Monday Poster Session
Category: IBD
P3352 - Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Colonoscopy - A Meta-Analysis on Its Diagnostic Accuracy in Ulcerative Colitis
Monday, October 27, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall
- AG
Aryan Gupta
bangalore medical college and research institute
Bangalore, Karnataka, India
Presenting Author(s)
Vinay Chandramouli Bellur, 1, Aryan Gupta, 2, Ananya Prasad, 3, Omar Oudit, DO4, Kushal Prasad, 5, Vardhini Ganesh Iyer, 6, Era Gupta, 5, Shekhar Kalra, 7
1Ramaiah medical college, Bangalore, Karnataka, India; 2bangalore medical college and research institute, Bangalore, Karnataka, India; 3ramaiah medical college, Bangalore, Karnataka, India; 4Brookdale University Hospital Medical Center, Brooklyn, NY; 5Bangalore Medical College and Research Institute, Bangalore, Karnataka, India; 6BGS Global Institute of Medical Sciences, Bangalore, Karnataka, India; 7Maulana Azad Medical College, Bangalore, Karnataka, India
Introduction: Artificial intelligence (AI) has emerged as a promising tool in gastroenterology, particularly in the realm of colonoscopies. AI-powered systems can analyze endoscopic images in real-time, enhancing the detection and characterization of mucosal abnormalities associated with Ulcerative Colitis (UC). These systems utilize deep learning algorithms trained on vast datasets of colonoscopy images, enabling them to recognize subtle patterns and features that may be challenging for human observers to discern consistently. The integration of AI in colonoscopy procedures has the potential to improve diagnostic accuracy, standardize assessment criteria, and reduce inter-observer variability. Furthermore, AI-assisted colonoscopy may facilitate early detection of UC-related dysplasia and optimize treatment strategies by providing objective measures of disease activity and extent.
Methods: The meta-analysis conducted follows the PRISMA guidelines and major medical databases, which include PUBMED, Google Scholar and Science-Direct, were extensively searched using a comprehensive search term to identify and retrieve the available relevant articles. The articles that assessed the diagnostic potential of the AI model, ie, Accuracy, were included in the final analysis.
The data was analysed using the Meta, Metadata and the Metafor packages of R Studio. The pooled accuracy was assessed in the study to estimate the diagnostic potential of AI-assisted colonoscopy in ulcerative colitis patients.The random effects model via the linear (mixed-effects) model framework was considered for statistical analysis.
Results: The review included a total of 10,632 diagnostic events from 5 included studies that used various AI models in colonoscopy procedures for diagnosis of ulcerative colitis. The pooled accuracy was analysed to be 0.78 [0.68;0.86, CI 95%, p< 0.0001]. The Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) was the most accurate and widely used AI model.
Discussion: This meta-analysis has statistically established the clinical prowess of AI models in colonoscopy and its diagnostic utility in ulcerative colitis, as suggested by its high pooled accuracy.
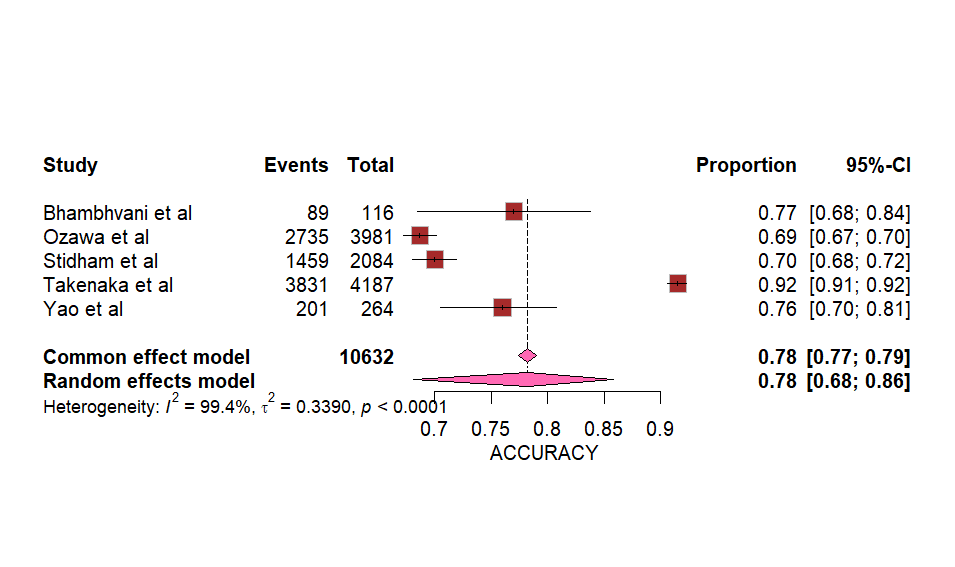
Figure: Pooled Accuracy of AI models.
