Monday Poster Session
Category: Liver
P3635 - Statin Use Is Associated With Reduced Risk of Hepatic Decompensation and Overall Mortality in Patients With Compensated Cirrhosis: A Propensity Score-Matched Analysis of a Population-Based Cohort of 14,034 Adults
Monday, October 27, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall
- TA
Tarek Aboursheid, MD
MedStar Georgetown University Hospital, Washington, DC, USA
Washington, DC
Presenting Author(s)
Award: ACG Outstanding Research Award in the Liver Category (Trainee)
Award: ACG Presidential Poster Award
Mohammed Abu-Rumaileh, MD1, Abdallah Hussein, MD2, Bisher Sawaf, MD3, Yusuf Omar Hallak, MD1, Sana Rabeeah, MD1, Tarek Abou Rashid, MD4, Obada Daaboul, MD5, Elias Battikh, MD6, Amine Rakab, MD7, Monica Tincopa, MD8
1The University of Toledo, Toledo, OH; 2Virtua Our Lady of Lourdes Hospital, Camden, NJ; 3University of Toledo Medical Center, Toledo, OH; 4MedStar Georgetown University Hospital, Washington, DC, USA, Washington, DC; 5Southern Illinois University, Springfield, IL; 6John H. Stroger, Jr. Hospital of Cook County, Toledo, OH; 7Division of Medical Education, Weill Cornell Medicine, Doha, Ad Dawhah, Qatar; 8UCSD, San Diego, CA
Introduction: Statin use is often avoided in cirrhosis due to hepatotoxicity concerns. However, emerging data suggests a potential clinical benefit of statins in compensated cirrhosis. The aim of this study was to assess the impact of statin therapy on risk of hepatic decompensation, hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and overall mortality in a large population-based cohort.
Methods: Using a large, federated electronic health based (EHR) database (TriNetX), we identified patients with compensated cirrhosis using ICD-10 codes. Statin users were defined as individuals taking statins at any dose for at least 1 year. Statin users were propensity score-matched 1:1 using demographics, labs, BMI, alcohol use, medical comorbidities, cirrhosis etiology, beta-blocker, opioid, and benzodiazepine use. Outcomes assessed at 1 and 4 years included composite hepatic decompensation [ascites, variceal bleeding, hepatic encephalopathy (HE), hepatorenal syndrome (HRS) spontaneous bacterial peritonitis (SBP) or hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)]. Secondary outcomes included individual decompensation outcomes and overall mortality.
Results: After matching, 14,034 patients were included in each group for 1-year outcomes, and 13,853 for 4-year outcomes. Statin use was associated with significantly lower 1-year rates of composite hepatic decompensation (6.4% vs. 9.8%; OR: 0.64; 95% CI: 0.58–0.70; p< 0.0001) and overall mortality (4.5% vs. 8.5%; OR: 0.51; 95% CI: 0.46–0.57; p< 0.0001) (Table 1a). At 4 years, the statin group continued to show reduced risk of composite hepatic decompensation (10.8% vs. 14.8%; OR: 0.70; 95% CI: 0.65–0.75; p< 0.0001) and overall mortality (14.6% vs. 20.8%; OR: 0.65; 95% CI: 0.61–0.69; p< 0.0001) (Table 1b). Statin use was particularly associated with reduced rates of ascites and portal hypertension, though not with reduced risk of HCC.
Discussion: In a large population-based propensity score-matched cohort of patients with compensated cirrhosis, statin therapy was associated with significantly lower rates of hepatic decompensation and overall mortality at 1 and 4 years of follow-up. These data suggest potential preventative benefit of statin therapy in adults with compensated cirrhosis that should be further assessed in future randomized clinical trials.
