Monday Poster Session
Category: Small Intestine
P4154 - Beyond the Colon: Unmasking Pembrolizumab-Induced Duodenitis in the Setting of Rectosigmoid Colitis
Monday, October 27, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Raahi Patel, DO
Franciscan Health Olympia Fields
Chicago, IL
Presenting Author(s)
Raahi Patel, DO1, Navin Naik, DO2, Nick Baur, DO1, Shil Punatar, DO3, Nabiha Haider, DO1, Amer Alsamman, MD1, Tilemahos Spyratos, DO1
1Franciscan Health Olympia Fields, Olympia Fields, IL; 2Franciscan Health Olympia Fields, Chicago, IL; 3Franciscan Health Olympia Fields, Homewood, IL
Introduction: Pembrolizumab, also known mechanistically as an immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) targets programmed death-1 (PD-1) receptors on cells in order to combat various malignancies. While its use may be efficacious towards fighting cancer, upregulation of the immune system may lead to immune-related adverse events (irAEs) including pneumonitis, colitis, hepatitis, etc. While irAEs can cause colitis throughout the gastrointestinal (GI) tract, it rarely affects the upper GI tract. We present a case of pembrolizumab induced rectosigmoid colitis and duodenitis.
Case Description/
Methods: A 64 year old female with a history of cervical cancer on pembrolizumab presented with diarrhea, fatigue and near syncope. Physical exam was unremarkable. Labs revealed elevated creatinine consistent with acute kidney injury. She underwent a flexible sigmoidoscopy that revealed rectosigmoid ulcerations. After biopsies confirmed ICI induced colitis, a corticosteroid protocol was initiated. Few days later, she developed bright red blood per rectum and hypotension, raising concern for a lower GI bleed versus brisk upper GI bleed. Repeat colonoscopy was unrevealing while an esophagogastroduodenoscopy showed LA grade C esophagitis and multiple, large, cratered, non-bleeding ulcers (Forrest Class III) in the duodenum. Biopsies were consistent with ICI induced duodenitis. Due to a lack of improvement on continued steroid treatment, she was started on infliximab. She was then transferred for higher level of care where she underwent repeat EGD for a bleeding duodenal ulcer. However, due to a severe duodenal stricture, the ulcer could not be clipped or cauterized. Instead, a hemolytic agent was applied and a decision to pursue comfort care and hospice were made.
Discussion: Although anti- PD-1 is crucial in cancer treatment, it carries a 3% chance of developing ICI colitis; and the even more rare complication of ICI induced duodenitis. While 50% of irAEs affect the GI tract, only a few cases report ICI induced duodenitis.. Prednisone is the first line treatment for moderate to severe disease, but can be replaced by methylprednisolone if no improvement is seen. Infliximab or vedolizumab may be added to steroids, in patients with high risk endoscopic features such as ulcers. Due to the increased use of pembrolizumab, there may be more ICI associated complications. We would like to shed light on the atypical presentation of ICI duodenitis and the current diagnostic and treatment modalities.
