Monday Poster Session
Category: IBD
P3353 - ARMOR Study: Immunogenicity and Safety of Recombinant Spike Protein Vaccine in Patients With Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Liver Transplant Recipients Comparable to Healthy Controls
Monday, October 27, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Ahamed Lazim Vattoth, MD
University of Wisconsin Hospitals and Clinics
Madison, WI
Presenting Author(s)
Ahamed Lazim Vattoth, MD1, Mary S. Hayney, PharmD, MPH2, Freddy Caldera, DO, PhD, MS1
1University of Wisconsin Hospitals and Clinics, Madison, WI; 2University of Wisconsin-Madison School of Pharmacy, Madison, WI
Introduction: mRNA COVID-19 vaccines are safe in immunosuppressed populations, data on protein-based vaccines remain limited. We evaluated the immunogenicity and safety of Novavax COVID-19 vaccine (NVX-CoV2601) in immunosuppressed patients.
Methods: This single-center, prospective ARMOR study included adults with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) or solid organ transplant recipients receiving immunosuppressive therapy with ≥3 prior COVID-19 vaccine doses. Participants received one NVX-CoV2601 booster with follow-up at one and six months. Antibody concentrations were measured using anti-spike IgG ELISA and pseudovirus neutralization. The primary outcome was change in antibody concentration from baseline to one month post-vaccination in ARMOR participants. Secondary outcomes included evaluating sustained antibody concentration at 6 months post-immunization, humoral immunogenicity in the ARMOR cohort compared to an age/sex-matched healthy control cohort, adverse events, and safety (IBD flares or transplant rejection). Statistical analyses included paired t-tests for antibody concentration changes and ANCOVA with baseline adjustment for between-group comparisons. GMTs and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were calculated using log-transformed values.
Results: Twenty-one patients, 18 IBD and 3 liver transplant recipients, were enrolled in ARMOR and compared with 42 age/sex-matched healthy controls (Mean age 47.65, 60% males) (Table 1). In the ARMOR cohort, anti-spike IgG GMT increased significantly post-immunization (22,969 to 66,639 EU/mL at one month; 2.9-fold increase, p=0.001). Healthy controls showed an increase from 54,812 to 129,813 EU/mL (2.4-fold increase; p< 0.001). Neutralizing antibody analysis showed similar trends, with ARMOR participants demonstrating a 3.6-fold increase from baseline (GMT 174.6 ID50 to 628.0 ID50; p=0.002) versus controls' 1.6-fold increase (p=0.001), with no statistically significant difference between groups at day 28 after baseline adjustment (GMTR 1.12; p=0.728). At 6 months, both binding and neutralizing antibodies waned faster in immunosuppressed subjects (GMTR 0.60, p=0.009 for binding; GMTR 0.44, p=0.008 for neutralizing) compared to controls. NVX-CoV2601 was well tolerated, with mild reactogenicity, and was not associated with IBD flares or solid organ rejection.
Discussion: NVX-CoV2601 was safe and immunogenic with similar antibody responses in immunosuppressed patients compared to healthy controls, in contrast to that seen with mRNA vaccines.
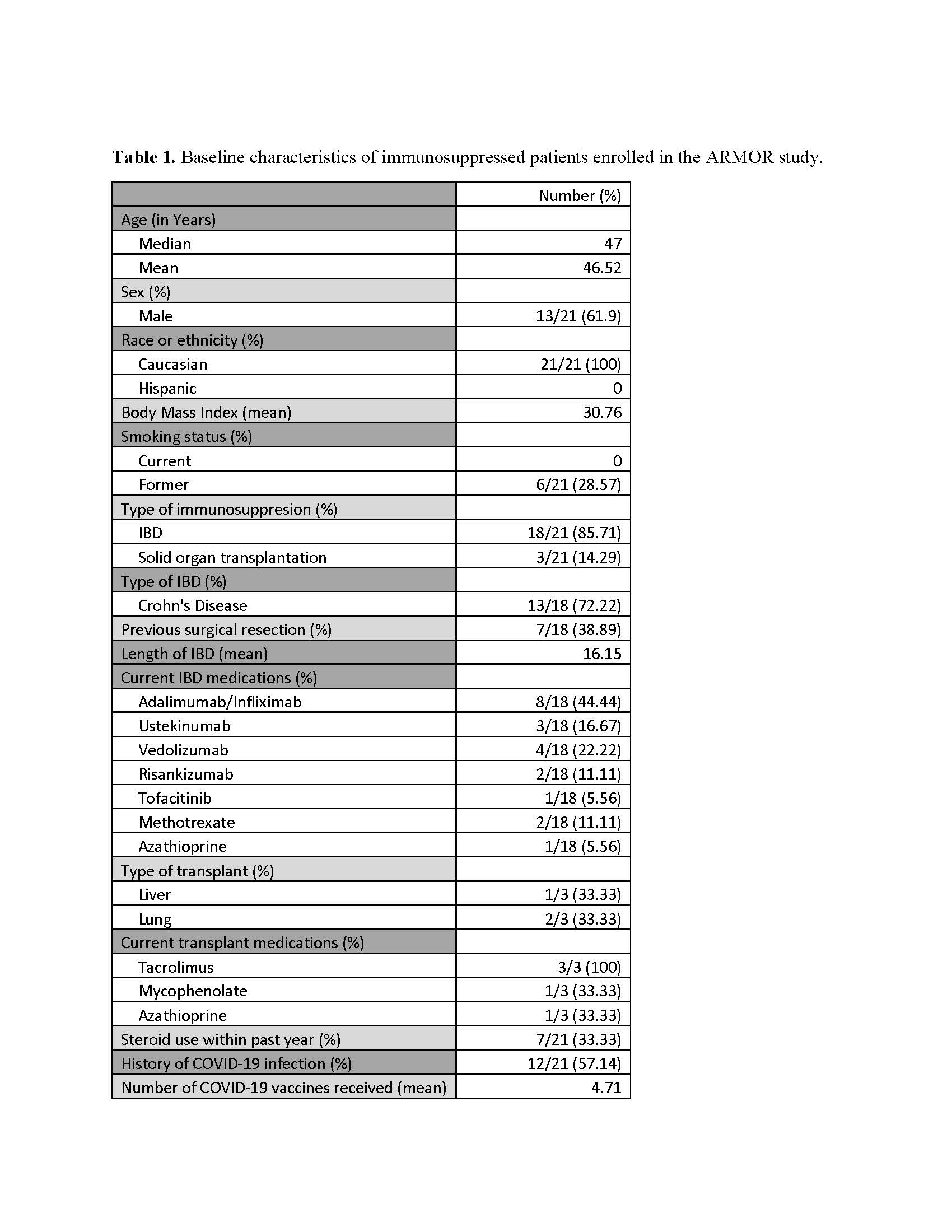
Figure: Table 1. Baseline characteristics of immunosuppressed patients enrolled in the ARMOR study.
