Monday Poster Session
Category: Liver
P3774 - Association of Sex Hormone Binding Globulin and Sex Hormones With Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease and Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatohepatitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Monday, October 27, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Saniya Ishtiaq, MD (she/her/hers)
Rawalpindi Medical University
Rawalpindi, Punjab, Pakistan
Presenting Author(s)
Rubab Zahra, MBBS1, Adnan Bhat, MD2, Allah Dad, MD3, Kinza Bakht, MBBS4, Shizra Jawed, MBBS5, Marhaba Fatima, 6, Muhammad Ansab, 7, Adil Ahmed, 8, Debankur Dey, MBBS9, Muhammad Hamza, MBBS10, Maulinkumar Patel, MBBS, MPH11, Anchit Chauhan, 12, Omar Al-Radideh, MD13, Saniya Ishtiaq, 14
1Allama iqbal medical college, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan; 2University of Florida, Gainesville, FL; 3Shiekh Zayed Medical College Rahim Yar Khan, Pakistan, Kot Addu, Punjab, Pakistan; 4Sheikh Zayed Medical College Rahim Yar Khan, Muzaffargarh, Punjab, Pakistan; 5Dow Medical College, Karachi, Sindh, Pakistan; 6People’s University of Medical and Health Sciences for Women, Nawabshah, Sindh, Pakistan; 7Services Institute of Medical Sciences, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan; 8Northwest School of Medicine, Peshawar, North-West Frontier, Pakistan; 9Medical College Kolkata, Kolkata, West Bengal, India; 10Saidu medical college swat, Saidu Sharif, North-West Frontier, Pakistan; 11The University of Texas Health Science Centre at Houston, Philadelphia, PA; 12Maulana Azad Medical College, New Delhi, Delhi, India; 13University of Florida College of Medicine, Gainesville, FL; 14Rawalpindi Medical University, Rawalpindi, Pakistan, Rawalpindi, Punjab, Pakistan
Introduction: Metabolic dysfunction-associated liver disease (MASLD) and metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH) are among the leading causes of chronic liver disease worldwide. Sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG) and endogenous sex hormones have been shown to play an important role in hepatic steatosis. We conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis to evaluate the association between these sex hormones, MASLD, and MASH.
Methods: A comprehensive systematic literature search was conducted on PubMed, Cochrane CENTRAL, Embase, and Scopus from inception through March 2025. Studies showing an association between SHBG or endogenous sex hormones with either MASLD or MASH were included. Pooled odds ratios (OR) with 95% confidence intervals (CI) were calculated using a generalized linear model (GLM) on Rstudio (v4.1.1). Statistical significance was defined as p-value < 0.05.
Results: A total of 27 observational studies comprising 582,698 patients (419,196 in the MASLD/MASH group and 163,502 in the control group) were included in this meta-analysis. SHBG was significantly associated with reduced odds of MASLD/MASH (OR: 0.53; 95% CI: 0.36-0.79; p=0.0016) [Figure 1]. Among sex hormones, estrogen demonstrated a modest but significant protective association (OR: 0.96; 95% CI: 0.93-1.00; p=0.0252) [Figure 2]. No significant associations were observed with testosterone (OR: 1.18; 95% CI: 0.85-1.62; p=0.3183), luteinizing hormone (OR: 1.09; 95% CI: 0.83-1.45; p=0.5351), or follicle stimulating hormone (OR: 0.79; 95% CI: 0.46-1,38; p=0.4131).
Discussion: Our study suggests that SHBG and estrogen are significantly associated with lower odds of MASLD/MASH, suggesting a potential protective endocrine mechanism. Testosterone, follicle-stimulating hormone, and luteinizing hormone, however, were not found to be associated with disease risk. Further prospective studies and trials are required to elucidate causal pathways, clinical utility in risk stratification, and to generate more robust evidence of the outcomes among patients with either MASLD or MASH.