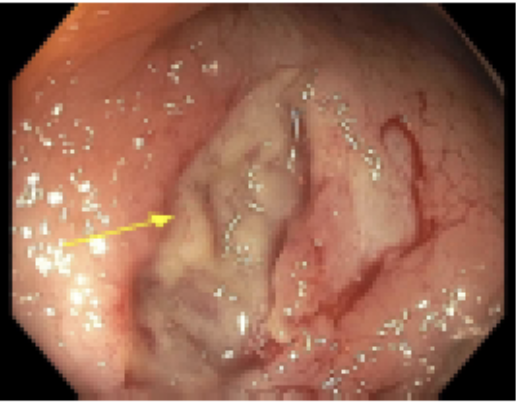
Figure: Duodenal ulcers in the second portion of the duodenum
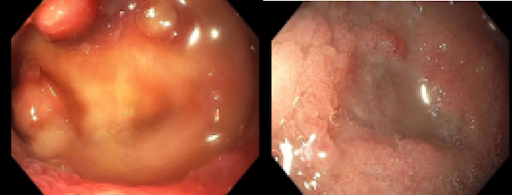
Figure: Ulcer in the rectosigmoid junction
Disclosures:
Raahi Patel indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Navin Naik indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nick Baur indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Shil Punatar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nabiha Haider indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Amer Alsamman indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Tilemahos Spyratos indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Raahi Patel, DO1, Navin Naik, DO2, Nick Baur, DO1, Shil Punatar, DO3, Nabiha Haider, DO1, Amer Alsamman, MD1, Tilemahos Spyratos, DO1. P4154 - Beyond the Colon: Unmasking Pembrolizumab-Induced Duodenitis in the Setting of Rectosigmoid Colitis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Franciscan Health Olympia Fields, Olympia Fields, IL; 2Franciscan Health Olympia Fields, Chicago, IL; 3Franciscan Health Olympia Fields, Homewood, IL
Introduction: Pembrolizumab, also known mechanistically as an immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) targets programmed death-1 (PD-1) receptors on cells in order to combat various malignancies. While its use may be efficacious towards fighting cancer, upregulation of the immune system may lead to immune-related adverse events (irAEs) including pneumonitis, colitis, hepatitis, etc. While irAEs can cause colitis throughout the gastrointestinal (GI) tract, it rarely affects the upper GI tract. We present a case of pembrolizumab induced rectosigmoid colitis and duodenitis.
Case Description/
Methods: A 64 year old female with a history of cervical cancer on pembrolizumab presented with diarrhea, fatigue and near syncope. Physical exam was unremarkable. Labs revealed elevated creatinine consistent with acute kidney injury. She underwent a flexible sigmoidoscopy that revealed rectosigmoid ulcerations. After biopsies confirmed ICI induced colitis, a corticosteroid protocol was initiated. Few days later, she developed bright red blood per rectum and hypotension, raising concern for a lower GI bleed versus brisk upper GI bleed. Repeat colonoscopy was unrevealing while an esophagogastroduodenoscopy showed LA grade C esophagitis and multiple, large, cratered, non-bleeding ulcers (Forrest Class III) in the duodenum. Biopsies were consistent with ICI induced duodenitis. Due to a lack of improvement on continued steroid treatment, she was started on infliximab. She was then transferred for higher level of care where she underwent repeat EGD for a bleeding duodenal ulcer. However, due to a severe duodenal stricture, the ulcer could not be clipped or cauterized. Instead, a hemolytic agent was applied and a decision to pursue comfort care and hospice were made.
Discussion: Although anti- PD-1 is crucial in cancer treatment, it carries a 3% chance of developing ICI colitis; and the even more rare complication of ICI induced duodenitis. While 50% of irAEs affect the GI tract, only a few cases report ICI induced duodenitis.. Prednisone is the first line treatment for moderate to severe disease, but can be replaced by methylprednisolone if no improvement is seen. Infliximab or vedolizumab may be added to steroids, in patients with high risk endoscopic features such as ulcers. Due to the increased use of pembrolizumab, there may be more ICI associated complications. We would like to shed light on the atypical presentation of ICI duodenitis and the current diagnostic and treatment modalities.

Figure: Duodenal ulcers in the second portion of the duodenum

Figure: Ulcer in the rectosigmoid junction
Disclosures:
Raahi Patel indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Navin Naik indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nick Baur indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Shil Punatar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nabiha Haider indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Amer Alsamman indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Tilemahos Spyratos indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Raahi Patel, DO1, Navin Naik, DO2, Nick Baur, DO1, Shil Punatar, DO3, Nabiha Haider, DO1, Amer Alsamman, MD1, Tilemahos Spyratos, DO1. P4154 - Beyond the Colon: Unmasking Pembrolizumab-Induced Duodenitis in the Setting of Rectosigmoid Colitis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