Disclosures:
Ahamed Lazim Vattoth indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mary Hayney: GSK Vaccines – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Speakers Bureau. Novavax – Grant/Research Support. Takeda – Grant/Research Support.
Freddy Caldera: GSK – Consultant. GSK – Grant/Research Support. Janssen – Consultant. Novavax – Grant/Research Support.
Ahamed Lazim Vattoth, MD1, Mary S. Hayney, PharmD, MPH2, Freddy Caldera, DO, PhD, MS1. P3353 - ARMOR Study: Immunogenicity and Safety of Recombinant Spike Protein Vaccine in Patients With Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Liver Transplant Recipients Comparable to Healthy Controls, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1University of Wisconsin Hospitals and Clinics, Madison, WI; 2University of Wisconsin-Madison School of Pharmacy, Madison, WI
Introduction: mRNA COVID-19 vaccines are safe in immunosuppressed populations, data on protein-based vaccines remain limited. We evaluated the immunogenicity and safety of Novavax COVID-19 vaccine (NVX-CoV2601) in immunosuppressed patients.
Methods: This single-center, prospective ARMOR study included adults with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) or solid organ transplant recipients receiving immunosuppressive therapy with ≥3 prior COVID-19 vaccine doses. Participants received one NVX-CoV2601 booster with follow-up at one and six months. Antibody concentrations were measured using anti-spike IgG ELISA and pseudovirus neutralization. The primary outcome was change in antibody concentration from baseline to one month post-vaccination in ARMOR participants. Secondary outcomes included evaluating sustained antibody concentration at 6 months post-immunization, humoral immunogenicity in the ARMOR cohort compared to an age/sex-matched healthy control cohort, adverse events, and safety (IBD flares or transplant rejection). Statistical analyses included paired t-tests for antibody concentration changes and ANCOVA with baseline adjustment for between-group comparisons. GMTs and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were calculated using log-transformed values.
Results: Twenty-one patients, 18 IBD and 3 liver transplant recipients, were enrolled in ARMOR and compared with 42 age/sex-matched healthy controls (Mean age 47.65, 60% males) (Table 1). In the ARMOR cohort, anti-spike IgG GMT increased significantly post-immunization (22,969 to 66,639 EU/mL at one month; 2.9-fold increase, p=0.001). Healthy controls showed an increase from 54,812 to 129,813 EU/mL (2.4-fold increase; p< 0.001). Neutralizing antibody analysis showed similar trends, with ARMOR participants demonstrating a 3.6-fold increase from baseline (GMT 174.6 ID50 to 628.0 ID50; p=0.002) versus controls' 1.6-fold increase (p=0.001), with no statistically significant difference between groups at day 28 after baseline adjustment (GMTR 1.12; p=0.728). At 6 months, both binding and neutralizing antibodies waned faster in immunosuppressed subjects (GMTR 0.60, p=0.009 for binding; GMTR 0.44, p=0.008 for neutralizing) compared to controls. NVX-CoV2601 was well tolerated, with mild reactogenicity, and was not associated with IBD flares or solid organ rejection.
Discussion: NVX-CoV2601 was safe and immunogenic with similar antibody responses in immunosuppressed patients compared to healthy controls, in contrast to that seen with mRNA vaccines.

Figure: Table 1. Baseline characteristics of immunosuppressed patients enrolled in the ARMOR study.
Disclosures:
Ahamed Lazim Vattoth indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mary Hayney: GSK Vaccines – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Speakers Bureau. Novavax – Grant/Research Support. Takeda – Grant/Research Support.
Freddy Caldera: GSK – Consultant. GSK – Grant/Research Support. Janssen – Consultant. Novavax – Grant/Research Support.
Ahamed Lazim Vattoth, MD1, Mary S. Hayney, PharmD, MPH2, Freddy Caldera, DO, PhD, MS1. P3353 - ARMOR Study: Immunogenicity and Safety of Recombinant Spike Protein Vaccine in Patients With Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Liver Transplant Recipients Comparable to Healthy Controls, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
