Monday Poster Session
Category: Small Intestine
P4144 - Isolated Acute Ileal Diverticulitis: An Unexpected Cause of Abdominal Pain
Monday, October 27, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall
- PR
Patricia Rivera, MD (she/her/hers)
VA Caribbean Healthcare System
San Juan, PR
Presenting Author(s)
Carla Cepero-Jimenez, MD, Patricia Rivera-Cariño, MD, Loscar Santiago-Rivera, MD, Eduardo Acosta-Pumarejo, MD
VA Caribbean Healthcare System, San Juan, Puerto Rico
Introduction: Small bowel diverticula are rare, more often located in the duodenum, and mainly asymptomatic. When present, it is most often found in elderly males. Although uncommon, small bowel diverticula can rise complications including acute diverticulitis, which can mimic of other diseases. Here we present a case of an elderly male with acute ileal diverticulitis as the cause of abdominal pain.
Case Description/
Methods: A 90-year-old man with history of chronic constipation and severe colonic universal diverticulosis with previous bouts of acute diverticulitis, presents to our Emergency Department complaining of subjective fever and right lower quadrant abdominal pain since the day before evaluation. Other symptoms were denied. Physical exam revealed normal vital signs and tenderness on deep palpation in the right lower quadrant without signs of peritonitis. Laboratories showed neutrophilic leukocytosis, and normal hemoglobin, platelets, renal function and liver enzymes. Abdominopelvic CT scan with oral contrast was remarkable for diverticulosis of the terminal ileum with moderate wall thickening and surrounding inflammation consistent with acute ileal diverticulitis. The appendix was normal (Figure 1). The patient was discharged home with a 10-day course of oral antibiotics with complete resolution of his symptoms.
Discussion: Diverticula of the small bowel are relatively uncommon, affecting 0.07 to 2% of the population. Although it can affect any part of the small bowel, the terminal ileum is the least common location. Acute ileal diverticulitis is a rare cause of right lower quadrant abdominal pain, which can mimic other more prevalent disorders such as acute appendicitis and Crohn’s disease. Physicians should be aware of this uncommon manifestation of small bowel diverticulosis and should consider it in the differential diagnosis of right lower quadrant abdominal pain.
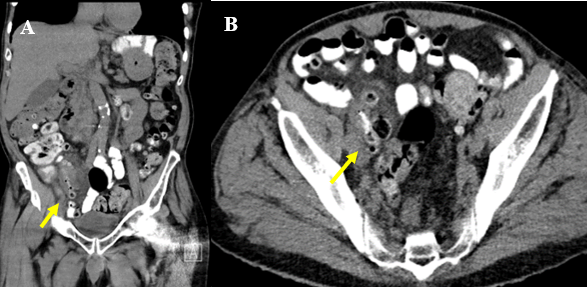
Figure: Figure 1: Coronal (A) and axial (B) views of abdominopelvic CT scan with oral contrast demonstrating diverticulosis of the terminal ileum with moderate wall thickening and surrounding inflammation (yellow arrows).
Disclosures:
Carla Cepero-Jimenez indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Patricia Rivera-Cariño indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Loscar Santiago-Rivera indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Eduardo Acosta-Pumarejo indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Carla Cepero-Jimenez, MD, Patricia Rivera-Cariño, MD, Loscar Santiago-Rivera, MD, Eduardo Acosta-Pumarejo, MD. P4144 - Isolated Acute Ileal Diverticulitis: An Unexpected Cause of Abdominal Pain, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
VA Caribbean Healthcare System, San Juan, Puerto Rico
Introduction: Small bowel diverticula are rare, more often located in the duodenum, and mainly asymptomatic. When present, it is most often found in elderly males. Although uncommon, small bowel diverticula can rise complications including acute diverticulitis, which can mimic of other diseases. Here we present a case of an elderly male with acute ileal diverticulitis as the cause of abdominal pain.
Case Description/
Methods: A 90-year-old man with history of chronic constipation and severe colonic universal diverticulosis with previous bouts of acute diverticulitis, presents to our Emergency Department complaining of subjective fever and right lower quadrant abdominal pain since the day before evaluation. Other symptoms were denied. Physical exam revealed normal vital signs and tenderness on deep palpation in the right lower quadrant without signs of peritonitis. Laboratories showed neutrophilic leukocytosis, and normal hemoglobin, platelets, renal function and liver enzymes. Abdominopelvic CT scan with oral contrast was remarkable for diverticulosis of the terminal ileum with moderate wall thickening and surrounding inflammation consistent with acute ileal diverticulitis. The appendix was normal (Figure 1). The patient was discharged home with a 10-day course of oral antibiotics with complete resolution of his symptoms.
Discussion: Diverticula of the small bowel are relatively uncommon, affecting 0.07 to 2% of the population. Although it can affect any part of the small bowel, the terminal ileum is the least common location. Acute ileal diverticulitis is a rare cause of right lower quadrant abdominal pain, which can mimic other more prevalent disorders such as acute appendicitis and Crohn’s disease. Physicians should be aware of this uncommon manifestation of small bowel diverticulosis and should consider it in the differential diagnosis of right lower quadrant abdominal pain.

Figure: Figure 1: Coronal (A) and axial (B) views of abdominopelvic CT scan with oral contrast demonstrating diverticulosis of the terminal ileum with moderate wall thickening and surrounding inflammation (yellow arrows).
Disclosures:
Carla Cepero-Jimenez indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Patricia Rivera-Cariño indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Loscar Santiago-Rivera indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Eduardo Acosta-Pumarejo indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Carla Cepero-Jimenez, MD, Patricia Rivera-Cariño, MD, Loscar Santiago-Rivera, MD, Eduardo Acosta-Pumarejo, MD. P4144 - Isolated Acute Ileal Diverticulitis: An Unexpected Cause of Abdominal Pain, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
