Monday Poster Session
Category: Small Intestine
P4025 - Non-Celiac Wheat Sensitivity in Refractory Functional Dyspepsia and Irritable Bowel Syndrome: A Prospective, Randomized Study
Monday, October 27, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall
- MG
Manjeet Goyal, MBBS, MD, DM, DNB (he/him/his)
Cleveland Clinic Akron General
Akron, OH
Presenting Author(s)
Award: ACG Outstanding Research Award in the Small Intestine Category (Trainee)
Award: ACG Presidential Poster Award
Omesh Goyal, MBBS, MD, DM1, Manjeet Kumar Goyal, MBBS, MD, DM, DNB2, Prerna Goyal, MBBS, MD3, Paraag Kumar, MBBS, MD, DM1, Ajit Sood, MBBS, MD, DM1
1Dayanand Medical College and Hospital, Ludhiana, Punjab, India; 2Cleveland Clinic Akron General, Akron, OH; 3R.G. stone and superspeciality Hospital, Ludhiana, Punjab, India, Ludhiana, Punjab, India
Introduction:
Introduction:
Non-celiac gluten/wheat sensitivity (NCGWS) is characterized by gastrointestinal and extra-intestinal symptoms triggered by gluten or wheat ingestion. Its symptoms often overlap with those of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and functional dyspepsia (FD), making diagnosis challenging. Limited data exist on the prevalence and predictors of NCGWS among patients with refractory IBS or FD.
Methods: We conducted a prospective, multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover trial in India (Oct 2021–Mar 2023; CTRI/2021/10/037323). Adults aged 18–65 years with Rome IV-defined refractory IBS or FD, after excluding celiac disease, wheat allergy, and alarm features, were enrolled. The diagnostic protocol involved two steps. Step I: a 6-week strict gluten-free diet (GFD) under dietitian supervision, with weekly symptom, quality-of-life (QoL), and psychological assessments using validated tools. Responders (≥30% reduction in one to three key symptoms) proceeded to Step II: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled gluten challenge (DBPCGC). Participants received gluten or placebo cookies (8 g/day) for 1 week, followed by a 1-week washout and crossover. NCGWS was diagnosed if symptoms worsened by ≥30% on gluten compared to placebo. Primary outcome was NCGWS prevalence; secondary outcomes included symptom/QoL changes post-GFD and predictors of NCGWS. Statistical analysis included intention-to-treat and multivariable regression.
Results: Of 252 screened, 177 entered GFD phase; 154 completed it (mean age 41.9 ± 14.2 years; 53.2% male). Eighty-two (52.3%) responded to GFD, of whom 77 underwent DBPCGC. Thirty-one patients (20.1%) showed significant symptom worsening with gluten, confirming NCGWS. Independent predictors included female gender, FD-IBS overlap, headache, fatigue, and anxiety. GFD led to marked improvement in gastrointestinal, QoL, and psychological scores. No carry-over or sequence effects were noted.
Discussion: Approximately one in five patients with refractory IBS or FD met criteria for NCGWS using a structured DBPCGC. Identifying NCGWS enables targeted dietary therapy and reduces reliance on pharmacologic interventions. A supervised GFD significantly improved symptoms and QoL in responders, supporting the role of structured evaluation in select functional GI patients.
