Monday Poster Session
Category: Interventional Endoscopy
P3548 - Safety and Efficacy of Hybrid versus Conventional Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection for Removal of Gastrointestinal Lesions: A Meta-Analysis
Monday, October 27, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall
- AB
Adnan Bhat, MD
University of Florida
Gainesville, FL
Presenting Author(s)
Adnan Bhat, MD1, Allah Dad, MD2, Kinza Bakht, MBBS3, Muhammad Arham, 4, Humza Saeed, 5, Zahra Ali, 6, Faseeh Haider, MD7, Saniya Ishtiaq, 8, Anchit Chauhan, 9, Danyal Bakht, MBBS10, Adil Ahmed, 11, Ali Naseem, 12, Imran A. Reshi, MBBS13, Dennis Yang, MD, FACG14, Peter Draganov, MD, FACG1
1University of Florida, Gainesville, FL; 2Shiekh Zayed Medical College Rahim Yar Khan, Pakistan, Kot Addu, Punjab, Pakistan; 3Sheikh Zayed Medical College Rahim Yar Khan, Muzaffargarh, Punjab, Pakistan; 4Sheikh Zayed Medical College, Pakistan, Rahim Yar Khan, Punjab, Pakistan; 5Rawalpindi Medical University, Rawalpindi, Punjab, Pakistan; 6Bolan Medical College, Quetta, Balochistan, Pakistan; 7Allama Iqbal Medical college, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan; 8Rawalpindi Medical University, Rawalpindi, Pakistan, Rawalpindi, Punjab, Pakistan; 9Maulana Azad Medical College, New Delhi, Delhi, India; 10King Edward Medical University, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan; 11Northwest School of Medicine, Peshawar, North-West Frontier, Pakistan; 12King edward medical university lahore, Okara, Punjab, Pakistan; 13Sher i Kashmir Institute of Medical Sciences, Srinagar, Jammu and Kashmir, India; 14Center for Interventional Endoscopic, AdventHealth Orlando, Orlando, FL
Introduction: Endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) is an established method for en-bloc resection of large or complex gastrointestinal (GI) lesions. Conventional ESD (C-ESD) is technically demanding and time-intensive, leading to the development of hybrid ESD (H-ESD) to improve procedural ease and speed. This systematic review and meta-analysis compares the clinical outcomes between H-ESD and C-ESD.
Methods: We searched PubMed, Scopus, Embase, Cochrane Library, ScienceDirect, and ClinicalTrials.gov for eligible studies. Meta-analysis was conducted using R software with random-effects models. Dichotomous outcomes were pooled as risk ratios (RRs) and continuous outcomes as mean differences (MDs), both with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) and a significance threshold of p < 0.05.
Results: 38 studies (7,226 patients; 8,129 lesions) were included. H-ESD was associated with significantly lower en-bloc (RR = 0.91; 95% CI: 0.87 - 0.95; p < 0.001) and complete (R0) resection rates (RR = 0.94; 95% CI: 0.91 - 0.98; p = 0.005), higher local recurrence (RR = 3.03; 95% CI: 1.55 - 5.92; p = 0.001), but shorter procedure time (MD = −16.56 minutes; p < 0.01). There was no significant difference in intra-procedure bleeding (RR = 1.24; p = 0.388), intra-procedure perforation (RR = 0.96; p = 0.831), post-procedure bleeding (RR = 0.81; p = 0.439), and post-procedure perforation (RR = 0.63; p = 0.574). H-ESD showed no significant difference versus C-ESD in lateral margin involvement (p = 0.106), deep margin positivity (p = 0.265), or piecemeal resection rates (p=0.185). In colorectal lesions, H-ESD showed lower en-bloc and complete resection rates vs. C-ESD (p < 0.0001).
Discussion: In conclusion, H-ESD offers shorter procedure times for GI lesions with comparable efficacy in upper GI and small intestinal lesions but shows inferior outcomes in colorectal lesions. However, C-ESD is preferred for lesions >20 mm to achieve optimal oncological outcomes.
