Monday Poster Session
Category: Liver
P3884 - Therapeutic Plasma Exchange for Treatment of Sickle Cell-Related Acute Liver Failure
Monday, October 27, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall
- SG
Sirisha Gaddipati, MD
University of Miami Health System
Miami, FL
Presenting Author(s)
Sirisha Gaddipati, MD1, Kimberlee Woo Ling, MBBS2, Eric F. Martin, MD3
1University of Miami Health System, Miami, FL; 2Queen's University, Miami, FL; 3University of Miami Miller School of Medicine at Jackson Memorial Hospital, Miami, FL
Introduction: Sickle cell disease (SCD) has been well-described to cause chronic liver injury, with cirrhosis in up to 30% of patients. Acute liver failure (ALF) however is a fatal complication of sickle cell hepatopathy, and there is limited data on optimal management strategies. We present a case of SCD-associated ALF, with clinical improvement from therapeutic plasma exchange (TPE).
Case Description/
Methods: A 63-year-old woman with reported sickle cell trait was admitted to the intensive care with fever (101.2 F), hypotension. Laboratory studies showed hemoglobin 7.3 mg/dL, creatinine 4.10 mg/dL lactic acid 13.5 mmol/L, and INR 1.8. Liver enzymes peaked with ALT 10367 u/L, AST 4813 u/L, ALP 82 u/L and total bilirubin 5.1 mg/dL. Computed tomography showed hepatomegaly with edematous and heterogenous parenchyma. Workup for viral, drug, and inherited causes of liver disease were negative. Parvovirus B19 returned positive. She developed hepatic encephalopathy (HE) with INR 4.38, diagnostic for ALF, with worsening MELD score of 40, prompting liver transplantation (LT) workup. Hemoglobin electrophoresis confirmed hemoglobin SC (HbSC) disease, supportive of ALF due to sickle cell crisis, and aplastic crisis due to parvovirus infection. The patient deteriorated despite red blood cell exchange (RBCE), thus TPE was initiated in addition to renal replacement therapy with clinical improvement and resolution of HE and renal failure (Figure 1). MELD decreased to 14 by discharge, supporting a successful response to TPE without need for LT.
Discussion: ALF is a potentially fatal consequence of acute sickle cell crisis. TPE removes pro-inflammatory cytokines and complements associated with erythrocyte sickling and is postulated to provide additional benefit to RBCE. However, the use of TPE for ALF due to SCD is limited to case reports in the literature, with one prior case series suggesting a survival benefit in patients with multiorgan failure secondary to SCD refractory to RBCE. TPE is used for drug or viral induced ALF and has been shown to improve survival in patients as well as serve as a bridge to LT—however, it has not been specifically studied in SCD-related ALF, a unique population with marked morbidity and mortality rates associated with LT. Identifying cases of SCD-associated ALF and indications for TPE can have significant implications for future management.
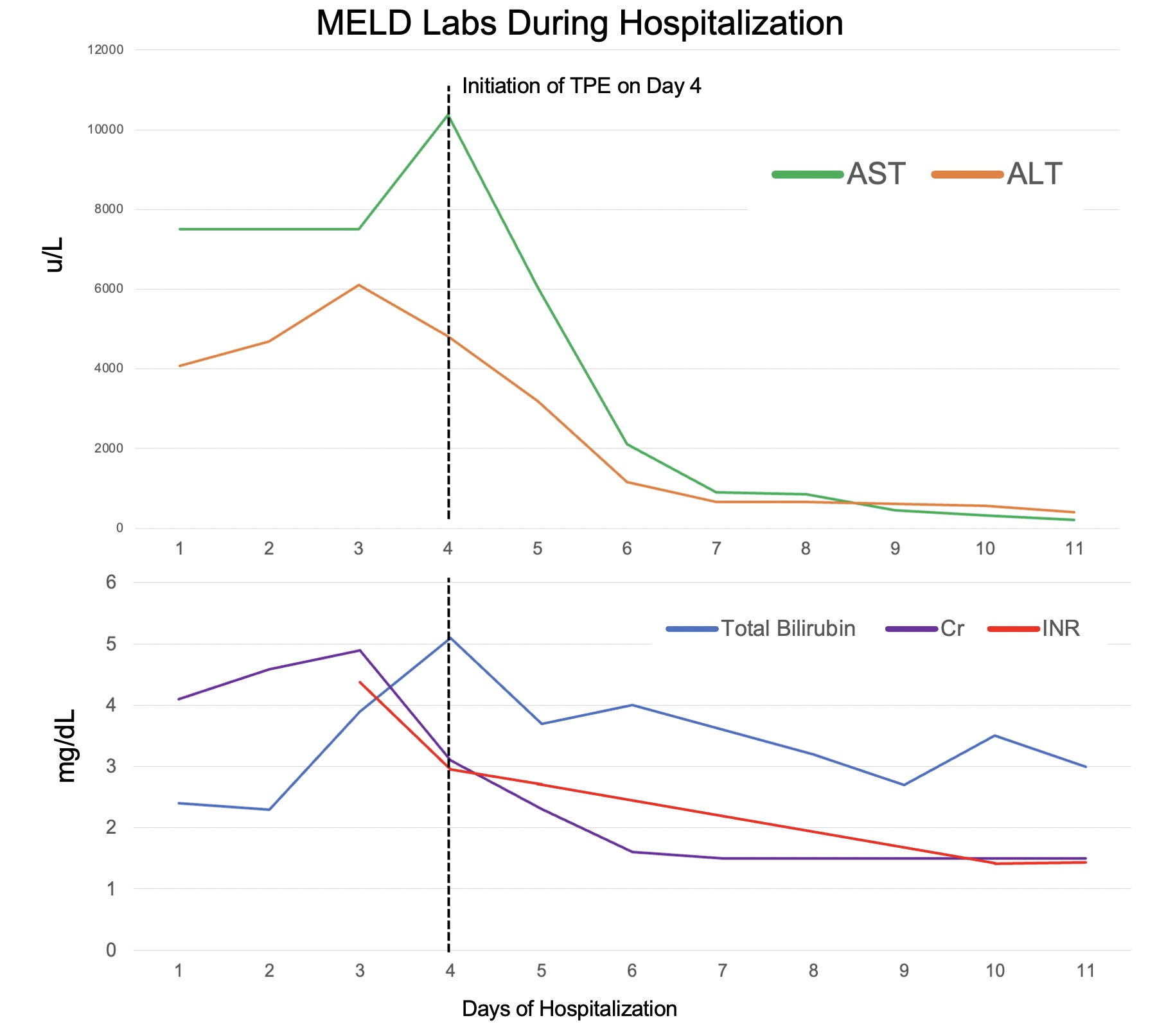
Figure: Figure 1: Model of End Stage Liver Disease (MELD) lab values during patient’s hospitalization. Lab values include aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alanine transaminase (ALT), total bilirubin, serum creatinine (Cr), and International Normalized Ratio (INR). MELD labs peaked on Day 4 of hospitalization, the day that therapeutic plasma exchange (TPE) was initiated and improved afterwards.
Disclosures:
