Monday Poster Session
Category: IBD
P3280 - Analyzing Treatment Safety: A Comparative Review of Reported Adverse Events in Ulcerative Colitis Patients Treated With Upadacitinib, Ustekinumab, and Adalimumab Using Nationwide Pharmacovigilance Data
Monday, October 27, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall
.jpg)
Yash P. Ashara, MBBS (he/him/his)
Detroit Medical Center/Wayne State University
Detroit, MI
Presenting Author(s)
Yash P. Ashara, MBBS1, Ruchir Paladiya, MBBS2, Madhav Changela, MD3, Bhavtosh Dedania, MD4
1Detroit Medical Center/Wayne State University, Detroit, MI; 2University of Connecticut School of Medicine, Farmington, CT; 3One Brooklyn Health-Interfaith Medical Center, Brooklyn, NY; 4HCA Florida Healthcare, Brandon, FL
Introduction: Ulcerative colitis (UC) is a chronic gut mucosa inflammation requiring long-term management. Recent advances include target-specific immune therapies, ranging from small-molecule therapies like upadacitinib to large, protein-based biologics like ustekinumab and adalimumab. While biologics are administered intravenously or subcutaneously, small molecules offer oral convenience. Analyzing real-world post-marketing data, we aim to identify the distinct adverse events pattern for patient specific therapeutic decision.
Methods: The US Food and Drug Administration’s Adverse Event Reports System (FAERS) was queried to identify adverse events report for upadacitnib, ustekinumab and adalimumab in UC. Data collected include frequency of infections and infestations, nervous system disorders, musculoskeletal, skin and subcutaneous, respiratory disorders. AI tool was used to generate images. Comparative safety analysis was conducted using reported risk ratio (RR) with 95% confidence interval (CI) and statistical significance < 0.05.
Results: A dataset of 26,004 adverse events in UC patients treated with upadacitnib, ustekinumab and adalimumab was extracted with data until September 30, 2024. 11,148 (42.87%) patients were male. The risk of serious event was significantly higher in both upadacitnib and ustekinumab as compared to adalimumab. Patients on upadacitinib had a 46% increased risk of hospitalization compared to adalimumab, while ustekinumab showed a 22% reduction. Additionally, the mortality risk was 45% higher with upadacitinib (RR 1.45, 95% CI 1.05-2.01) and 32% lower with ustekinumab (RR 0.68, 95% CI 0.47-0.99) relative to adalimumab. The risk of infection with upadacitnib was higher than adalimumab with most common infection being covid-19, nasopharyngitis, C. difficle. There was significant reduction of nervous and musculoskeletal disorders with ustekinumab and upadacitnib as compared to adalimumab. Respiratory events were reduced by 39% in ustekinumab. There was no statistical significance difference in skin and respiratory events with upadacitinib, or in infection and skin events with ustekinumab. Incorporating gender and age did not yield any statistical significance.
Discussion: In UC patients, ustekinumab was associated with reduced rates of hospitalization and mortality compared to upadacitinib, highlighting the differential safety profiles. Upadacitnib is associated with increased risk of infection. Additionally, there was significant reduction of respiratory events in ustekinumab.
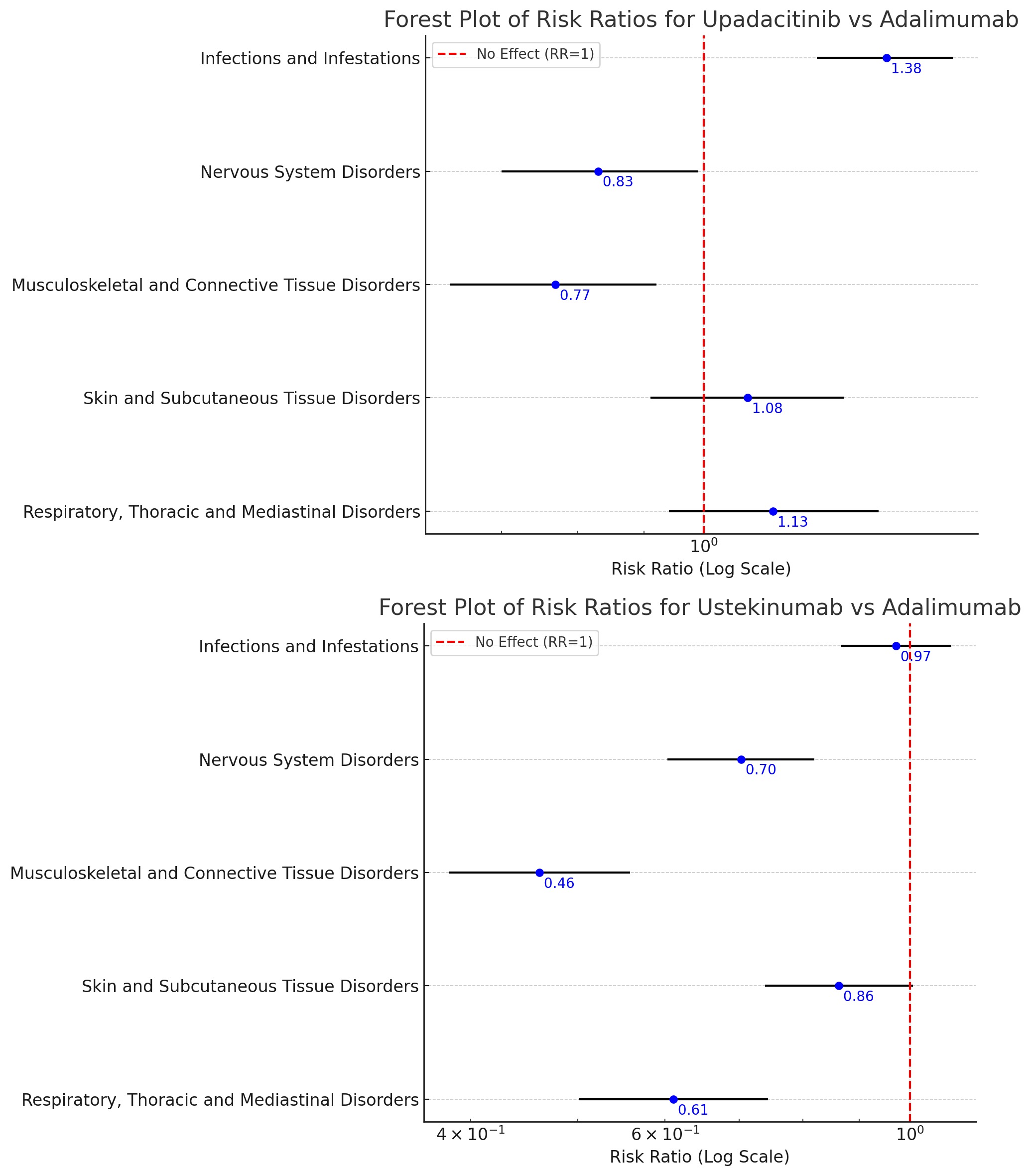
Figure: Forest Plot of Risk Ration for Upadacitinib vs Adalimumab and Ustekinumab vs Adalimumab in UC

