Monday Poster Session
Category: Stomach and Spleen
P4168 - Gastric Polyps Prevalence, Characteristics, and Associated Factors in a Middle Eastern Population: Insights From a 5-Year Retrospective Analysis in a Tertiary Hospital
Monday, October 27, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Ahmad Mohammad Abdulraheem, MD (he/him/his)
MedStar Washington Hospital Center
Washington, DC
Presenting Author(s)
Tarek Abu-Rajab Tamimi, MD1, Mohammed Aloqaily, MD2, Alexander Rabadi, MD3, Ahmad Al-Quraan, MD1, Ahmad Al-Momani, MD1, Zeyad Fraij, MD1, Saleh Aljbour, MD1, Basel Al-Khalidi, MD1, Ahmad Abdulraheem, MD4, Yaser Rayyan, MD5, Ra'Ed Ababneh, MD6
1School of Medicine, The University of Jordan, Amman, 'Amman, Jordan; 2University of Maryland Medical Center Midtown Campus, Baltimore, MD; 3McLaren Flint Hospital, Flint, MI; 4MedStar Washington Hospital Center, Washington, DC; 5The University of Jordan, Amman, 'Amman, Jordan; 6MD, Amman, 'Amman, Jordan
Introduction: Gastric polyps (GPs) are mucosal growths with unclear etiology, though Helicobacter pylori infection and proton pump inhibitor (PPI) use are known risk factors. Their prevalence ranges from 0.6% to 6%, varying by ethnicity, geography, and clinical setting. Often asymptomatic, GPs can present with anemia, bleeding, or epigastric pain. Hyperplastic and fundic gland polyps are the most common subtypes. Despite their clinical relevance, data from Middle Eastern populations remain limited. This study aims to assess the prevalence and potential risk factors of GPs in a Middle Eastern cohort.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective analysis of patients who underwent esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) for any indication at a tertiary hospital in the Middle East between 2017 and 2022. Institutional Review Board (IRB) approval was obtained. Two cohorts were identified: patients with GPs (cohort 1) and those without (cohort 2). Collected data included demographics, H. pylori status, PPI use, endoscopic findings, and histopathological results. Patients with missing data from EGD or clinical records were excluded. Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS.
Results: GPs were identified in 312 (4.9%) out f 6,389 EGDs. Demographics are shown in Table 1. Among patients with GPs, the mean age was 61.7 years, and 65.7% were female. Epigastric pain was the most frequently reported symptom (47.6%), while gastritis was the most common endoscopic finding (60.9%). PPI use was observed in 76% of patients with GPs compared to 31.48% in the comparison cohort. H. pylori was detected in 57.4% of patients with GPs versus 47.14% in the comparison cohort. Hyperplastic polyps (59.3%) and fundic gland polyps (36.5%) were the most common subtypes. Gastric polyps were associated with female gender (p < 0.001), older age (p < 0.001), and PPI use (p < 0.001). Subtype analysis showed fundic gland polyps were associated with female gender (p = 0.008) and PPI use (p = 0.011), while hyperplastic polyps were associated with PPI use (p < 0.001) and iron deficiency anemia (p = 0.011).
Discussion: In this study, gastric polyps were identified in 4.9% of patients, with hyperplastic and fundic gland polyps as the most common subtypes. PPI use was associated with GPs and their subtypes, while no association was found with H. pylori, in contrast to the existing literature. These findings contribute to understanding GP patterns and emphasize the need for further research on risk factors and management in Middle Eastern populations.
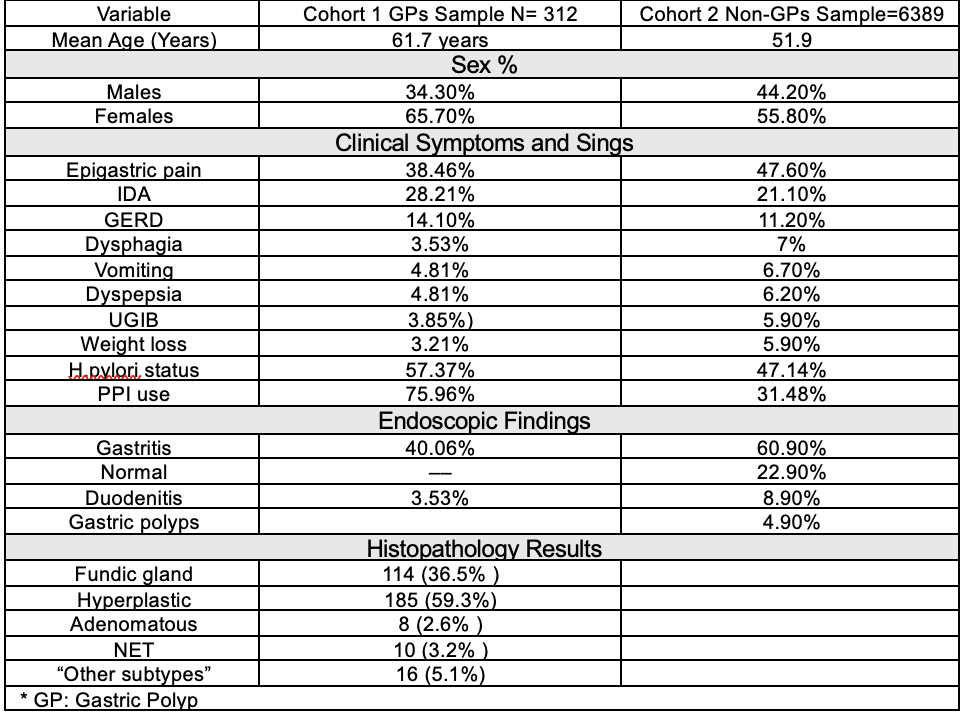
Figure: Table 1 shows the demographics of the total sample and Gastric polyps’ sample with subtypes
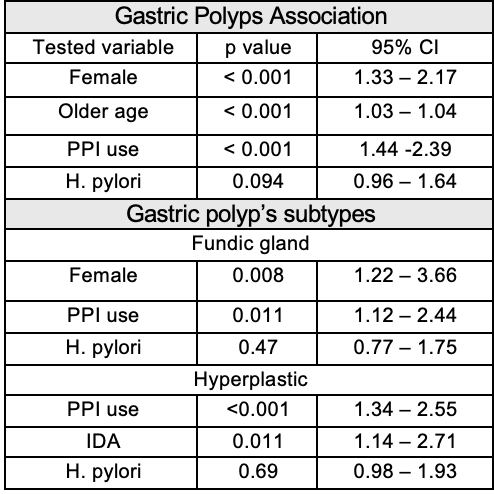
Figure: Table 2 shows the variables significantly associated with a higher likelihood of gastric polyps and their subtypes.