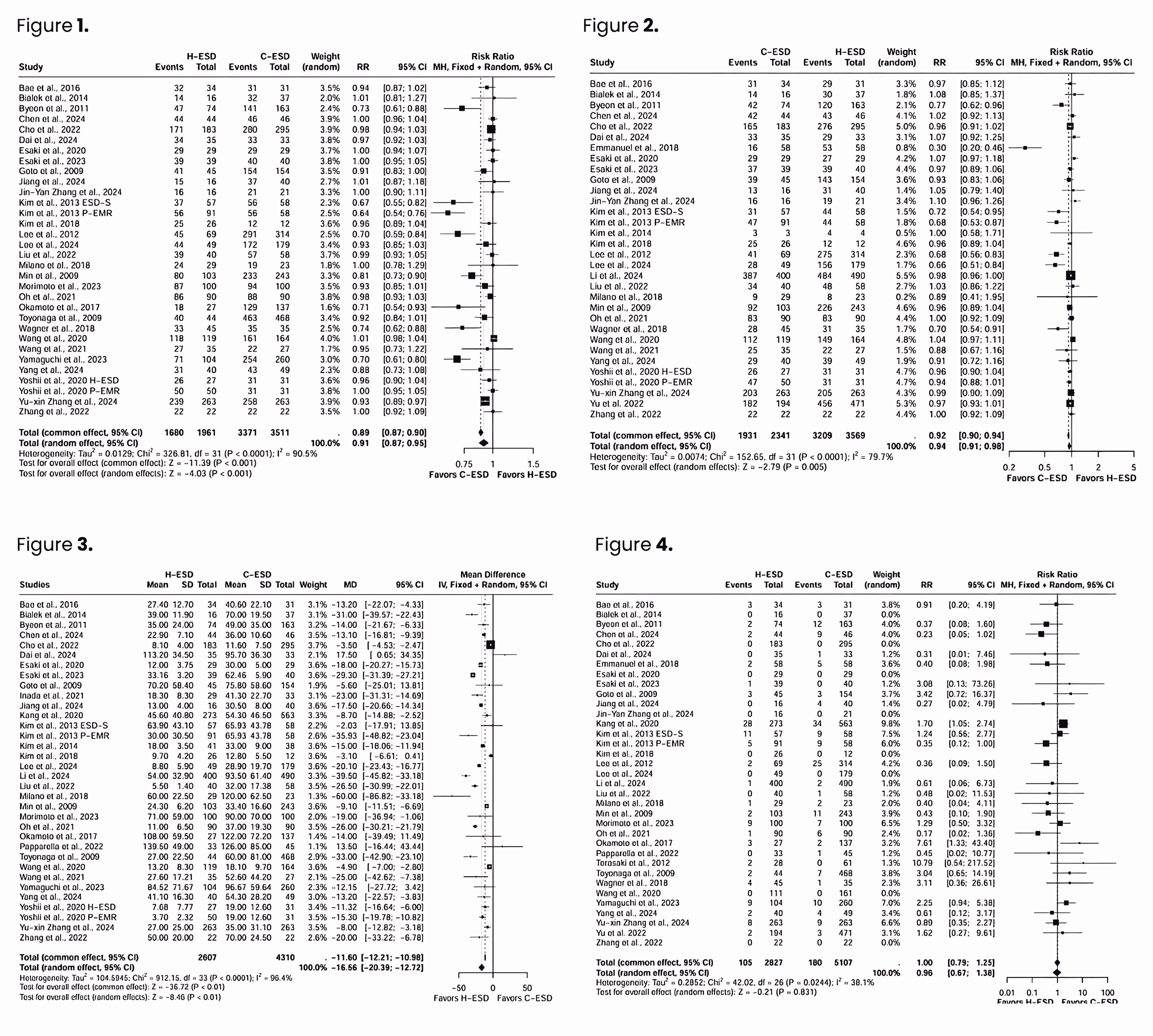
Figure: Graphic 1.