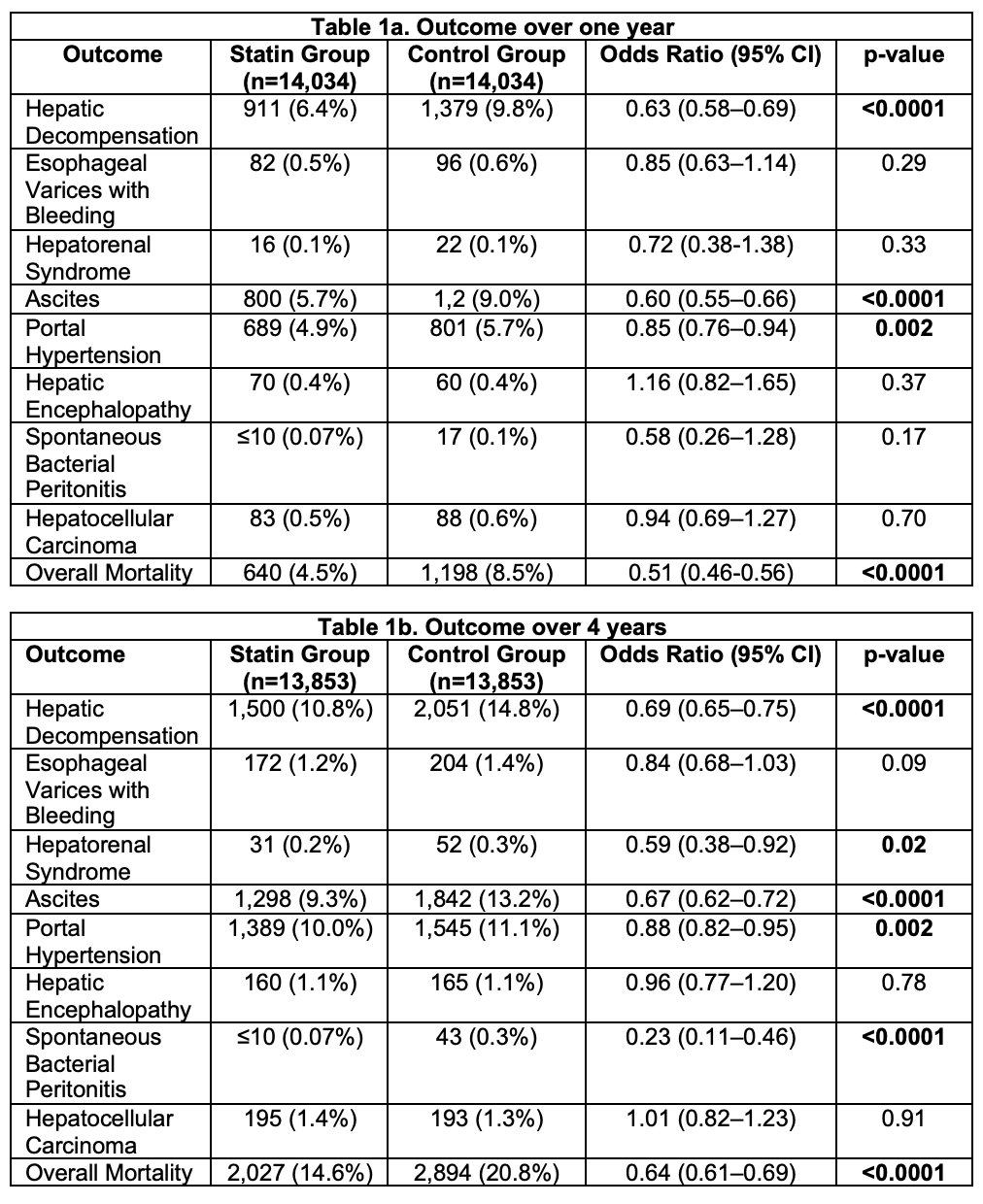
Figure: Table: Comparison of clinical outcomes between statin users and matched controls with compensated cirrhosis at 1-year (Table 1a) and 4-year (Table 1b) follow-up.
