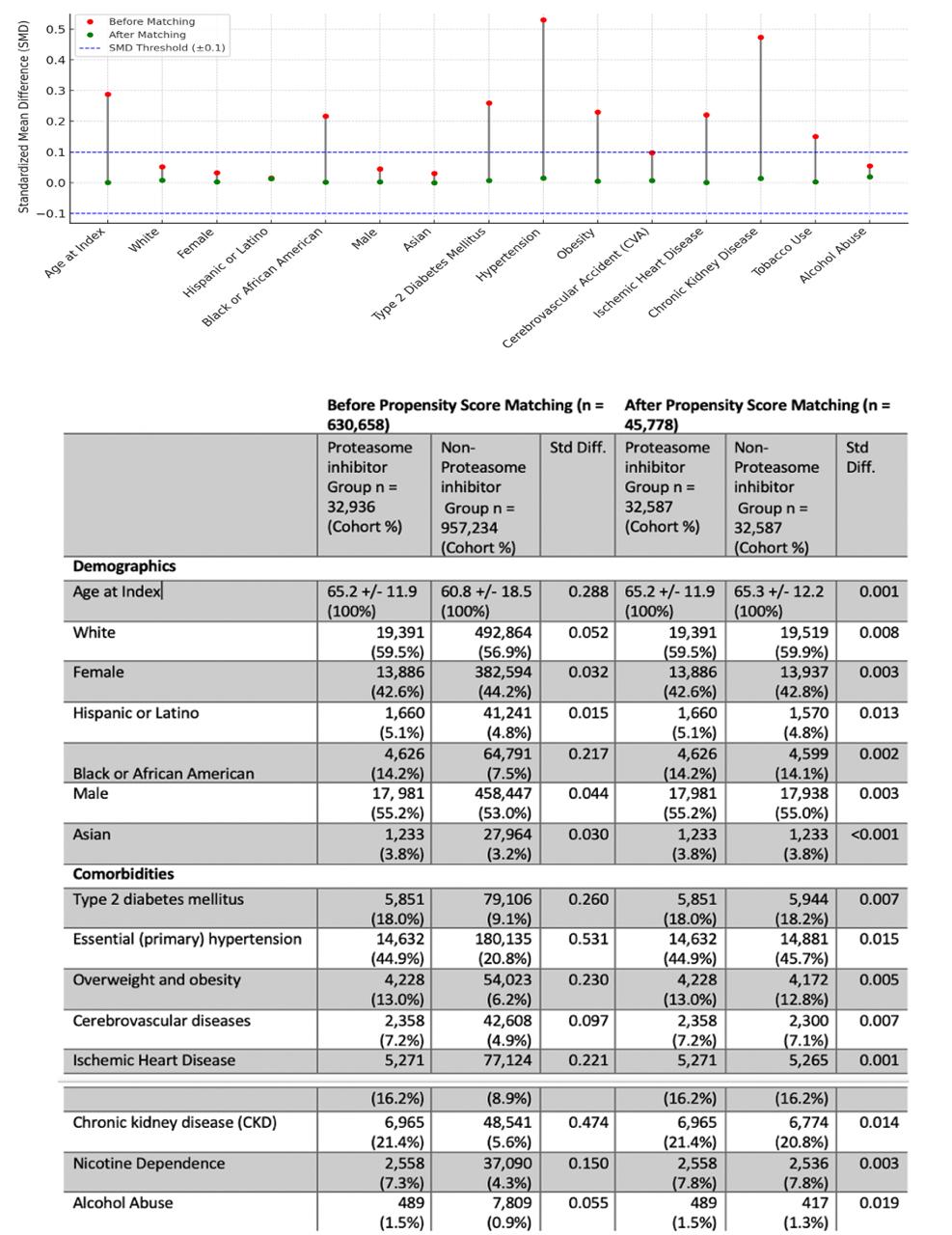
Figure: Figure 1: Comparison of Demographics and Comorbidities of Proteasome inhibitor Users and Non- Proteasome inhibitor Users Before and After Propensity Score Matching
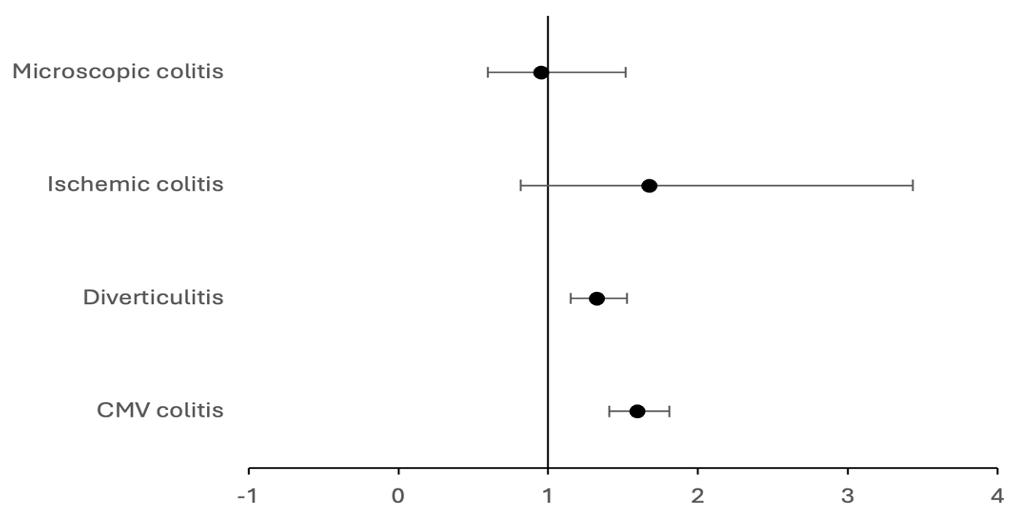
Figure: Figure 2: Forest plot comparing Hazard ratios in Proteasome inhibitor group versus Non-Proteasome inhibitor group.