Title: Forest Plots
Caption
Figure 1. Forest Plot of En-Bloc Resection
Figure 2. Forest Plot of Complete Resection
Figure 3. Forest Plot of Procedure Time
Figure 4. Forest Plot of Intra-procedure Perforation
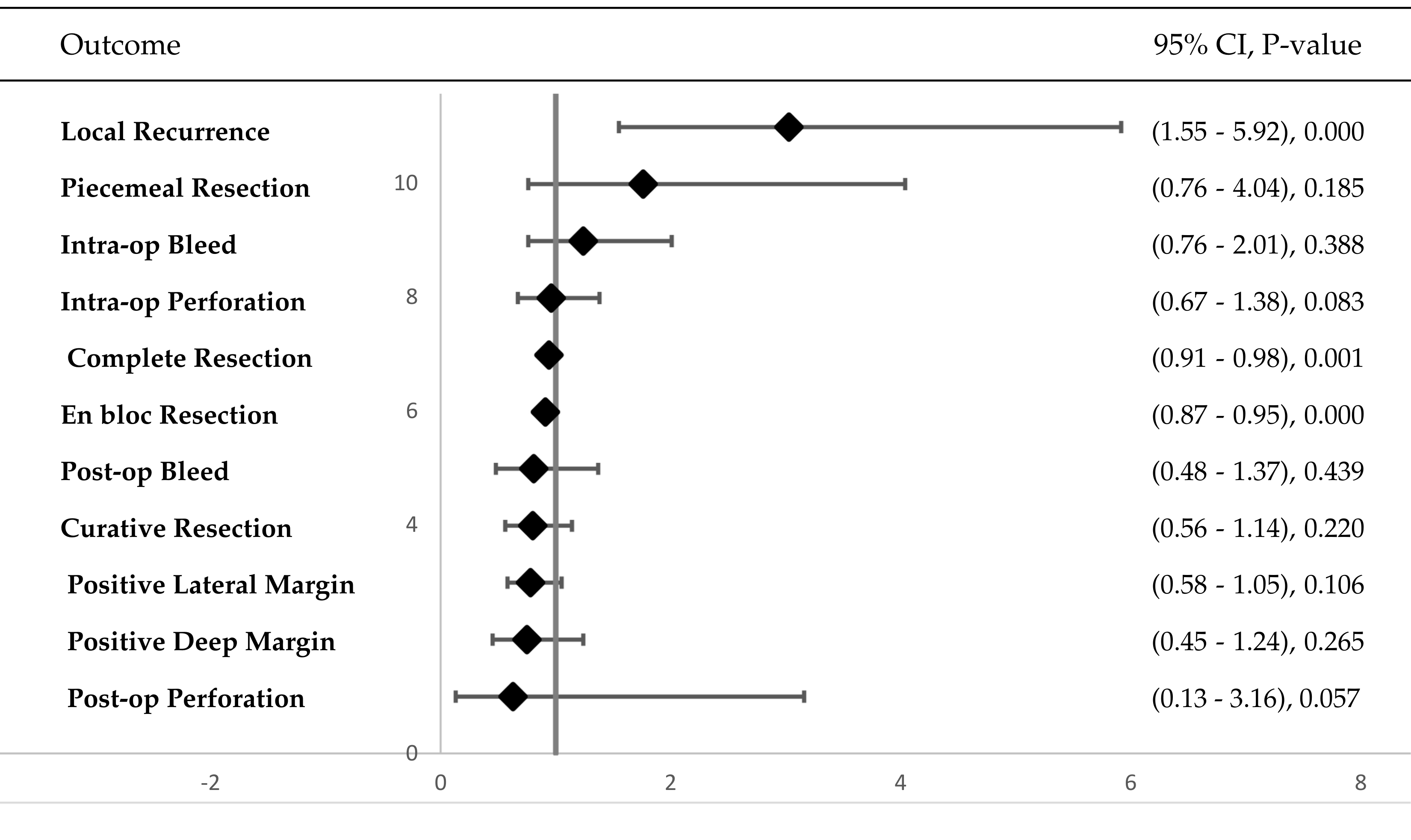
Figure: Graphic 2.
Title: Combined Forest Plot of Outcomes
Disclosures:
Adnan Bhat indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Allah Dad indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kinza Bakht indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Arham indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Humza Saeed indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Zahra Ali indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Faseeh Haider indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Saniya Ishtiaq indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Anchit Chauhan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Danyal Bakht indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Adil Ahmed indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ali Naseem indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Imran Reshi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Dennis Yang: 3D-Matrix – Consultant. Apollo Endosurgery – Consultant. ERBE – Consultant. Fujifilm – Consultant. Medtronic – Consultant. MicroTech – Consultant. Olympus – Consultant.
Peter Draganov: Boston Scientific – Consultant. Cook Medical – Consultant. Fujifilm – Consultant. Medtronic – Consultant. Olympus – Consultant.
