Monday Poster Session
Category: Liver
P3844 - Late Onset Wilson Disease Presenting With Elevated Transaminases and Abnormal Ultrasound
Monday, October 27, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall
- KM
Kalee Moore, DO
Baylor Scott & White Medical Center
Round Rock, TX
Presenting Author(s)
Kalee Moore, DO1, Neel Shah, MD1, Raja Dhanekula, MD1, Josy Adams, MD2
1Baylor Scott & White Medical Center, Round Rock, TX; 2Baylor Scott & White, Temple, TX
Introduction: Wilson's disease (WD) is a rare autosomal recessive disorder caused by mutations in the ATP7B gene, which leads to copper accumulation in various tissues. The disease frequently presents with hepatic or neuropsychiatric manifestations. Ocular findings, such as Kayser-Fleischer rings, are not present in every case. Most cases of WD are diagnosed in patients less than 40 years old. Our case introduces late WD diagnosed in a 60-year-old male.
Case Description/
Methods: Patient has a past medical history of metabolic disorders and obesity. He presented for elevated aspartate aminotransferase (AST) and alanine transaminase (ALT) onset for 2 years. He has gained approximately 40 lbs and recently started tirzepatide. He reports alcohol use of 1 beer/week. There is no history of recreational drug use or family history of liver disease. He has an allergy to penicillin. Patient had an ophthalmology visit recently with a slit lamp exam that was normal. On physical exam, an obese abdomen is noted, otherwise exam is normal.
Repeated labs for 2 years show AST 33-56 U/L and ALT 85-130 U/L. Most recent labs with AST 56 U/L and ALT 109 U/L. Antinuclear antibody titer was 1:160. Antimitochondrial antibody, anti-smooth muscle antibodies, and acute hepatitis panel, iron, iron binding capacity, transferrin saturation, ferritin, alpha-1-antitrypsin level were unremarkable. Ceruloplasmin level was low at 10 mg/dL. A 24-hour urinary copper was elevated at 175.5 ug/day. An abdominal ultrasound showed a heterogenous, echogenic liver and hepatomegaly. A percutaneous liver biopsy revealed mildly active steatohepatitis, moderate steatosis, stage 1-2 fibrosis, and copper quantification at 786 ug/g.
After the workup was completed, hepatology discussed treatment options. Patient agreed to start trientine at 750 mg twice daily using weight-based dosing. Repeat labs 6 weeks after initiating trientine show improvement of both AST and ALT, 45 U/L and 94 U/L respectively. Repeat 24-hour urinary copper has increased to 485 ug/day.
Discussion: Our case is unique in that the presentation was purely hepatic, without neuropsychiatric symptoms or Kayser-Fleischer rings. It challenges the prevailing belief that WD is confined to younger individuals. WD can clinically mimic other liver condition. In our patient, obesity initially directed the evaluation toward fatty liver disease. However, the subsequent workup led to the diagnosis of WD. Early recognition and treatment are critical to prevent progression to cirrhosis and hepatic failure.
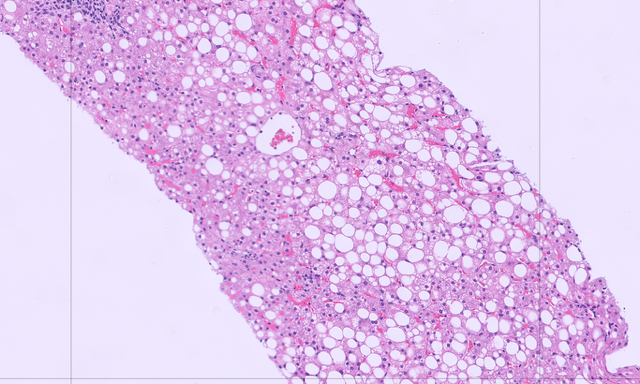
Figure: Figure 1. H&E Stain
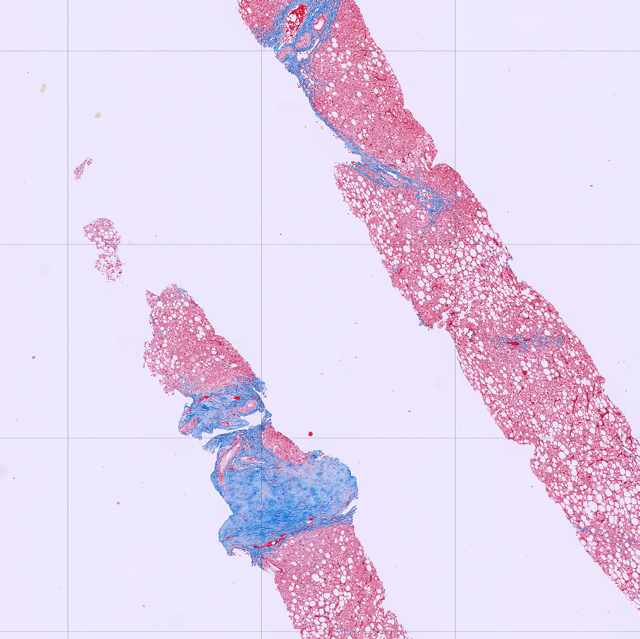
Figure: Figure 2. Trichrome Stain
Disclosures:
