Monday Poster Session
Category: IBD
P3410 - Risankizumab-Associated Drug-Induced Liver Injury in Ulcerative Colitis: A Case Report
Monday, October 27, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Joseph Adrian D. Lapasaran, MS, BA (he/him/his)
GI Alliance of Illinois - Glenview
Glenview, IL
Presenting Author(s)
Joseph Adrian Lapasaran, MS, BA1, Meghana Doniparthi, MD2
1GI Alliance of Illinois - Glenview, Glenview, IL; 2Advocate Lutheran General, Park Ridge, IL
Introduction: Risanzikumab (Skyrizi) is a humanized monoclonal IgG-1 antibody that selectively targets the p19 subunit of interleukin-23 (IL-23). Risankizumab has been most recently approved for Ulcerative Colitis (UC) with an induction dose of 1200 mg IV at week 0, week 4, and week 8 with maintenance doses of 180 mg or 360 mg at week 12 and every 8 weeks after. Due to an occurrence of drug-induced liver injury (DILI) during the induction studies, it is recommended to repeat a hepatic function panel (HFP) at 12 weeks. Risankizumab-related DILI has been rarely reported in patients with rheumatologic conditions or Crohn's disease. We describe the first case in a patient with UC.
Case Description/
Methods: A 43-year-old Caucasian female presented with abdominal cramping and hematochezia. Colonoscopy revealed Mayo 3 severe proctosigmoid/left-sided colitis with deep, confluent ulcerations and cobblestoning of the mucosa. She started prednisone 40 mg daily at the time of endoscopy. She began risankizumab 1200 mg IV induction with concomitant tapering of her prednisone by completion of induction. Baseline laboratory results were normal; however, a post-induction HFP at 12 weeks revealed mild elevation of AST 33 U/L and ALT 40 U/L. Her subcutaneous maintenance dose was reduced to 180 mg every 8 weeks. Subsequent HFP showed stable and trending down transaminases but noted to rise again after her third maintenance dose (Table 1). Liver serologies (Table 2) were overall negative except for a positive ANA titer of 1:320. Ultrasound suggested mild hepatic steatosis. She did have an observed weight gain from 125 lbs to 165 lbs over the treatment period. She reports clinical remission with improved fecal calprotectin from 5830 mcg/g at time of diagnosis to 144 mcg/g currently.
Discussion: Long-term safety data available for risankizumab in rheumatologic conditions suggest a mild to moderate transaminase elevation in up to 10% of patients, rarely requiring drug discontinuation. There are a few case reports describing a similar pattern of DILI confirmed by liver biopsy in patients with Crohn’s disease. The higher induction dose for UC may necessitate close monitoring particularly in patients with co-existing liver disease, such as steatohepatitis. Her transaminases have remained elevated within 2-3x ULN at the lower maintenance dose, and despite clinical response to risankizumab further doses have been held pending investigation of positive ANA with rheumatology and normalization of liver enzymes.
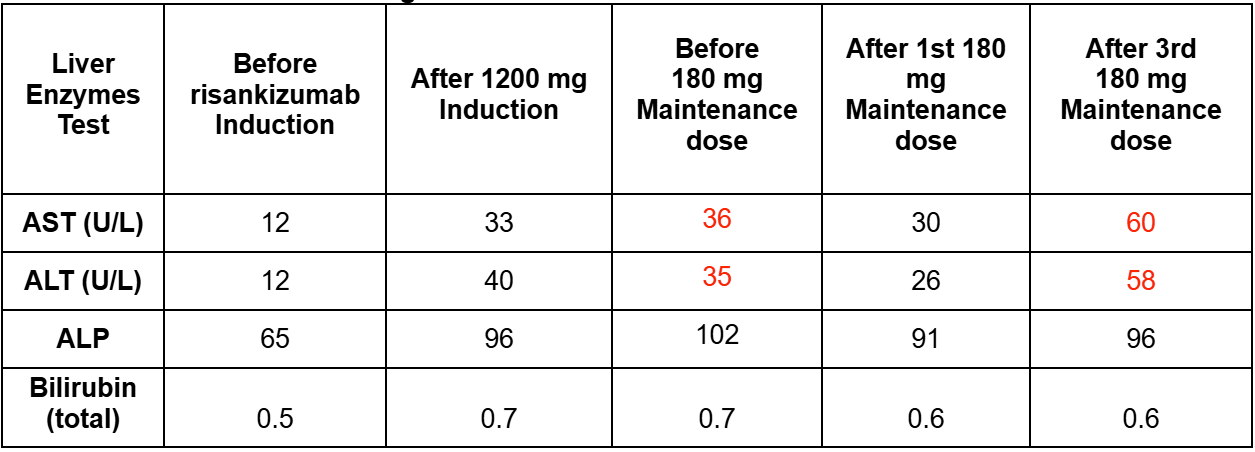
Figure: Table 1: Aspartate aminotransferase (AST; reference range: 10-30 U/L),alanine transaminase (ALT; reference range: 6-29 U/L), alkaline phosphatase (ALP; reference range: 31-125 U/L) enzyme levels and bilirubin (total)(reference range: 0.2-1.2 mg/dL) over the course of risankizumab treatment. Red font = out of range.