Adnan Bhat, MD1, Allah Dad, MD2, Kinza Bakht, MBBS3, Muhammad Arham, 4, Humza Saeed, 5, Zahra Ali, 6, Faseeh Haider, MD7, Saniya Ishtiaq, 8, Anchit Chauhan, 9, Danyal Bakht, MBBS10, Adil Ahmed, 11, Ali Naseem, 12, Imran A. Reshi, MBBS13, Dennis Yang, MD, FACG14, Peter Draganov, MD, FACG1. P3548 - Safety and Efficacy of Hybrid versus Conventional Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection for Removal of Gastrointestinal Lesions: A Meta-Analysis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1University of Florida, Gainesville, FL; 2Shiekh Zayed Medical College Rahim Yar Khan, Pakistan, Kot Addu, Punjab, Pakistan; 3Sheikh Zayed Medical College Rahim Yar Khan, Muzaffargarh, Punjab, Pakistan; 4Sheikh Zayed Medical College, Pakistan, Rahim Yar Khan, Punjab, Pakistan; 5Rawalpindi Medical University, Rawalpindi, Punjab, Pakistan; 6Bolan Medical College, Quetta, Balochistan, Pakistan; 7Allama Iqbal Medical college, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan; 8Rawalpindi Medical University, Rawalpindi, Pakistan, Rawalpindi, Punjab, Pakistan; 9Maulana Azad Medical College, New Delhi, Delhi, India; 10King Edward Medical University, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan; 11Northwest School of Medicine, Peshawar, North-West Frontier, Pakistan; 12King edward medical university lahore, Okara, Punjab, Pakistan; 13Sher i Kashmir Institute of Medical Sciences, Srinagar, Jammu and Kashmir, India; 14Center for Interventional Endoscopic, AdventHealth Orlando, Orlando, FL
Introduction: Endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) is an established method for en-bloc resection of large or complex gastrointestinal (GI) lesions. Conventional ESD (C-ESD) is technically demanding and time-intensive, leading to the development of hybrid ESD (H-ESD) to improve procedural ease and speed. This systematic review and meta-analysis compares the clinical outcomes between H-ESD and C-ESD.
Methods: We searched PubMed, Scopus, Embase, Cochrane Library, ScienceDirect, and ClinicalTrials.gov for eligible studies. Meta-analysis was conducted using R software with random-effects models. Dichotomous outcomes were pooled as risk ratios (RRs) and continuous outcomes as mean differences (MDs), both with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) and a significance threshold of p < 0.05.
Results: 38 studies (7,226 patients; 8,129 lesions) were included. H-ESD was associated with significantly lower en-bloc (RR = 0.91; 95% CI: 0.87 - 0.95; p < 0.001) and complete (R0) resection rates (RR = 0.94; 95% CI: 0.91 - 0.98; p = 0.005), higher local recurrence (RR = 3.03; 95% CI: 1.55 - 5.92; p = 0.001), but shorter procedure time (MD = −16.56 minutes; p < 0.01). There was no significant difference in intra-procedure bleeding (RR = 1.24; p = 0.388), intra-procedure perforation (RR = 0.96; p = 0.831), post-procedure bleeding (RR = 0.81; p = 0.439), and post-procedure perforation (RR = 0.63; p = 0.574). H-ESD showed no significant difference versus C-ESD in lateral margin involvement (p = 0.106), deep margin positivity (p = 0.265), or piecemeal resection rates (p=0.185). In colorectal lesions, H-ESD showed lower en-bloc and complete resection rates vs. C-ESD (p < 0.0001).
Discussion: In conclusion, H-ESD offers shorter procedure times for GI lesions with comparable efficacy in upper GI and small intestinal lesions but shows inferior outcomes in colorectal lesions. However, C-ESD is preferred for lesions >20 mm to achieve optimal oncological outcomes.

Figure: Graphic 1.
Title: Forest Plots
Caption
Figure 1. Forest Plot of En-Bloc Resection
Figure 2. Forest Plot of Complete Resection
Figure 3. Forest Plot of Procedure Time
Figure 4. Forest Plot of Intra-procedure Perforation

Figure: Graphic 2.
Title: Combined Forest Plot of Outcomes
Disclosures:
Adnan Bhat indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Allah Dad indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kinza Bakht indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Arham indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Humza Saeed indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Zahra Ali indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Faseeh Haider indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Saniya Ishtiaq indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Anchit Chauhan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Danyal Bakht indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Adil Ahmed indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ali Naseem indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Imran Reshi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Dennis Yang: 3D-Matrix – Consultant. Apollo Endosurgery – Consultant. ERBE – Consultant. Fujifilm – Consultant. Medtronic – Consultant. MicroTech – Consultant. Olympus – Consultant.
Peter Draganov: Boston Scientific – Consultant. Cook Medical – Consultant. Fujifilm – Consultant. Medtronic – Consultant. Olympus – Consultant.
Adnan Bhat, MD1, Allah Dad, MD2, Kinza Bakht, MBBS3, Muhammad Arham, 4, Humza Saeed, 5, Zahra Ali, 6, Faseeh Haider, MD7, Saniya Ishtiaq, 8, Anchit Chauhan, 9, Danyal Bakht, MBBS10, Adil Ahmed, 11, Ali Naseem, 12, Imran A. Reshi, MBBS13, Dennis Yang, MD, FACG14, Peter Draganov, MD, FACG1. P3548 - Safety and Efficacy of Hybrid versus Conventional Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection for Removal of Gastrointestinal Lesions: A Meta-Analysis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