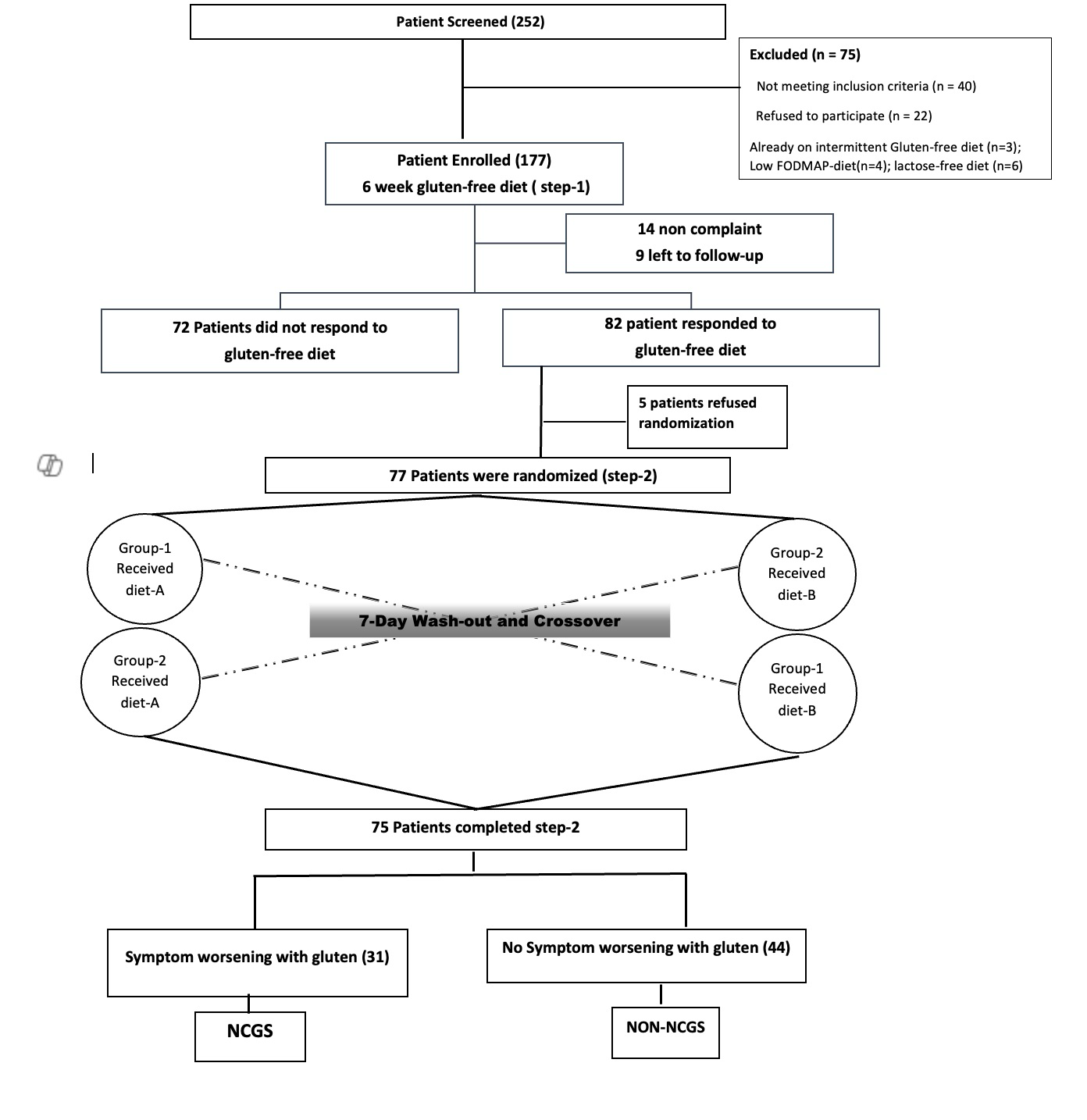
Figure: Figure 1.: CONSORT Diagram of Patient Flow.