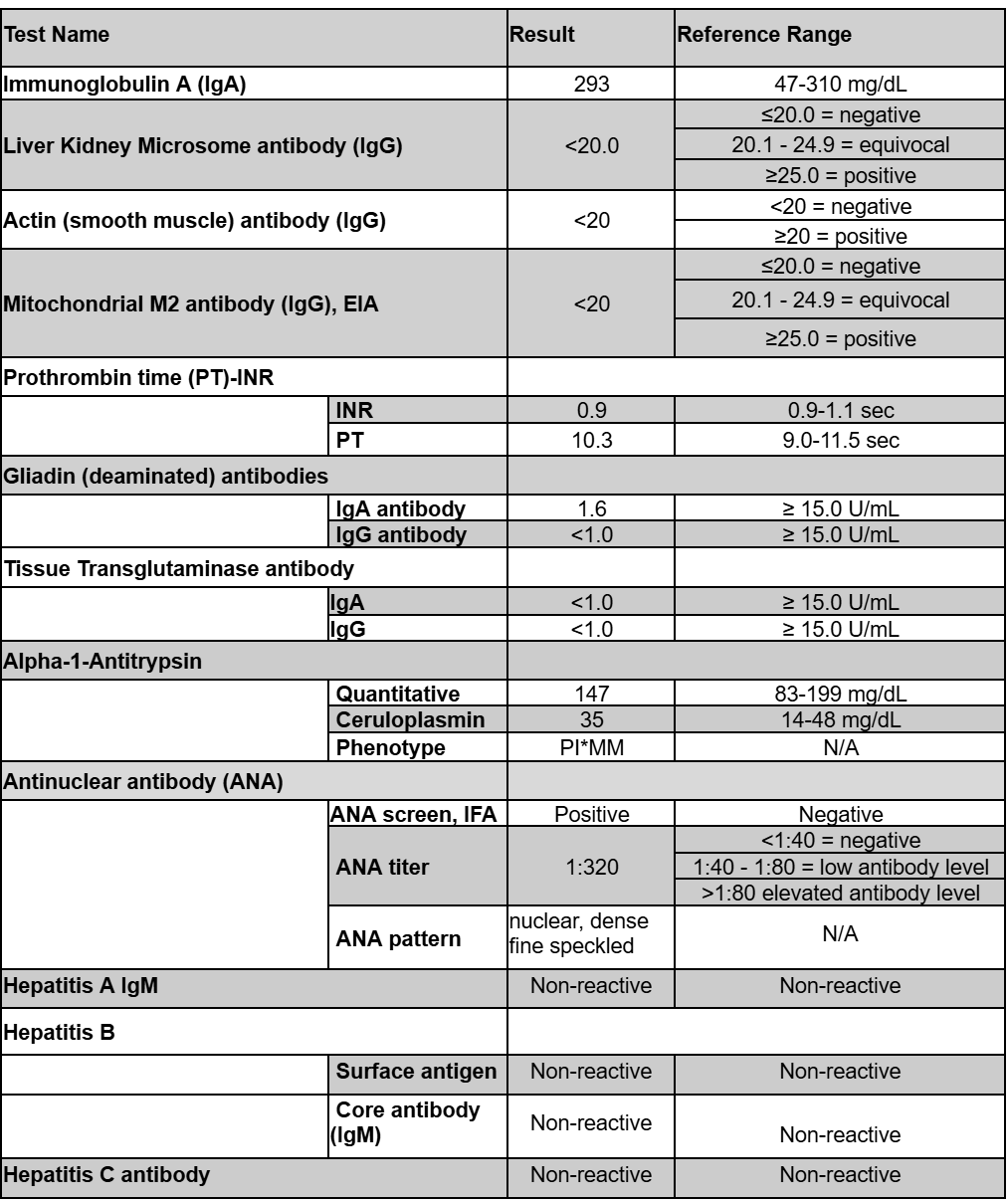
Figure: Table 2: Liver serologic test results to rule out alternate causes of elevated liver enzymes after the third maintenance dose.
