Monday Poster Session
Category: Liver
P3926 - A Rare Case of Fusobacterium Nucleatum Causing Greater Than 20 Pyogenic Hepatic Abscesses
Monday, October 27, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Gurjot Singh, DO
The Warren Alpert Medical School of Brown University
Warwick, RI
Presenting Author(s)
Gurjot Singh, DO1, Muhammad Ali, MBChB1, Tamara Koritarov, DO, MSc2, Kyle Rollheiser, MD3, John Cribb, MD4
1The Warren Alpert Medical School of Brown University, Warwick, RI; 2Kent Hospital, Providence, RI; 3Warren Alpert Medical School of Brown University, Warwick, RI; 4Kent Hospital, Warwick, RI
Introduction: Fusobacterium nucleatum is a bacteria that is commonly associated with periodontal disease. Here we present a case of a patient found to have Fusobacterium nucleatum bacteremia with greater than 20 pyogenic hepatic abscesses characterized on CT and MRI.
Case Description/
Methods: A 60-year-old male with past medical history of alcoholic pancreatitis status post Whipple procedure presented with complaints of abdominal pain. The patient reported nausea and vomiting for 3 days along, scleral icterus, chills, but denied any hematochezia. On admission, vital signs were stable, with the patient afebrile, and no periodontal disease noted on physical examination. CT of the chest, abdomen, and pelvis demonstrated complex cystic appearing hepatic lesions with concern for metastasis versus hepatic abscess, nonocclusive portal vein thrombus, and multiple cystic lesions in the pancreatic head with evidence of chronic pancreatitis. Labs were significant for a white blood cells 15.6 x 103/mcl, INR of 1.4, bilirubin of 3.6 mg/dL, with direct bilirubin of 2.1 mg/dL. HIV, CEA, and CA 19-9 were unremarkable. The patient underwent an MRI of the abdomen and pelvis which revealed numerous complex cystic appearing hepatic lesions, nonocclusive portal vein thrombus, and a mass in the pancreatic head. He was started on a heparin drip for the nonocclusive portal vein thrombus and piperacillin/tazobactam. Blood cultures were found to be positive for Fusobacterium nucleatum. Ultrasound-guided biopsy of the hepatic lesion yielded 4 cc of dark, green, foul-smelling pus with cultures found to grow a gram-negative, beta-lactamase negative, rod, similar to blood cultures. The patient was advised for inpatient colonoscopy however, denied any intervention. He was advised for outpatient follow-up with an advanced gastroenterologist for endoscopic ultrasound of cystic lesions in the pancreatic head, hematology for portal vein thrombus, and repeat MRI with infectious disease follow-up. The patient was discharged against medical advice with amoxicillin/clavulanic acid and apixaban.
Discussion: This case presents a patient with no significant periodontal disease however, found to have Fusobacterium nucleatum bacteremia. There have been some associations of the bacteria with colon cancer, which remains a risk in this patient has he had no historical colonoscopies. However, this case highlights the extensive disease with numerous abscess that may be formed with the organism requiring both drainage and long-term antibiotic therapy.
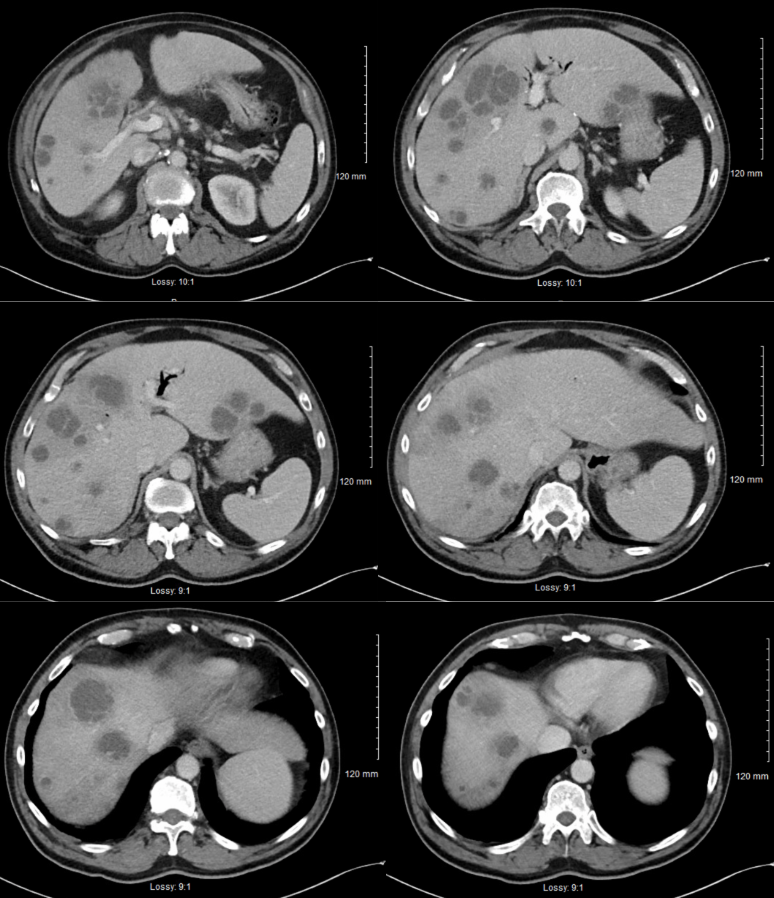
Figure: Computed tomography of the abdomen demonstrating multi-level views of the liver with numerous, complex cystic appearing lesions with largest hepatic lesion measuring 6 cm.