Sirisha Gaddipati indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kimberlee Woo Ling indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Eric Martin indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sirisha Gaddipati, MD1, Kimberlee Woo Ling, MBBS2, Eric F. Martin, MD3. P3884 - Therapeutic Plasma Exchange for Treatment of Sickle Cell-Related Acute Liver Failure, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1University of Miami Health System, Miami, FL; 2Queen's University, Miami, FL; 3University of Miami Miller School of Medicine at Jackson Memorial Hospital, Miami, FL
Introduction: Sickle cell disease (SCD) has been well-described to cause chronic liver injury, with cirrhosis in up to 30% of patients. Acute liver failure (ALF) however is a fatal complication of sickle cell hepatopathy, and there is limited data on optimal management strategies. We present a case of SCD-associated ALF, with clinical improvement from therapeutic plasma exchange (TPE).
Case Description/
Methods: A 63-year-old woman with reported sickle cell trait was admitted to the intensive care with fever (101.2 F), hypotension. Laboratory studies showed hemoglobin 7.3 mg/dL, creatinine 4.10 mg/dL lactic acid 13.5 mmol/L, and INR 1.8. Liver enzymes peaked with ALT 10367 u/L, AST 4813 u/L, ALP 82 u/L and total bilirubin 5.1 mg/dL. Computed tomography showed hepatomegaly with edematous and heterogenous parenchyma. Workup for viral, drug, and inherited causes of liver disease were negative. Parvovirus B19 returned positive. She developed hepatic encephalopathy (HE) with INR 4.38, diagnostic for ALF, with worsening MELD score of 40, prompting liver transplantation (LT) workup. Hemoglobin electrophoresis confirmed hemoglobin SC (HbSC) disease, supportive of ALF due to sickle cell crisis, and aplastic crisis due to parvovirus infection. The patient deteriorated despite red blood cell exchange (RBCE), thus TPE was initiated in addition to renal replacement therapy with clinical improvement and resolution of HE and renal failure (Figure 1). MELD decreased to 14 by discharge, supporting a successful response to TPE without need for LT.
Discussion: ALF is a potentially fatal consequence of acute sickle cell crisis. TPE removes pro-inflammatory cytokines and complements associated with erythrocyte sickling and is postulated to provide additional benefit to RBCE. However, the use of TPE for ALF due to SCD is limited to case reports in the literature, with one prior case series suggesting a survival benefit in patients with multiorgan failure secondary to SCD refractory to RBCE. TPE is used for drug or viral induced ALF and has been shown to improve survival in patients as well as serve as a bridge to LT—however, it has not been specifically studied in SCD-related ALF, a unique population with marked morbidity and mortality rates associated with LT. Identifying cases of SCD-associated ALF and indications for TPE can have significant implications for future management.

Figure: Figure 1: Model of End Stage Liver Disease (MELD) lab values during patient’s hospitalization. Lab values include aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alanine transaminase (ALT), total bilirubin, serum creatinine (Cr), and International Normalized Ratio (INR). MELD labs peaked on Day 4 of hospitalization, the day that therapeutic plasma exchange (TPE) was initiated and improved afterwards.
Disclosures:
Sirisha Gaddipati indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kimberlee Woo Ling indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Eric Martin indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sirisha Gaddipati, MD1, Kimberlee Woo Ling, MBBS2, Eric F. Martin, MD3. P3884 - Therapeutic Plasma Exchange for Treatment of Sickle Cell-Related Acute Liver Failure, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