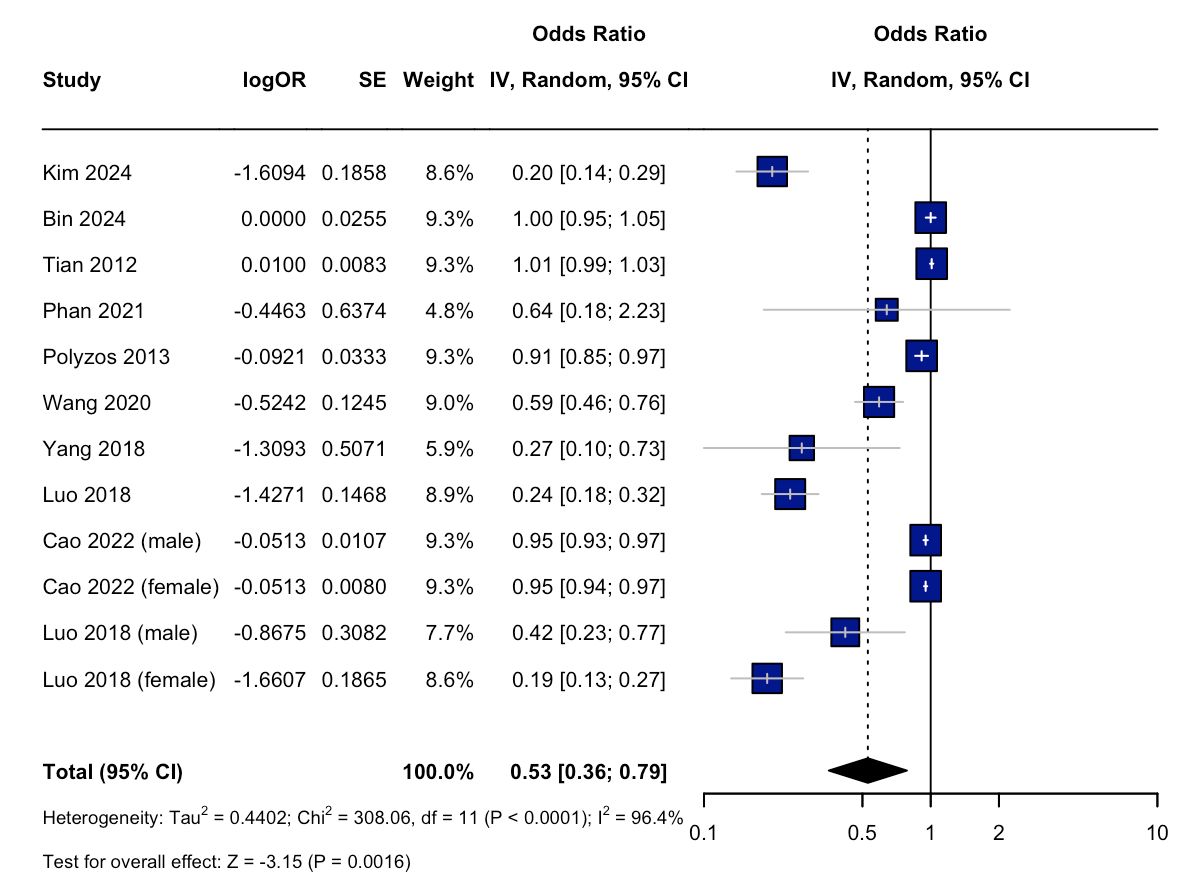
Figure: Figure 1: Forest Plot showing association between SHBG and MASLD/MASH.