Flowchart illustrating patient screening, enrolment, allocation, follow-up, and analysis according to CONSORT guidelines for randomized diagnostic studies
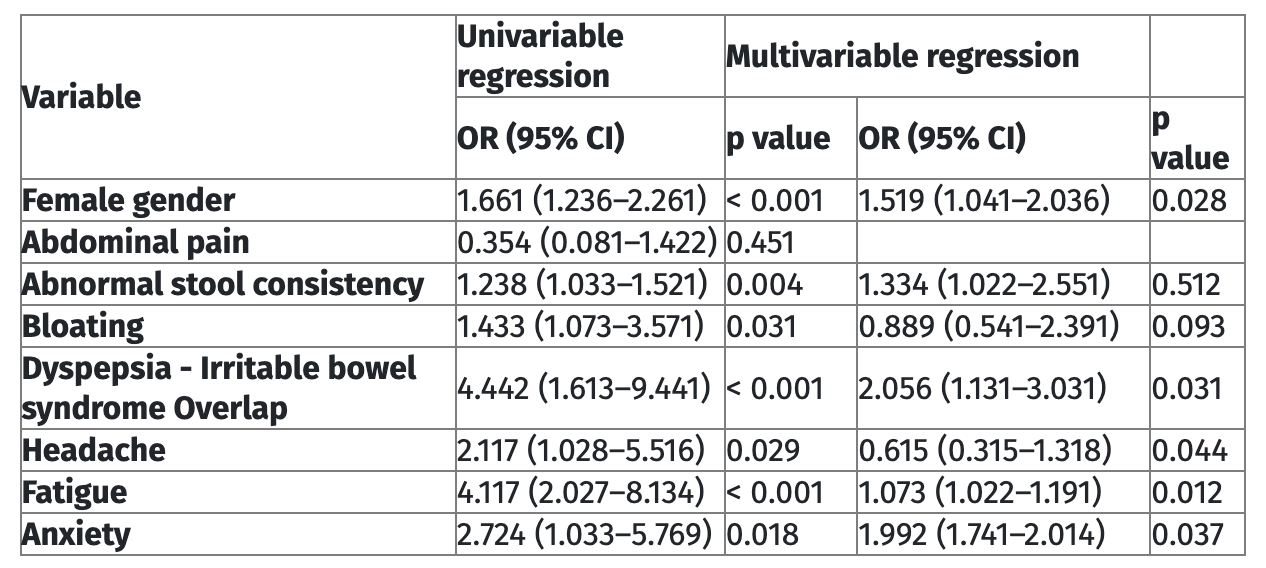
Figure: Univariable and multivariable logistic regression analyses identifying predictors of non-celiac gluten/wheat sensitivity (NCGWS) among patients with refractory irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) or functional dyspepsia (FD). Variables significantly associated with NCGWS on multivariable analysis included female gender (OR 1.519; 95% CI 1.041–2.036; p=0.028), dyspepsia–IBS overlap (OR 2.056; 95% CI 1.131–3.031; p=0.031), fatigue (OR 1.073; 95% CI 1.022–1.191; p=0.012), and anxiety (OR 1.992; 95% CI 1.741–2.014; p=0.037). Headache was significant on univariable analysis but not retained in multivariable analysis. Results are expressed as odds ratios (OR) with 95% confidence intervals (CI); statistical significance was set at p<0.05.
Disclosures:
Omesh Goyal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Manjeet Kumar Goyal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Prerna Goyal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Paraag Kumar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ajit Sood indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Omesh Goyal, MBBS, MD, DM1, Manjeet Kumar Goyal, MBBS, MD, DM, DNB2, Prerna Goyal, MBBS, MD3, Paraag Kumar, MBBS, MD, DM1, Ajit Sood, MBBS, MD, DM1. P4025 - Non-Celiac Wheat Sensitivity in Refractory Functional Dyspepsia and Irritable Bowel Syndrome: A Prospective, Randomized Study, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
Award: ACG Presidential Poster Award
Omesh Goyal, MBBS, MD, DM1, Manjeet Kumar Goyal, MBBS, MD, DM, DNB2, Prerna Goyal, MBBS, MD3, Paraag Kumar, MBBS, MD, DM1, Ajit Sood, MBBS, MD, DM1
1Dayanand Medical College and Hospital, Ludhiana, Punjab, India; 2Cleveland Clinic Akron General, Akron, OH; 3R.G. stone and superspeciality Hospital, Ludhiana, Punjab, India, Ludhiana, Punjab, India
Introduction:
Introduction:
Non-celiac gluten/wheat sensitivity (NCGWS) is characterized by gastrointestinal and extra-intestinal symptoms triggered by gluten or wheat ingestion. Its symptoms often overlap with those of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and functional dyspepsia (FD), making diagnosis challenging. Limited data exist on the prevalence and predictors of NCGWS among patients with refractory IBS or FD.