Disclosures:
Vinay Chandramouli Bellur indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Aryan Gupta indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ananya Prasad indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Omar Oudit indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kushal Prasad indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Vardhini Ganesh Iyer indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Era Gupta indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Shekhar Kalra indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Vinay Chandramouli Bellur, 1, Aryan Gupta, 2, Ananya Prasad, 3, Omar Oudit, DO4, Kushal Prasad, 5, Vardhini Ganesh Iyer, 6, Era Gupta, 5, Shekhar Kalra, 7. P3352 - Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Colonoscopy - A Meta-Analysis on Its Diagnostic Accuracy in Ulcerative Colitis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Ramaiah medical college, Bangalore, Karnataka, India; 2bangalore medical college and research institute, Bangalore, Karnataka, India; 3ramaiah medical college, Bangalore, Karnataka, India; 4Brookdale University Hospital Medical Center, Brooklyn, NY; 5Bangalore Medical College and Research Institute, Bangalore, Karnataka, India; 6BGS Global Institute of Medical Sciences, Bangalore, Karnataka, India; 7Maulana Azad Medical College, Bangalore, Karnataka, India
Introduction: Artificial intelligence (AI) has emerged as a promising tool in gastroenterology, particularly in the realm of colonoscopies. AI-powered systems can analyze endoscopic images in real-time, enhancing the detection and characterization of mucosal abnormalities associated with Ulcerative Colitis (UC). These systems utilize deep learning algorithms trained on vast datasets of colonoscopy images, enabling them to recognize subtle patterns and features that may be challenging for human observers to discern consistently. The integration of AI in colonoscopy procedures has the potential to improve diagnostic accuracy, standardize assessment criteria, and reduce inter-observer variability. Furthermore, AI-assisted colonoscopy may facilitate early detection of UC-related dysplasia and optimize treatment strategies by providing objective measures of disease activity and extent.
Methods: The meta-analysis conducted follows the PRISMA guidelines and major medical databases, which include PUBMED, Google Scholar and Science-Direct, were extensively searched using a comprehensive search term to identify and retrieve the available relevant articles. The articles that assessed the diagnostic potential of the AI model, ie, Accuracy, were included in the final analysis.
The data was analysed using the Meta, Metadata and the Metafor packages of R Studio. The pooled accuracy was assessed in the study to estimate the diagnostic potential of AI-assisted colonoscopy in ulcerative colitis patients.The random effects model via the linear (mixed-effects) model framework was considered for statistical analysis.
Results: The review included a total of 10,632 diagnostic events from 5 included studies that used various AI models in colonoscopy procedures for diagnosis of ulcerative colitis. The pooled accuracy was analysed to be 0.78 [0.68;0.86, CI 95%, p< 0.0001]. The Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) was the most accurate and widely used AI model.
Discussion: This meta-analysis has statistically established the clinical prowess of AI models in colonoscopy and its diagnostic utility in ulcerative colitis, as suggested by its high pooled accuracy.

Figure: Pooled Accuracy of AI models.
Disclosures:
Vinay Chandramouli Bellur indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Aryan Gupta indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ananya Prasad indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Omar Oudit indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kushal Prasad indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Vardhini Ganesh Iyer indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Era Gupta indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Shekhar Kalra indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Vinay Chandramouli Bellur, 1, Aryan Gupta, 2, Ananya Prasad, 3, Omar Oudit, DO4, Kushal Prasad, 5, Vardhini Ganesh Iyer, 6, Era Gupta, 5, Shekhar Kalra, 7. P3352 - Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Colonoscopy - A Meta-Analysis on Its Diagnostic Accuracy in Ulcerative Colitis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