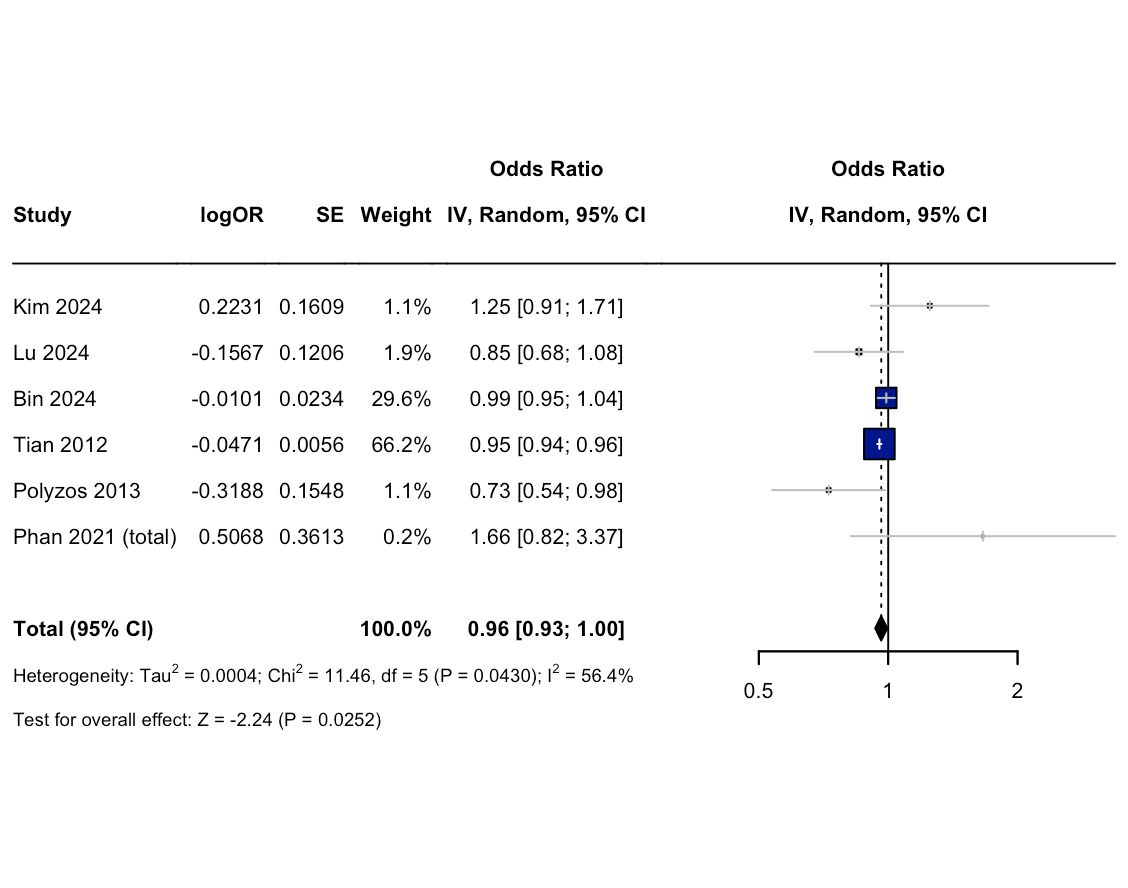
Figure: Figure 2: Forest Plot showing association between estrogen and MASLD/MASH.
Disclosures:
Rubab Zahra indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Adnan Bhat indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Allah Dad indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kinza Bakht indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Shizra Jawed indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Marhaba Fatima indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Ansab indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Adil Ahmed indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Debankur Dey indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Hamza indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Maulinkumar Patel indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Anchit Chauhan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Omar Al-Radideh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Saniya Ishtiaq indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rubab Zahra, MBBS1, Adnan Bhat, MD2, Allah Dad, MD3, Kinza Bakht, MBBS4, Shizra Jawed, MBBS5, Marhaba Fatima, 6, Muhammad Ansab, 7, Adil Ahmed, 8, Debankur Dey, MBBS9, Muhammad Hamza, MBBS10, Maulinkumar Patel, MBBS, MPH11, Anchit Chauhan, 12, Omar Al-Radideh, MD13, Saniya Ishtiaq, 14. P3774 - Association of Sex Hormone Binding Globulin and Sex Hormones With Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease and Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatohepatitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Allama iqbal medical college, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan; 2University of Florida, Gainesville, FL; 3Shiekh Zayed Medical College Rahim Yar Khan, Pakistan, Kot Addu, Punjab, Pakistan; 4Sheikh Zayed Medical College Rahim Yar Khan, Muzaffargarh, Punjab, Pakistan; 5Dow Medical College, Karachi, Sindh, Pakistan; 6People’s University of Medical and Health Sciences for Women, Nawabshah, Sindh, Pakistan; 7Services Institute of Medical Sciences, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan; 8Northwest School of Medicine, Peshawar, North-West Frontier, Pakistan; 9Medical College Kolkata, Kolkata, West Bengal, India; 10Saidu medical college swat, Saidu Sharif, North-West Frontier, Pakistan; 11The University of Texas Health Science Centre at Houston, Philadelphia, PA; 12Maulana Azad Medical College, New Delhi, Delhi, India; 13University of Florida College of Medicine, Gainesville, FL; 14Rawalpindi Medical University, Rawalpindi, Pakistan, Rawalpindi, Punjab, Pakistan
Introduction: Metabolic dysfunction-associated liver disease (MASLD) and metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH) are among the leading causes of chronic liver disease worldwide. Sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG) and endogenous sex hormones have been shown to play an important role in hepatic steatosis. We conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis to evaluate the association between these sex hormones, MASLD, and MASH.