Kalee Moore indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Neel Shah indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Raja Dhanekula indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Josy Adams indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kalee Moore, DO1, Neel Shah, MD1, Raja Dhanekula, MD1, Josy Adams, MD2. P3844 - Late Onset Wilson Disease Presenting With Elevated Transaminases and Abnormal Ultrasound, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Baylor Scott & White Medical Center, Round Rock, TX; 2Baylor Scott & White, Temple, TX
Introduction: Wilson's disease (WD) is a rare autosomal recessive disorder caused by mutations in the ATP7B gene, which leads to copper accumulation in various tissues. The disease frequently presents with hepatic or neuropsychiatric manifestations. Ocular findings, such as Kayser-Fleischer rings, are not present in every case. Most cases of WD are diagnosed in patients less than 40 years old. Our case introduces late WD diagnosed in a 60-year-old male.
Case Description/
Methods: Patient has a past medical history of metabolic disorders and obesity. He presented for elevated aspartate aminotransferase (AST) and alanine transaminase (ALT) onset for 2 years. He has gained approximately 40 lbs and recently started tirzepatide. He reports alcohol use of 1 beer/week. There is no history of recreational drug use or family history of liver disease. He has an allergy to penicillin. Patient had an ophthalmology visit recently with a slit lamp exam that was normal. On physical exam, an obese abdomen is noted, otherwise exam is normal.
Repeated labs for 2 years show AST 33-56 U/L and ALT 85-130 U/L. Most recent labs with AST 56 U/L and ALT 109 U/L. Antinuclear antibody titer was 1:160. Antimitochondrial antibody, anti-smooth muscle antibodies, and acute hepatitis panel, iron, iron binding capacity, transferrin saturation, ferritin, alpha-1-antitrypsin level were unremarkable. Ceruloplasmin level was low at 10 mg/dL. A 24-hour urinary copper was elevated at 175.5 ug/day. An abdominal ultrasound showed a heterogenous, echogenic liver and hepatomegaly. A percutaneous liver biopsy revealed mildly active steatohepatitis, moderate steatosis, stage 1-2 fibrosis, and copper quantification at 786 ug/g.
After the workup was completed, hepatology discussed treatment options. Patient agreed to start trientine at 750 mg twice daily using weight-based dosing. Repeat labs 6 weeks after initiating trientine show improvement of both AST and ALT, 45 U/L and 94 U/L respectively. Repeat 24-hour urinary copper has increased to 485 ug/day.
Discussion: Our case is unique in that the presentation was purely hepatic, without neuropsychiatric symptoms or Kayser-Fleischer rings. It challenges the prevailing belief that WD is confined to younger individuals. WD can clinically mimic other liver condition. In our patient, obesity initially directed the evaluation toward fatty liver disease. However, the subsequent workup led to the diagnosis of WD. Early recognition and treatment are critical to prevent progression to cirrhosis and hepatic failure.

Figure: Figure 1. H&E Stain

Figure: Figure 2. Trichrome Stain
Disclosures:
Kalee Moore indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Neel Shah indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Raja Dhanekula indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Josy Adams indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kalee Moore, DO1, Neel Shah, MD1, Raja Dhanekula, MD1, Josy Adams, MD2. P3844 - Late Onset Wilson Disease Presenting With Elevated Transaminases and Abnormal Ultrasound, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.