Figure: Bar Graph of Relative Risks for Serious Cases, Hospitalization, Death in Upadacitinib vs Adalimumab and Ustekinumab vs Adalimumab in UC
Disclosures:
Yash Ashara indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ruchir Paladiya indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Madhav Changela indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Bhavtosh Dedania indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Yash P. Ashara, MBBS1, Ruchir Paladiya, MBBS2, Madhav Changela, MD3, Bhavtosh Dedania, MD4. P3280 - Analyzing Treatment Safety: A Comparative Review of Reported Adverse Events in Ulcerative Colitis Patients Treated With Upadacitinib, Ustekinumab, and Adalimumab Using Nationwide Pharmacovigilance Data, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Detroit Medical Center/Wayne State University, Detroit, MI; 2University of Connecticut School of Medicine, Farmington, CT; 3One Brooklyn Health-Interfaith Medical Center, Brooklyn, NY; 4HCA Florida Healthcare, Brandon, FL
Introduction: Ulcerative colitis (UC) is a chronic gut mucosa inflammation requiring long-term management. Recent advances include target-specific immune therapies, ranging from small-molecule therapies like upadacitinib to large, protein-based biologics like ustekinumab and adalimumab. While biologics are administered intravenously or subcutaneously, small molecules offer oral convenience. Analyzing real-world post-marketing data, we aim to identify the distinct adverse events pattern for patient specific therapeutic decision.
Methods: The US Food and Drug Administration’s Adverse Event Reports System (FAERS) was queried to identify adverse events report for upadacitnib, ustekinumab and adalimumab in UC. Data collected include frequency of infections and infestations, nervous system disorders, musculoskeletal, skin and subcutaneous, respiratory disorders. AI tool was used to generate images. Comparative safety analysis was conducted using reported risk ratio (RR) with 95% confidence interval (CI) and statistical significance < 0.05.
Results: A dataset of 26,004 adverse events in UC patients treated with upadacitnib, ustekinumab and adalimumab was extracted with data until September 30, 2024. 11,148 (42.87%) patients were male. The risk of serious event was significantly higher in both upadacitnib and ustekinumab as compared to adalimumab. Patients on upadacitinib had a 46% increased risk of hospitalization compared to adalimumab, while ustekinumab showed a 22% reduction. Additionally, the mortality risk was 45% higher with upadacitinib (RR 1.45, 95% CI 1.05-2.01) and 32% lower with ustekinumab (RR 0.68, 95% CI 0.47-0.99) relative to adalimumab. The risk of infection with upadacitnib was higher than adalimumab with most common infection being covid-19, nasopharyngitis, C. difficle. There was significant reduction of nervous and musculoskeletal disorders with ustekinumab and upadacitnib as compared to adalimumab. Respiratory events were reduced by 39% in ustekinumab. There was no statistical significance difference in skin and respiratory events with upadacitinib, or in infection and skin events with ustekinumab. Incorporating gender and age did not yield any statistical significance.
Discussion: In UC patients, ustekinumab was associated with reduced rates of hospitalization and mortality compared to upadacitinib, highlighting the differential safety profiles. Upadacitnib is associated with increased risk of infection. Additionally, there was significant reduction of respiratory events in ustekinumab.

Figure: Forest Plot of Risk Ration for Upadacitinib vs Adalimumab and Ustekinumab vs Adalimumab in UC

Figure: Bar Graph of Relative Risks for Serious Cases, Hospitalization, Death in Upadacitinib vs Adalimumab and Ustekinumab vs Adalimumab in UC
Disclosures:
Yash Ashara indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ruchir Paladiya indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Madhav Changela indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Bhavtosh Dedania indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Yash P. Ashara, MBBS1, Ruchir Paladiya, MBBS2, Madhav Changela, MD3, Bhavtosh Dedania, MD4. P3280 - Analyzing Treatment Safety: A Comparative Review of Reported Adverse Events in Ulcerative Colitis Patients Treated With Upadacitinib, Ustekinumab, and Adalimumab Using Nationwide Pharmacovigilance Data, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