Disclosures:
Joseph Adrian Lapasaran indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Meghana Doniparthi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Joseph Adrian Lapasaran, MS, BA1, Meghana Doniparthi, MD2. P3410 - Risankizumab-Associated Drug-Induced Liver Injury in Ulcerative Colitis: A Case Report, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1GI Alliance of Illinois - Glenview, Glenview, IL; 2Advocate Lutheran General, Park Ridge, IL
Introduction: Risanzikumab (Skyrizi) is a humanized monoclonal IgG-1 antibody that selectively targets the p19 subunit of interleukin-23 (IL-23). Risankizumab has been most recently approved for Ulcerative Colitis (UC) with an induction dose of 1200 mg IV at week 0, week 4, and week 8 with maintenance doses of 180 mg or 360 mg at week 12 and every 8 weeks after. Due to an occurrence of drug-induced liver injury (DILI) during the induction studies, it is recommended to repeat a hepatic function panel (HFP) at 12 weeks. Risankizumab-related DILI has been rarely reported in patients with rheumatologic conditions or Crohn's disease. We describe the first case in a patient with UC.
Case Description/
Methods: A 43-year-old Caucasian female presented with abdominal cramping and hematochezia. Colonoscopy revealed Mayo 3 severe proctosigmoid/left-sided colitis with deep, confluent ulcerations and cobblestoning of the mucosa. She started prednisone 40 mg daily at the time of endoscopy. She began risankizumab 1200 mg IV induction with concomitant tapering of her prednisone by completion of induction. Baseline laboratory results were normal; however, a post-induction HFP at 12 weeks revealed mild elevation of AST 33 U/L and ALT 40 U/L. Her subcutaneous maintenance dose was reduced to 180 mg every 8 weeks. Subsequent HFP showed stable and trending down transaminases but noted to rise again after her third maintenance dose (Table 1). Liver serologies (Table 2) were overall negative except for a positive ANA titer of 1:320. Ultrasound suggested mild hepatic steatosis. She did have an observed weight gain from 125 lbs to 165 lbs over the treatment period. She reports clinical remission with improved fecal calprotectin from 5830 mcg/g at time of diagnosis to 144 mcg/g currently.
Discussion: Long-term safety data available for risankizumab in rheumatologic conditions suggest a mild to moderate transaminase elevation in up to 10% of patients, rarely requiring drug discontinuation. There are a few case reports describing a similar pattern of DILI confirmed by liver biopsy in patients with Crohn’s disease. The higher induction dose for UC may necessitate close monitoring particularly in patients with co-existing liver disease, such as steatohepatitis. Her transaminases have remained elevated within 2-3x ULN at the lower maintenance dose, and despite clinical response to risankizumab further doses have been held pending investigation of positive ANA with rheumatology and normalization of liver enzymes.

Figure: Table 1: Aspartate aminotransferase (AST; reference range: 10-30 U/L),alanine transaminase (ALT; reference range: 6-29 U/L), alkaline phosphatase (ALP; reference range: 31-125 U/L) enzyme levels and bilirubin (total)(reference range: 0.2-1.2 mg/dL) over the course of risankizumab treatment. Red font = out of range.

Figure: Table 2: Liver serologic test results to rule out alternate causes of elevated liver enzymes after the third maintenance dose.
Disclosures:
Joseph Adrian Lapasaran indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Meghana Doniparthi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Joseph Adrian Lapasaran, MS, BA1, Meghana Doniparthi, MD2. P3410 - Risankizumab-Associated Drug-Induced Liver Injury in Ulcerative Colitis: A Case Report, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.

