Monday Poster Session
Category: IBD
P3281 - A Comparison of Adverse Events of Upadacitinib and Vedolizumab with Adalimumab in Ulcerative Colitis: Insights into Real-World Data From a Pharmacovigilance Database
Monday, October 27, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall
.jpg)
Yash P. Ashara, MBBS (he/him/his)
Detroit Medical Center/Wayne State University
Detroit, MI
Presenting Author(s)
Yash P. Ashara, MBBS1, Ruchir Paladiya, MBBS2, Madhav Changela, MD3, Bhavtosh Dedania, MD4
1Detroit Medical Center/Wayne State University, Detroit, MI; 2University of Connecticut School of Medicine, Farmington, CT; 3One Brooklyn Health-Interfaith Medical Center, Brooklyn, NY; 4HCA Florida Healthcare, Brandon, FL
Introduction: Inflammatory bowel disease treatment has evolved within last decade with development of targeted therapies. As therapeutic efficacy has improved, evaluating safety profiles has become critical in selecting right therapy. Adalimumab (TNF-α inhibitor) has now established well-documented efficacy and safety in clinical trials and real world settings. Upadacitinib, JAK inhibitor has quicker symptom relief action as compared to other biologics, while Vedolizumab, a gut specific α4β7 integrin inhibitor offers localized effects. Here, we compare their safety profile.
Methods: The US Food and Drug Administration’s Adverse Event Reports System (FAERS) database was queried for upadacitinib, vedolizumab and adalimumab in UC patients with data updated until September 30, 2024. Patient demographics were recorded with rates of infection, musculoskeletal, nervous, skin and respiratory disorders. AI tool was used for generation of images. Analysis was performed and reporting risk ratio (RR) was calculated with 95% confidence interval (CI) and statistical significance p < 0.05.
Results: Dataset of 40,317 adverse events in UC patients treated with upadacitnib, vedolizumab and adalimumab reported 22077 (54.76%) females. The risk of serious reactions was 83% higher with upadacitinib and more than double with vedolizumab compared to adalimumab. The hospitalization rate with upadacitinib and vedolizumab was 46% and 27% higher compared to adalimumab, respectively. Death risk was about 45% higher with both the drugs compared to adalimumab. The risk of contracting infection with upadacitinib was 37.5% higher with upadacitinib compared to adalimumab (95 % CI 1.22-1.55) while with vedolizumab was 27.9% higher compared to adalimumab (95% CI 1.22-1.34). There was lower risk of nervous (RR 0.83, 95% CI 0.70-0.99) and musculoskeletal (RR 0.77, 95% CI 0.64-0.92) disorders with upadacitinib when compared to adalimumab, but no statistical significant difference between respiratory and skin disorders.
Discussion: UC patients on upadacitinib and vedolizumab have significantly higher rate of infections, and lower rate of nervous and musculoskeletal disorders when compared to adalimumab. Also, vedolizumab have lower rate of skin and respiratory disorders as compared to adalimumab. Although vedolizumab leads to more serious side effects, it causes less hospitalization than upadacitinib, presenting a complex but manageable risk profile.
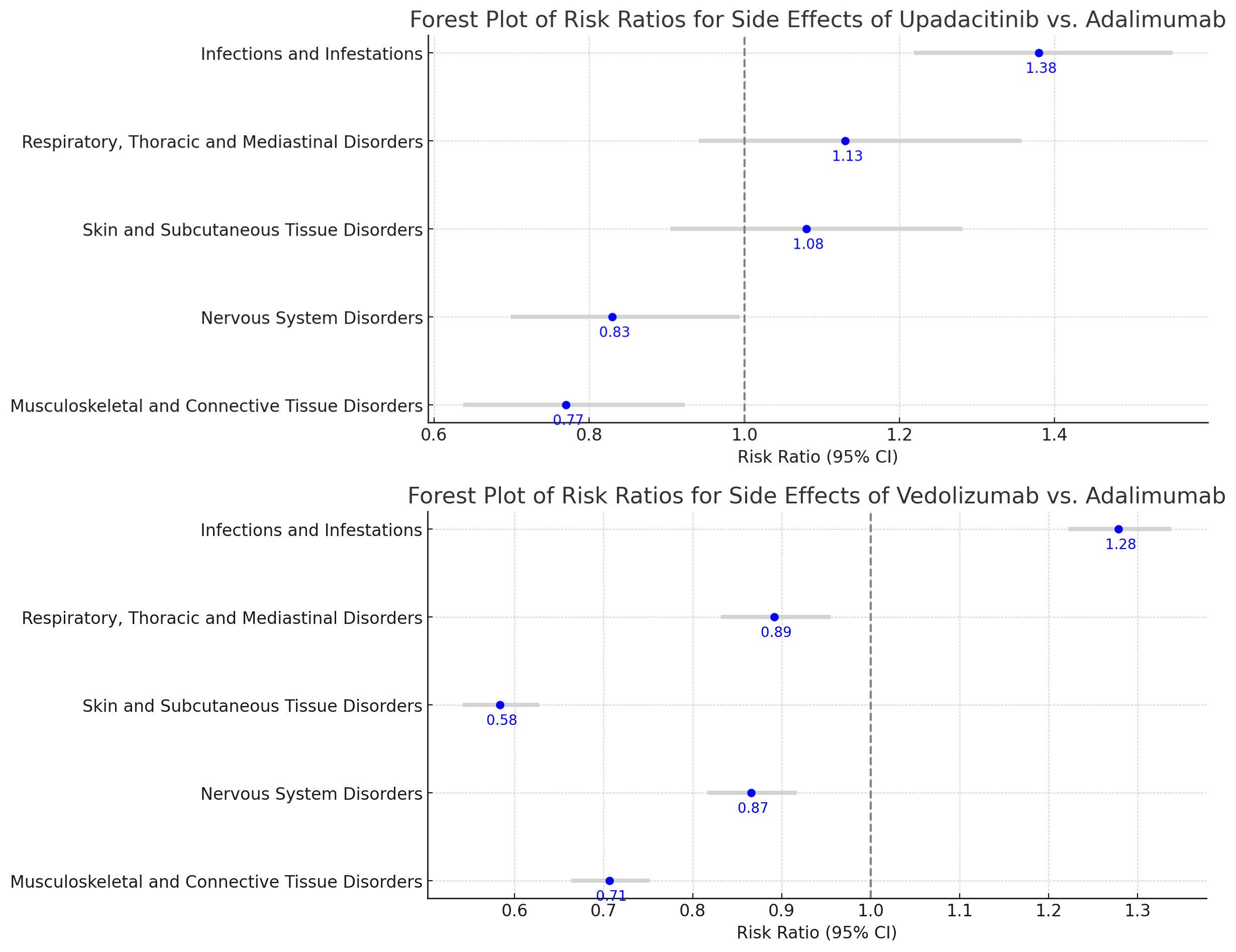
Figure: A) Forest Plot of Risk Ratios of Upadacitinib vs Adalimumab
B) Forest Plot of Risk Ratios of Vedolizumab vs Adalimumab