Methods: A comprehensive systematic literature search was conducted on PubMed, Cochrane CENTRAL, Embase, and Scopus from inception through March 2025. Studies showing an association between SHBG or endogenous sex hormones with either MASLD or MASH were included. Pooled odds ratios (OR) with 95% confidence intervals (CI) were calculated using a generalized linear model (GLM) on Rstudio (v4.1.1). Statistical significance was defined as p-value < 0.05.
Results: A total of 27 observational studies comprising 582,698 patients (419,196 in the MASLD/MASH group and 163,502 in the control group) were included in this meta-analysis. SHBG was significantly associated with reduced odds of MASLD/MASH (OR: 0.53; 95% CI: 0.36-0.79; p=0.0016) [Figure 1]. Among sex hormones, estrogen demonstrated a modest but significant protective association (OR: 0.96; 95% CI: 0.93-1.00; p=0.0252) [Figure 2]. No significant associations were observed with testosterone (OR: 1.18; 95% CI: 0.85-1.62; p=0.3183), luteinizing hormone (OR: 1.09; 95% CI: 0.83-1.45; p=0.5351), or follicle stimulating hormone (OR: 0.79; 95% CI: 0.46-1,38; p=0.4131).
Discussion: Our study suggests that SHBG and estrogen are significantly associated with lower odds of MASLD/MASH, suggesting a potential protective endocrine mechanism. Testosterone, follicle-stimulating hormone, and luteinizing hormone, however, were not found to be associated with disease risk. Further prospective studies and trials are required to elucidate causal pathways, clinical utility in risk stratification, and to generate more robust evidence of the outcomes among patients with either MASLD or MASH.

Figure: Figure 1: Forest Plot showing association between SHBG and MASLD/MASH.

Figure: Figure 2: Forest Plot showing association between estrogen and MASLD/MASH.
Disclosures:
Rubab Zahra indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Adnan Bhat indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Allah Dad indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kinza Bakht indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Shizra Jawed indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Marhaba Fatima indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Ansab indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Adil Ahmed indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Debankur Dey indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Hamza indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Maulinkumar Patel indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Anchit Chauhan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Omar Al-Radideh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Saniya Ishtiaq indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rubab Zahra, MBBS1, Adnan Bhat, MD2, Allah Dad, MD3, Kinza Bakht, MBBS4, Shizra Jawed, MBBS5, Marhaba Fatima, 6, Muhammad Ansab, 7, Adil Ahmed, 8, Debankur Dey, MBBS9, Muhammad Hamza, MBBS10, Maulinkumar Patel, MBBS, MPH11, Anchit Chauhan, 12, Omar Al-Radideh, MD13, Saniya Ishtiaq, 14. P3774 - Association of Sex Hormone Binding Globulin and Sex Hormones With Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease and Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatohepatitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