Disclosures:
Gurjot Singh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Ali indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Tamara Koritarov indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kyle Rollheiser indicated no relevant financial relationships.
John Cribb indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Gurjot Singh, DO1, Muhammad Ali, MBChB1, Tamara Koritarov, DO, MSc2, Kyle Rollheiser, MD3, John Cribb, MD4. P3926 - A Rare Case of Fusobacterium Nucleatum Causing Greater Than 20 Pyogenic Hepatic Abscesses, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1The Warren Alpert Medical School of Brown University, Warwick, RI; 2Kent Hospital, Providence, RI; 3Warren Alpert Medical School of Brown University, Warwick, RI; 4Kent Hospital, Warwick, RI
Introduction: Fusobacterium nucleatum is a bacteria that is commonly associated with periodontal disease. Here we present a case of a patient found to have Fusobacterium nucleatum bacteremia with greater than 20 pyogenic hepatic abscesses characterized on CT and MRI.
Case Description/
Methods: A 60-year-old male with past medical history of alcoholic pancreatitis status post Whipple procedure presented with complaints of abdominal pain. The patient reported nausea and vomiting for 3 days along, scleral icterus, chills, but denied any hematochezia. On admission, vital signs were stable, with the patient afebrile, and no periodontal disease noted on physical examination. CT of the chest, abdomen, and pelvis demonstrated complex cystic appearing hepatic lesions with concern for metastasis versus hepatic abscess, nonocclusive portal vein thrombus, and multiple cystic lesions in the pancreatic head with evidence of chronic pancreatitis. Labs were significant for a white blood cells 15.6 x 103/mcl, INR of 1.4, bilirubin of 3.6 mg/dL, with direct bilirubin of 2.1 mg/dL. HIV, CEA, and CA 19-9 were unremarkable. The patient underwent an MRI of the abdomen and pelvis which revealed numerous complex cystic appearing hepatic lesions, nonocclusive portal vein thrombus, and a mass in the pancreatic head. He was started on a heparin drip for the nonocclusive portal vein thrombus and piperacillin/tazobactam. Blood cultures were found to be positive for Fusobacterium nucleatum. Ultrasound-guided biopsy of the hepatic lesion yielded 4 cc of dark, green, foul-smelling pus with cultures found to grow a gram-negative, beta-lactamase negative, rod, similar to blood cultures. The patient was advised for inpatient colonoscopy however, denied any intervention. He was advised for outpatient follow-up with an advanced gastroenterologist for endoscopic ultrasound of cystic lesions in the pancreatic head, hematology for portal vein thrombus, and repeat MRI with infectious disease follow-up. The patient was discharged against medical advice with amoxicillin/clavulanic acid and apixaban.
Discussion: This case presents a patient with no significant periodontal disease however, found to have Fusobacterium nucleatum bacteremia. There have been some associations of the bacteria with colon cancer, which remains a risk in this patient has he had no historical colonoscopies. However, this case highlights the extensive disease with numerous abscess that may be formed with the organism requiring both drainage and long-term antibiotic therapy.

Figure: Computed tomography of the abdomen demonstrating multi-level views of the liver with numerous, complex cystic appearing lesions with largest hepatic lesion measuring 6 cm.
Disclosures:
Gurjot Singh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Ali indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Tamara Koritarov indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kyle Rollheiser indicated no relevant financial relationships.
John Cribb indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Gurjot Singh, DO1, Muhammad Ali, MBChB1, Tamara Koritarov, DO, MSc2, Kyle Rollheiser, MD3, John Cribb, MD4. P3926 - A Rare Case of Fusobacterium Nucleatum Causing Greater Than 20 Pyogenic Hepatic Abscesses, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.