Disclosures:
Mohammed Abu-Rumaileh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Abdallah Hussein indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Bisher Sawaf indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Yusuf Omar Hallak indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sana Rabeeah indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Tarek Abou Rashid indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Obada Daaboul indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Elias Battikh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Amine Rakab indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Monica Tincopa indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohammed Abu-Rumaileh, MD1, Abdallah Hussein, MD2, Bisher Sawaf, MD3, Yusuf Omar Hallak, MD1, Sana Rabeeah, MD1, Tarek Abou Rashid, MD4, Obada Daaboul, MD5, Elias Battikh, MD6, Amine Rakab, MD7, Monica Tincopa, MD8. P3635 - Statin Use Is Associated With Reduced Risk of Hepatic Decompensation and Overall Mortality in Patients With Compensated Cirrhosis: A Propensity Score-Matched Analysis of a Population-Based Cohort of 14,034 Adults, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
Award: ACG Presidential Poster Award
Mohammed Abu-Rumaileh, MD1, Abdallah Hussein, MD2, Bisher Sawaf, MD3, Yusuf Omar Hallak, MD1, Sana Rabeeah, MD1, Tarek Abou Rashid, MD4, Obada Daaboul, MD5, Elias Battikh, MD6, Amine Rakab, MD7, Monica Tincopa, MD8
1The University of Toledo, Toledo, OH; 2Virtua Our Lady of Lourdes Hospital, Camden, NJ; 3University of Toledo Medical Center, Toledo, OH; 4MedStar Georgetown University Hospital, Washington, DC, USA, Washington, DC; 5Southern Illinois University, Springfield, IL; 6John H. Stroger, Jr. Hospital of Cook County, Toledo, OH; 7Division of Medical Education, Weill Cornell Medicine, Doha, Ad Dawhah, Qatar; 8UCSD, San Diego, CA
Introduction: Statin use is often avoided in cirrhosis due to hepatotoxicity concerns. However, emerging data suggests a potential clinical benefit of statins in compensated cirrhosis. The aim of this study was to assess the impact of statin therapy on risk of hepatic decompensation, hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and overall mortality in a large population-based cohort.
Methods: Using a large, federated electronic health based (EHR) database (TriNetX), we identified patients with compensated cirrhosis using ICD-10 codes. Statin users were defined as individuals taking statins at any dose for at least 1 year. Statin users were propensity score-matched 1:1 using demographics, labs, BMI, alcohol use, medical comorbidities, cirrhosis etiology, beta-blocker, opioid, and benzodiazepine use. Outcomes assessed at 1 and 4 years included composite hepatic decompensation [ascites, variceal bleeding, hepatic encephalopathy (HE), hepatorenal syndrome (HRS) spontaneous bacterial peritonitis (SBP) or hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)]. Secondary outcomes included individual decompensation outcomes and overall mortality.
Results: After matching, 14,034 patients were included in each group for 1-year outcomes, and 13,853 for 4-year outcomes. Statin use was associated with significantly lower 1-year rates of composite hepatic decompensation (6.4% vs. 9.8%; OR: 0.64; 95% CI: 0.58–0.70; p< 0.0001) and overall mortality (4.5% vs. 8.5%; OR: 0.51; 95% CI: 0.46–0.57; p< 0.0001) (Table 1a). At 4 years, the statin group continued to show reduced risk of composite hepatic decompensation (10.8% vs. 14.8%; OR: 0.70; 95% CI: 0.65–0.75; p< 0.0001) and overall mortality (14.6% vs. 20.8%; OR: 0.65; 95% CI: 0.61–0.69; p< 0.0001) (Table 1b). Statin use was particularly associated with reduced rates of ascites and portal hypertension, though not with reduced risk of HCC.
Discussion: In a large population-based propensity score-matched cohort of patients with compensated cirrhosis, statin therapy was associated with significantly lower rates of hepatic decompensation and overall mortality at 1 and 4 years of follow-up. These data suggest potential preventative benefit of statin therapy in adults with compensated cirrhosis that should be further assessed in future randomized clinical trials.

Figure: Table: Comparison of clinical outcomes between statin users and matched controls with compensated cirrhosis at 1-year (Table 1a) and 4-year (Table 1b) follow-up.
Disclosures:
Mohammed Abu-Rumaileh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Abdallah Hussein indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Bisher Sawaf indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Yusuf Omar Hallak indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sana Rabeeah indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Tarek Abou Rashid indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Obada Daaboul indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Elias Battikh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Amine Rakab indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Monica Tincopa indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohammed Abu-Rumaileh, MD1, Abdallah Hussein, MD2, Bisher Sawaf, MD3, Yusuf Omar Hallak, MD1, Sana Rabeeah, MD1, Tarek Abou Rashid, MD4, Obada Daaboul, MD5, Elias Battikh, MD6, Amine Rakab, MD7, Monica Tincopa, MD8. P3635 - Statin Use Is Associated With Reduced Risk of Hepatic Decompensation and Overall Mortality in Patients With Compensated Cirrhosis: A Propensity Score-Matched Analysis of a Population-Based Cohort of 14,034 Adults, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.