Methods: We conducted a prospective, multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover trial in India (Oct 2021–Mar 2023; CTRI/2021/10/037323). Adults aged 18–65 years with Rome IV-defined refractory IBS or FD, after excluding celiac disease, wheat allergy, and alarm features, were enrolled. The diagnostic protocol involved two steps. Step I: a 6-week strict gluten-free diet (GFD) under dietitian supervision, with weekly symptom, quality-of-life (QoL), and psychological assessments using validated tools. Responders (≥30% reduction in one to three key symptoms) proceeded to Step II: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled gluten challenge (DBPCGC). Participants received gluten or placebo cookies (8 g/day) for 1 week, followed by a 1-week washout and crossover. NCGWS was diagnosed if symptoms worsened by ≥30% on gluten compared to placebo. Primary outcome was NCGWS prevalence; secondary outcomes included symptom/QoL changes post-GFD and predictors of NCGWS. Statistical analysis included intention-to-treat and multivariable regression.
Results: Of 252 screened, 177 entered GFD phase; 154 completed it (mean age 41.9 ± 14.2 years; 53.2% male). Eighty-two (52.3%) responded to GFD, of whom 77 underwent DBPCGC. Thirty-one patients (20.1%) showed significant symptom worsening with gluten, confirming NCGWS. Independent predictors included female gender, FD-IBS overlap, headache, fatigue, and anxiety. GFD led to marked improvement in gastrointestinal, QoL, and psychological scores. No carry-over or sequence effects were noted.
Discussion: Approximately one in five patients with refractory IBS or FD met criteria for NCGWS using a structured DBPCGC. Identifying NCGWS enables targeted dietary therapy and reduces reliance on pharmacologic interventions. A supervised GFD significantly improved symptoms and QoL in responders, supporting the role of structured evaluation in select functional GI patients.

Figure: Figure 1.: CONSORT Diagram of Patient Flow.
Flowchart illustrating patient screening, enrolment, allocation, follow-up, and analysis according to CONSORT guidelines for randomized diagnostic studies

Figure: Univariable and multivariable logistic regression analyses identifying predictors of non-celiac gluten/wheat sensitivity (NCGWS) among patients with refractory irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) or functional dyspepsia (FD). Variables significantly associated with NCGWS on multivariable analysis included female gender (OR 1.519; 95% CI 1.041–2.036; p=0.028), dyspepsia–IBS overlap (OR 2.056; 95% CI 1.131–3.031; p=0.031), fatigue (OR 1.073; 95% CI 1.022–1.191; p=0.012), and anxiety (OR 1.992; 95% CI 1.741–2.014; p=0.037). Headache was significant on univariable analysis but not retained in multivariable analysis. Results are expressed as odds ratios (OR) with 95% confidence intervals (CI); statistical significance was set at p<0.05.
Disclosures:
Omesh Goyal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Manjeet Kumar Goyal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Prerna Goyal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Paraag Kumar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ajit Sood indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Omesh Goyal, MBBS, MD, DM1, Manjeet Kumar Goyal, MBBS, MD, DM, DNB2, Prerna Goyal, MBBS, MD3, Paraag Kumar, MBBS, MD, DM1, Ajit Sood, MBBS, MD, DM1. P4025 - Non-Celiac Wheat Sensitivity in Refractory Functional Dyspepsia and Irritable Bowel Syndrome: A Prospective, Randomized Study, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.

