Monday Poster Session
Category: Liver
P3873 - Interleukin-6 Is a Potential Therapeutic Target in Refractory Immunotherapy-Mediated Cholangiopathy
Monday, October 27, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Darine Daher, MD (she/her/hers)
Mayo Clinic
Rochester, MN
Presenting Author(s)
Darine Daher, MD1, Vijayvardhan Kamalumpundi, MD2, Rondell Graham, MBBS1, Svetomir Markovic, MD, PhD1, Lisa Kottschade, RN, CPN1, Yoshito Nishimura, MD, PhD1, Brian A.. Costello, MD1
1Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN; 2Mayo Clinic, Cedar Rapids, IA
Introduction: Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) have transformed cancer therapy but can cause immune-related adverse events (irAEs), including rare but serious hepatobiliary complications such as immunotherapy-mediated cholangiopathy (IMCp). Tocilizumab is an Interleukin-6 antagonist therapy used to treat ICI-toxicity. Management of ICI-cholangiopathy remains unclear, particularly in steroid-refractory cases.
Case Description/
Methods: A 61-year-old woman presents with nausea and severe jaundice. Her medical history is significant for stage IIIa chronic kidney disease and metastatic triple-negative breast cancer treated with bilateral mastectomy and adjuvant chemotherapy with 2 cycles of carboplatin, paclitaxel and pembrolizumab. A few months later, her labs were significant for AST 290, ALT 398, and Alkaline phosphatase 769, and normal bilirubin of 0.7. Pembrolizumab was discontinued, and she was started on prednisone 80mg for presumed ICI hepatitis with adequate response. Despite steroids and mycophenolate mofetil (MMF), her labs again worsened (ALP 1138, AST 158, ALT 397, bilirubin 11.9). In the interim, the patient developed liver abscesses and gram-negative bacteremia, therefore immunosuppression was held. Further evaluation with ERCP demonstrated sludge in the common bile duct, and LFTs improved after sphincterotomy, stone clearance, and cholecystectomy. Workup for autoimmune and viral hepatitides was negative. Liver biopsy demonstrated mild portal mixed inflammation with lymphocytic and focal neutrophilic cholangitis, bile duct proliferation, with 30% of bile ducts not being seen, consistent with IMCp. MMF was stopped and ursodiol 1000mg was started. Her bilirubin continued to rise despite treatment with high-dose prednisone, budesonide, ursodiol, and tacrolimus. A cytokine panel was then obtained which showed IL-6 of 5.6 pg/ml (Reference range < 5 pg/ml). She received 5 cycles of plasma exchange, was started on Tocilizumab, and her direct bilirubin plateaued to 5.5 mg/dL (Figure 1).
Discussion: IL-6 blockade may offer a viable therapeutic approach in steroid-refractory cases of ICI cholangiopathy, though advanced disease and concurrent infections may limit efficacy. IL-6 may serve as a biomarker predicting tocilizumab response with borderline elevation potentially being explained by steroid and tacrolimus administration. Further studies are warranted to establish diagnostic criteria and treatment strategies for this challenging irAE.
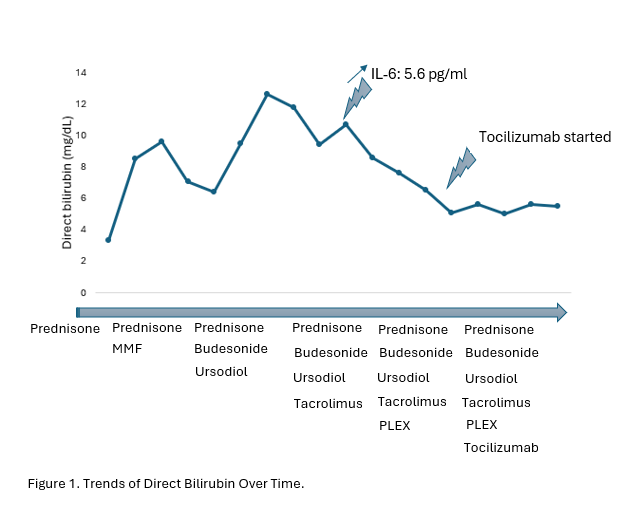
Figure: Trends of Direct Bilirubin Over Time
Disclosures:
Darine Daher indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Vijayvardhan Kamalumpundi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rondell Graham: Astellas Pharma – Grant/Research Support. Daiichi Sankyo – Advisory Committee/Board Member.