Disclosures:
Tarek Abu-Rajab Tamimi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohammed Aloqaily indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Alexander Rabadi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ahmad Al-Quraan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ahmad Al-Momani indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Zeyad Fraij indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Saleh Aljbour indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Basel Al-Khalidi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ahmad Abdulraheem indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Yaser Rayyan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ra'Ed Ababneh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Tarek Abu-Rajab Tamimi, MD1, Mohammed Aloqaily, MD2, Alexander Rabadi, MD3, Ahmad Al-Quraan, MD1, Ahmad Al-Momani, MD1, Zeyad Fraij, MD1, Saleh Aljbour, MD1, Basel Al-Khalidi, MD1, Ahmad Abdulraheem, MD4, Yaser Rayyan, MD5, Ra'Ed Ababneh, MD6. P4168 - Gastric Polyps Prevalence, Characteristics, and Associated Factors in a Middle Eastern Population: Insights From a 5-Year Retrospective Analysis in a Tertiary Hospital, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1School of Medicine, The University of Jordan, Amman, 'Amman, Jordan; 2University of Maryland Medical Center Midtown Campus, Baltimore, MD; 3McLaren Flint Hospital, Flint, MI; 4MedStar Washington Hospital Center, Washington, DC; 5The University of Jordan, Amman, 'Amman, Jordan; 6MD, Amman, 'Amman, Jordan
Introduction: Gastric polyps (GPs) are mucosal growths with unclear etiology, though Helicobacter pylori infection and proton pump inhibitor (PPI) use are known risk factors. Their prevalence ranges from 0.6% to 6%, varying by ethnicity, geography, and clinical setting. Often asymptomatic, GPs can present with anemia, bleeding, or epigastric pain. Hyperplastic and fundic gland polyps are the most common subtypes. Despite their clinical relevance, data from Middle Eastern populations remain limited. This study aims to assess the prevalence and potential risk factors of GPs in a Middle Eastern cohort.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective analysis of patients who underwent esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) for any indication at a tertiary hospital in the Middle East between 2017 and 2022. Institutional Review Board (IRB) approval was obtained. Two cohorts were identified: patients with GPs (cohort 1) and those without (cohort 2). Collected data included demographics, H. pylori status, PPI use, endoscopic findings, and histopathological results. Patients with missing data from EGD or clinical records were excluded. Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS.
Results: GPs were identified in 312 (4.9%) out f 6,389 EGDs. Demographics are shown in Table 1. Among patients with GPs, the mean age was 61.7 years, and 65.7% were female. Epigastric pain was the most frequently reported symptom (47.6%), while gastritis was the most common endoscopic finding (60.9%). PPI use was observed in 76% of patients with GPs compared to 31.48% in the comparison cohort. H. pylori was detected in 57.4% of patients with GPs versus 47.14% in the comparison cohort. Hyperplastic polyps (59.3%) and fundic gland polyps (36.5%) were the most common subtypes. Gastric polyps were associated with female gender (p < 0.001), older age (p < 0.001), and PPI use (p < 0.001). Subtype analysis showed fundic gland polyps were associated with female gender (p = 0.008) and PPI use (p = 0.011), while hyperplastic polyps were associated with PPI use (p < 0.001) and iron deficiency anemia (p = 0.011).
Discussion: In this study, gastric polyps were identified in 4.9% of patients, with hyperplastic and fundic gland polyps as the most common subtypes. PPI use was associated with GPs and their subtypes, while no association was found with H. pylori, in contrast to the existing literature. These findings contribute to understanding GP patterns and emphasize the need for further research on risk factors and management in Middle Eastern populations.

Figure: Table 1 shows the demographics of the total sample and Gastric polyps’ sample with subtypes

Figure: Table 2 shows the variables significantly associated with a higher likelihood of gastric polyps and their subtypes.
Disclosures:
Tarek Abu-Rajab Tamimi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohammed Aloqaily indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Alexander Rabadi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ahmad Al-Quraan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ahmad Al-Momani indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Zeyad Fraij indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Saleh Aljbour indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Basel Al-Khalidi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ahmad Abdulraheem indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Yaser Rayyan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ra'Ed Ababneh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Tarek Abu-Rajab Tamimi, MD1, Mohammed Aloqaily, MD2, Alexander Rabadi, MD3, Ahmad Al-Quraan, MD1, Ahmad Al-Momani, MD1, Zeyad Fraij, MD1, Saleh Aljbour, MD1, Basel Al-Khalidi, MD1, Ahmad Abdulraheem, MD4, Yaser Rayyan, MD5, Ra'Ed Ababneh, MD6. P4168 - Gastric Polyps Prevalence, Characteristics, and Associated Factors in a Middle Eastern Population: Insights From a 5-Year Retrospective Analysis in a Tertiary Hospital, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
