Monday Poster Session
Category: Liver
P3988 - Fulminant Liver Failure Linked to Tirzepatide (Mounjaro): A Case Report and Urgent Call for Vigilance
Monday, October 27, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Fatma Mahmoud, MD
Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi
Abu Dhabi, Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates
Presenting Author(s)
Fatma Mahmoud, MD, Ahmad Alduaij, MD, Sulieman Abdal Raheem, MD
Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi, Abu Dhabi, Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates
Introduction: GLP-1 agonists treat type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and obesity. Tirzepatide (Zepbound) was FDA-approved in November 2023 for weight management in obese or overweight individuals with weight-related comorbidities. These medications are also studied for off-label use in metabolic dysfunction-associated liver disease, showing potential benefits in liver fibrosis. Common adverse effects include gastrointestinal symptoms, acute pancreatitis, and gallbladder diseases. There are reports of GLP-1 agonist-induced liver injury, particularly liraglutide-related drug-induced autoimmune hepatitis.
Case Description/
Methods: A 19-year-old female with a BMI of 28.08 kg/m² presented with acute liver failure, coagulopathy with INR >7, grade II hepatic encephalopathy and MELD 3.0 score of 34. She reported receiving Tirzepatide (Mounjaro) at 5 mg for the past 2 months for weight reduction. Extensive investigations ruled out viral, vascular, metabolic, autoimmune, and obstructive etiologies. The patient denied taking any other supplements, herbal medications or drugs beside Tirzepatide. She denied alcohol consumption, illicit drug use, recent travel or any recent changes in her diet.
Patient was started on N-acetylcysteine infusion and CRRT was initiated as per guidelines which was followed by daily sessions of high-volume plasma exchange.
Urgent evaluation for liver transplantation was initiated, and she underwent deceased liver transplantation on day 3 of admission.
Pathological examination of the native liver revealed extensive centrizonal acinar hepatocellular necrosis accompanied by minimal inflammatory infiltrate with no evidence of significant steatosis or fibrosis. The overall features were consistent with acute hepatocellular necrosis with possible etiologies including metabolic/toxins, drug overdose associated acute hepatic failure with/without liver storage disease. (Figure 1)
Discussion: Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) accounts for 10-15% of acute liver failure (ALF) in the U.S. Diagnosing DILI is challenging due to varied presentations and lack of specific biomarkers. GLP-1 agonists are not typically associated with clinically apparent liver injury. To our knowledge this is the first case that may present Trizepatide induced fulminant liver failure requiring urgent liver transplantation with pathology proven drug induced liver injury. Long-term safety profile studies of GLP1 analogues are needed especially with the current wide use of these medications.
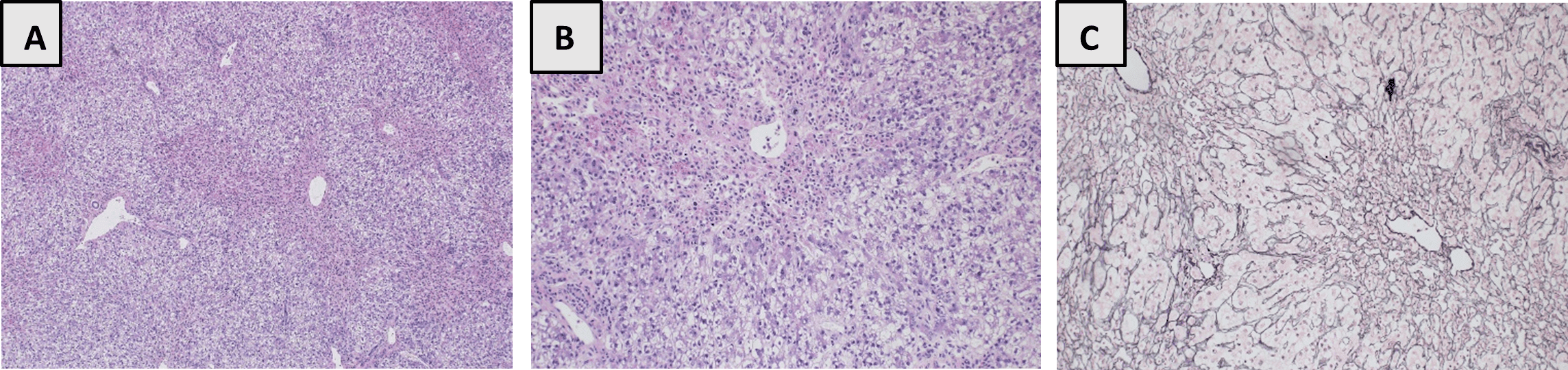
Figure: Figure 1: Liver explanted tissue histologic sections: Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining. Original magnification x40 (A) and x100 (B). Reticulin special staining. Original magnification x100 (C)
Disclosures:
Fatma Mahmoud indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ahmad Alduaij indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sulieman Abdal Raheem indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Fatma Mahmoud, MD, Ahmad Alduaij, MD, Sulieman Abdal Raheem, MD. P3988 - Fulminant Liver Failure Linked to Tirzepatide (Mounjaro): A Case Report and Urgent Call for Vigilance, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi, Abu Dhabi, Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates
Introduction: GLP-1 agonists treat type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and obesity. Tirzepatide (Zepbound) was FDA-approved in November 2023 for weight management in obese or overweight individuals with weight-related comorbidities. These medications are also studied for off-label use in metabolic dysfunction-associated liver disease, showing potential benefits in liver fibrosis. Common adverse effects include gastrointestinal symptoms, acute pancreatitis, and gallbladder diseases. There are reports of GLP-1 agonist-induced liver injury, particularly liraglutide-related drug-induced autoimmune hepatitis.
Case Description/
Methods: A 19-year-old female with a BMI of 28.08 kg/m² presented with acute liver failure, coagulopathy with INR >7, grade II hepatic encephalopathy and MELD 3.0 score of 34. She reported receiving Tirzepatide (Mounjaro) at 5 mg for the past 2 months for weight reduction. Extensive investigations ruled out viral, vascular, metabolic, autoimmune, and obstructive etiologies. The patient denied taking any other supplements, herbal medications or drugs beside Tirzepatide. She denied alcohol consumption, illicit drug use, recent travel or any recent changes in her diet.
Patient was started on N-acetylcysteine infusion and CRRT was initiated as per guidelines which was followed by daily sessions of high-volume plasma exchange.
Urgent evaluation for liver transplantation was initiated, and she underwent deceased liver transplantation on day 3 of admission.
Pathological examination of the native liver revealed extensive centrizonal acinar hepatocellular necrosis accompanied by minimal inflammatory infiltrate with no evidence of significant steatosis or fibrosis. The overall features were consistent with acute hepatocellular necrosis with possible etiologies including metabolic/toxins, drug overdose associated acute hepatic failure with/without liver storage disease. (Figure 1)
Discussion: Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) accounts for 10-15% of acute liver failure (ALF) in the U.S. Diagnosing DILI is challenging due to varied presentations and lack of specific biomarkers. GLP-1 agonists are not typically associated with clinically apparent liver injury. To our knowledge this is the first case that may present Trizepatide induced fulminant liver failure requiring urgent liver transplantation with pathology proven drug induced liver injury. Long-term safety profile studies of GLP1 analogues are needed especially with the current wide use of these medications.

Figure: Figure 1: Liver explanted tissue histologic sections: Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining. Original magnification x40 (A) and x100 (B). Reticulin special staining. Original magnification x100 (C)
Disclosures:
Fatma Mahmoud indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ahmad Alduaij indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sulieman Abdal Raheem indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Fatma Mahmoud, MD, Ahmad Alduaij, MD, Sulieman Abdal Raheem, MD. P3988 - Fulminant Liver Failure Linked to Tirzepatide (Mounjaro): A Case Report and Urgent Call for Vigilance, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