Figure: Bar Graph of Relative Risks of Serious Events, Hospitalizations, Deaths in Upadacitinib vs Adalimumab and Vedolizumab vs Adalimumab
Disclosures:
Yash Ashara indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ruchir Paladiya indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Madhav Changela indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Bhavtosh Dedania indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Yash P. Ashara, MBBS1, Ruchir Paladiya, MBBS2, Madhav Changela, MD3, Bhavtosh Dedania, MD4. P3281 - A Comparison of Adverse Events of Upadacitinib and Vedolizumab with Adalimumab in Ulcerative Colitis: Insights into Real-World Data From a Pharmacovigilance Database, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Detroit Medical Center/Wayne State University, Detroit, MI; 2University of Connecticut School of Medicine, Farmington, CT; 3One Brooklyn Health-Interfaith Medical Center, Brooklyn, NY; 4HCA Florida Healthcare, Brandon, FL
Introduction: Inflammatory bowel disease treatment has evolved within last decade with development of targeted therapies. As therapeutic efficacy has improved, evaluating safety profiles has become critical in selecting right therapy. Adalimumab (TNF-α inhibitor) has now established well-documented efficacy and safety in clinical trials and real world settings. Upadacitinib, JAK inhibitor has quicker symptom relief action as compared to other biologics, while Vedolizumab, a gut specific α4β7 integrin inhibitor offers localized effects. Here, we compare their safety profile.
Methods: The US Food and Drug Administration’s Adverse Event Reports System (FAERS) database was queried for upadacitinib, vedolizumab and adalimumab in UC patients with data updated until September 30, 2024. Patient demographics were recorded with rates of infection, musculoskeletal, nervous, skin and respiratory disorders. AI tool was used for generation of images. Analysis was performed and reporting risk ratio (RR) was calculated with 95% confidence interval (CI) and statistical significance p < 0.05.
Results: Dataset of 40,317 adverse events in UC patients treated with upadacitnib, vedolizumab and adalimumab reported 22077 (54.76%) females. The risk of serious reactions was 83% higher with upadacitinib and more than double with vedolizumab compared to adalimumab. The hospitalization rate with upadacitinib and vedolizumab was 46% and 27% higher compared to adalimumab, respectively. Death risk was about 45% higher with both the drugs compared to adalimumab. The risk of contracting infection with upadacitinib was 37.5% higher with upadacitinib compared to adalimumab (95 % CI 1.22-1.55) while with vedolizumab was 27.9% higher compared to adalimumab (95% CI 1.22-1.34). There was lower risk of nervous (RR 0.83, 95% CI 0.70-0.99) and musculoskeletal (RR 0.77, 95% CI 0.64-0.92) disorders with upadacitinib when compared to adalimumab, but no statistical significant difference between respiratory and skin disorders.
Discussion: UC patients on upadacitinib and vedolizumab have significantly higher rate of infections, and lower rate of nervous and musculoskeletal disorders when compared to adalimumab. Also, vedolizumab have lower rate of skin and respiratory disorders as compared to adalimumab. Although vedolizumab leads to more serious side effects, it causes less hospitalization than upadacitinib, presenting a complex but manageable risk profile.

Figure: A) Forest Plot of Risk Ratios of Upadacitinib vs Adalimumab
B) Forest Plot of Risk Ratios of Vedolizumab vs Adalimumab

Figure: Bar Graph of Relative Risks of Serious Events, Hospitalizations, Deaths in Upadacitinib vs Adalimumab and Vedolizumab vs Adalimumab
Disclosures:
Yash Ashara indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ruchir Paladiya indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Madhav Changela indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Bhavtosh Dedania indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Yash P. Ashara, MBBS1, Ruchir Paladiya, MBBS2, Madhav Changela, MD3, Bhavtosh Dedania, MD4. P3281 - A Comparison of Adverse Events of Upadacitinib and Vedolizumab with Adalimumab in Ulcerative Colitis: Insights into Real-World Data From a Pharmacovigilance Database, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