Disclosures:
Chidera Onwuzo indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Somtochukwu Onwuzo indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kojo-Frimpong B. Awuah indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rashid Abdel-Razeq indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Areeb Khan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Eloho Olojakpoke indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Solomon Anighoro indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Antoine Boustany indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Laith Alomari indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Al-Aman Shaukat indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Chidera Onwuzo, MBBS1, Somtochukwu Onwuzo, MD2, Kojo-Frimpong B. Awuah, MD3, Rashid Abdel-Razeq, MD4, Areeb Khan, MD1, Eloho Olojakpoke, MBBS1, Solomon Anighoro, MBBS5, Antoine Boustany, MD6, Laith Alomari, MD7, Al-Aman Shaukat, MBBS1. P3217 - Proteasome Inhibitors and Colitis: A Comparative Look at Gastrointestinal Complications in Lymphoid and Hematopoietic Malignancies, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1SUNY Upstate Medical University Hospital, Syracuse, NY; 2Allegheny Center for Digestive Health, Pittsburgh, PA; 3Allegheny Health Network, Pittsburgh, PA; 4Cleveland Clinic Foundation, Cleveland, OH; 5Guthrie Robert Packer Hospital, Sayre, PA; 6University of Florida College of Medicine, Jacksonville, FL; 7Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, PA
Introduction: Gastrointestinal complications, particularly various forms of colitis, are a major concern in patients with lymphoid and hematopoietic malignancies. Proteasome inhibitors are increasingly utilized in treatment, but their impact on specific colitis-related conditions, such as CMV colitis, Ischemic colitis, diverticulitis, remains underexplored. Given the potential severity of these complications, it is crucial to assess whether proteasome inhibitors increase the risk of colitis and other GI disorders in this vulnerable population. This study aims to provide a comparative analysis of colitis-related complications in patients treated with proteasome inhibitors to inform therapeutic decisions and patient management.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective cohort analysis using data from 32,589 patients with malignant lymphoid and hematopoietic neoplasms from the TriNetX research network. Two cohorts were identified: patients treated with proteasome inhibitors (Cohort 1) and those without (Cohort 2). Inclusion criteria were age ≥18 years, and patients with a diagnosis of ulcerative colitis or Crohn’s disease were excluded. Propensity score matching was performed to adjust for confounding variables, including age, sex, race, and comorbidities such as type 2 diabetes mellitus, essential hypertension, overweight/obesity, cerebrovascular disease, ischemic heart disease, chronic kidney disease, nicotine dependence, and alcohol abuse. Primary outcomes included colitis-related complications, such as microscopic colitis, CMV colitis, diverticulitis, and ischemic colitis. Hazard ratios (HR) and 95% confidence intervals (CI) were calculated using Cox proportional hazards regression.
Results: Proteasome inhibitor use was associated with increased risk of CMV colitis (HR 1.595, 95% CI 1.406–1.808), diverticulitis (HR 1.325, 95% CI 1.152–1.524), and ischemic colitis (HR 1.674, 95% CI 0.817–3.432), though the latter was not statistically significant. Microscopic colitis showed a lower, non-significant risk (HR 0.95, 95% CI 0.597–1.518).
Discussion: Proteasome inhibitor use in patients with lymphoid and hematopoietic malignancies was associated with a significantly higher risk of CMV colitis and diverticulitis, as well as an elevated risk of ischemic colitis. In contrast, the risk of microscopic colitis appeared lower. These findings suggest a potential for serious gastrointestinal complications, emphasizing the need for monitoring and a careful approach to proteasome inhibitor therapy.

Figure: Figure 1: Comparison of Demographics and Comorbidities of Proteasome inhibitor Users and Non- Proteasome inhibitor Users Before and After Propensity Score Matching

Figure: Figure 2: Forest plot comparing Hazard ratios in Proteasome inhibitor group versus Non-Proteasome inhibitor group.
Disclosures:
Chidera Onwuzo indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Somtochukwu Onwuzo indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kojo-Frimpong B. Awuah indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rashid Abdel-Razeq indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Areeb Khan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Eloho Olojakpoke indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Solomon Anighoro indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Antoine Boustany indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Laith Alomari indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Al-Aman Shaukat indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Chidera Onwuzo, MBBS1, Somtochukwu Onwuzo, MD2, Kojo-Frimpong B. Awuah, MD3, Rashid Abdel-Razeq, MD4, Areeb Khan, MD1, Eloho Olojakpoke, MBBS1, Solomon Anighoro, MBBS5, Antoine Boustany, MD6, Laith Alomari, MD7, Al-Aman Shaukat, MBBS1. P3217 - Proteasome Inhibitors and Colitis: A Comparative Look at Gastrointestinal Complications in Lymphoid and Hematopoietic Malignancies, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