Svetomir Markovic: Bristol-Myers Squibb – Grant/Research Support. Journey Therapeutics – Royalties. Sorrento Therapeutics, Inc. – Intellectual Property/Patents, Royalties.
Lisa Kottschade: Immunocore – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Consultant. Replimmune – Advisor or Review Panel Member.
Yoshito Nishimura indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Brian Costello indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Darine Daher, MD1, Vijayvardhan Kamalumpundi, MD2, Rondell Graham, MBBS1, Svetomir Markovic, MD, PhD1, Lisa Kottschade, RN, CPN1, Yoshito Nishimura, MD, PhD1, Brian A.. Costello, MD1. P3873 - Interleukin-6 Is a Potential Therapeutic Target in Refractory Immunotherapy-Mediated Cholangiopathy, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN; 2Mayo Clinic, Cedar Rapids, IA
Introduction: Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) have transformed cancer therapy but can cause immune-related adverse events (irAEs), including rare but serious hepatobiliary complications such as immunotherapy-mediated cholangiopathy (IMCp). Tocilizumab is an Interleukin-6 antagonist therapy used to treat ICI-toxicity. Management of ICI-cholangiopathy remains unclear, particularly in steroid-refractory cases.
Case Description/
Methods: A 61-year-old woman presents with nausea and severe jaundice. Her medical history is significant for stage IIIa chronic kidney disease and metastatic triple-negative breast cancer treated with bilateral mastectomy and adjuvant chemotherapy with 2 cycles of carboplatin, paclitaxel and pembrolizumab. A few months later, her labs were significant for AST 290, ALT 398, and Alkaline phosphatase 769, and normal bilirubin of 0.7. Pembrolizumab was discontinued, and she was started on prednisone 80mg for presumed ICI hepatitis with adequate response. Despite steroids and mycophenolate mofetil (MMF), her labs again worsened (ALP 1138, AST 158, ALT 397, bilirubin 11.9). In the interim, the patient developed liver abscesses and gram-negative bacteremia, therefore immunosuppression was held. Further evaluation with ERCP demonstrated sludge in the common bile duct, and LFTs improved after sphincterotomy, stone clearance, and cholecystectomy. Workup for autoimmune and viral hepatitides was negative. Liver biopsy demonstrated mild portal mixed inflammation with lymphocytic and focal neutrophilic cholangitis, bile duct proliferation, with 30% of bile ducts not being seen, consistent with IMCp. MMF was stopped and ursodiol 1000mg was started. Her bilirubin continued to rise despite treatment with high-dose prednisone, budesonide, ursodiol, and tacrolimus. A cytokine panel was then obtained which showed IL-6 of 5.6 pg/ml (Reference range < 5 pg/ml). She received 5 cycles of plasma exchange, was started on Tocilizumab, and her direct bilirubin plateaued to 5.5 mg/dL (Figure 1).
Discussion: IL-6 blockade may offer a viable therapeutic approach in steroid-refractory cases of ICI cholangiopathy, though advanced disease and concurrent infections may limit efficacy. IL-6 may serve as a biomarker predicting tocilizumab response with borderline elevation potentially being explained by steroid and tacrolimus administration. Further studies are warranted to establish diagnostic criteria and treatment strategies for this challenging irAE.

Figure: Trends of Direct Bilirubin Over Time
Disclosures:
Darine Daher indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Vijayvardhan Kamalumpundi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rondell Graham: Astellas Pharma – Grant/Research Support. Daiichi Sankyo – Advisory Committee/Board Member.
Svetomir Markovic: Bristol-Myers Squibb – Grant/Research Support. Journey Therapeutics – Royalties. Sorrento Therapeutics, Inc. – Intellectual Property/Patents, Royalties.
Lisa Kottschade: Immunocore – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Consultant. Replimmune – Advisor or Review Panel Member.
Yoshito Nishimura indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Brian Costello indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Darine Daher, MD1, Vijayvardhan Kamalumpundi, MD2, Rondell Graham, MBBS1, Svetomir Markovic, MD, PhD1, Lisa Kottschade, RN, CPN1, Yoshito Nishimura, MD, PhD1, Brian A.. Costello, MD1. P3873 - Interleukin-6 Is a Potential Therapeutic Target in Refractory Immunotherapy-Mediated Cholangiopathy, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
