Monday Poster Session
Category: Liver
P3813 - Prevalence and Risk Factors of Portopulmonary Hypertension in Chronic Liver Disease: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Monday, October 27, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall
- TA
Tareq Alsaleh, MD
Department of Internal Medicine, AdventHealth Orlando
Orlando, FL
Presenting Author(s)
Tareq Alsaleh, MD1, Amir Harb, DO1, Parikshit Chapagain, MD1, Bassel Dakkak, MD2, Nihal Khan, MD1, Mohamad Khaled Almujarkesh, MD3, Ayman Koteish, MD4
1Department of Internal Medicine, AdventHealth Orlando, Orlando, FL; 2Marshall University Joan C. Edwards School of Medicine, Huntington, WV; 3Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, AdventHealth Orlando, Orlando, FL; 4Gastroenterology, Transplant Hepatology, AdventHealth Orlando, Orlando, FL
Introduction: Portopulmonary hypertension (PPHTN) is a serious complication of chronic liver disease (CLD), characterized by pulmonary arterial hypertension in the presence of portal hypertension. In patients undergoing liver transplantation, it is associated with higher perioperative mortality, highlighting the significance of its early detection. Diagnostic modalities include transthoracic echocardiogram (TTE) and right heart catheterization (RHC). We conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis to report the prevalence and risk factors for development of PPHTN in CLD.
Methods: A systematic review of the literature from PubMed, EMBASE, Scopus, Web of Science, and Ovid was conducted from inception to April 2025 for studies reporting on PPHTN in CLD patients. We included studies comparing characteristics of CLD patients with PPHTN to those without PPHTN. Outcomes of interest included prevalence and risk factors for PPHTN. Standard meta-analysis methods were followed using the random-effects model. Treatment effect estimates were expressed as odds ratio (OR) and 95% confidence interval (CI). Heterogeneity was assessed using the I2% statistic.
Results: A total of 44 studies were included, comprising 14,025 CLD patients. These included 19 retrospective cohort, 14 prospective, 8 case-control, and 3 cross-sectional studies. Males comprised 53.1% of the study population. The pooled prevalence of PPHTN on TTE was 10.7% (95% CI 7.3-14.2; I2=94.2%), whereas the pooled prevalence of PPHTN confirmed by RHC was 2% (95% CI 1.3-2.6; I2=86.9%). Patients with PPHTN diagnosed by TTE had significantly higher odds of being female (OR 1.86; 95% CI 1.23-2.81; P=0.003) and having autoimmune hepatitis (AIH) (OR 1.72; 95% CI 1.03-2.88; P=0.002) (Figure 1).
Additionally, features of PPHTN on TTE were significantly associated with higher mean age and INR levels, but lower odds of viral hepatitis and hepatic encephalopathy. Other potential factors showed no statistically significant association (Table 1).
Discussion: This meta-analysis demonstrates that age, female sex, and AIH are significant risk factors for pulmonary hypertension on TTE, a finding suggestive of PPHTN. Lower screening threshold in these populations may aid earlier diagnosis, treatment, and improved outcomes. Although AIH showed a positive trend, no significant risk factors were identified for PPHTN confirmed by RHC. The lack of significance may be due to the small number of RHCs and inherent study limitations.
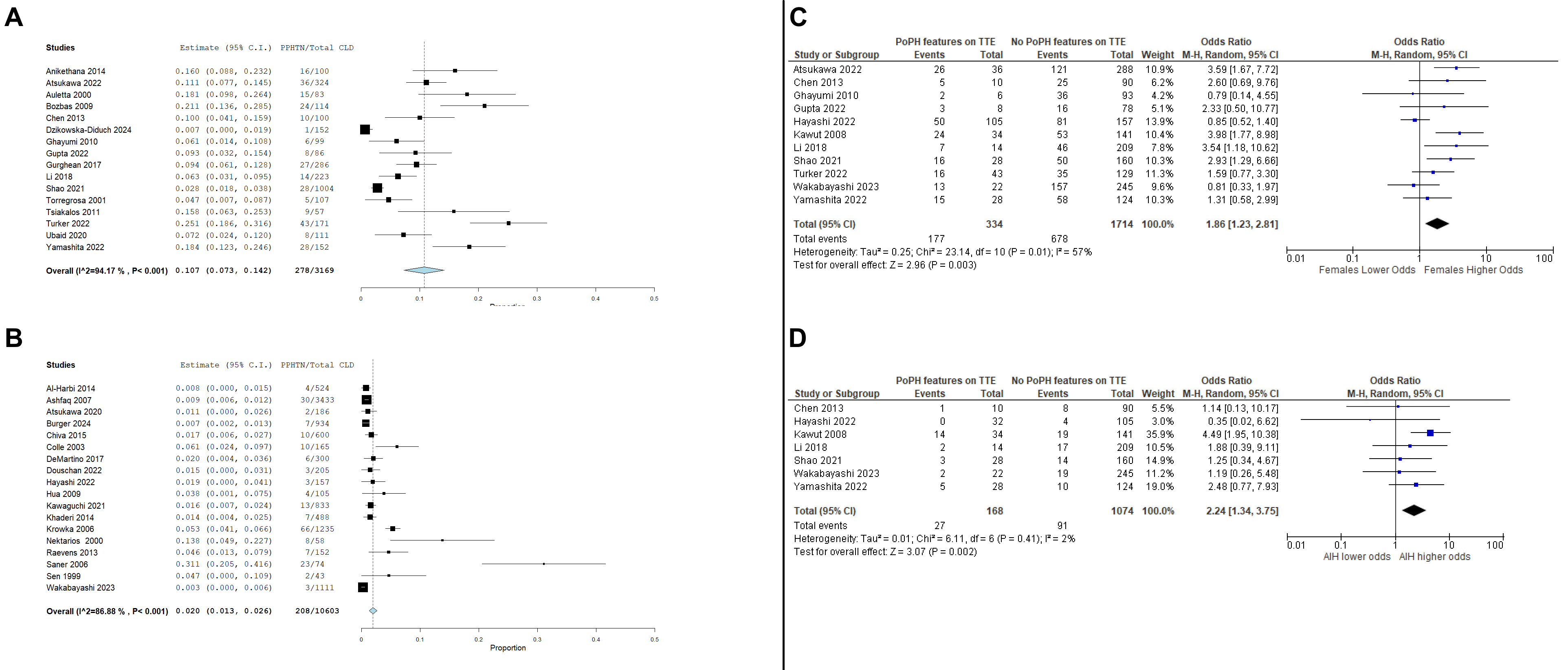
Figure: Figure 1. A – Pooled prevalence of TTE features of PPHTN in CLD. B – Pooled prevalence of PPHTN confirmed by RHC in CLD. C – Odds ratio of female sex in CLD patients with Figure 1. A – Prevalence of TTE features of PPHTN in CLD. B – Prevalence of PPHTN confirmed by RHC in CLD. C – Odds ratio of female sex in CLD patients with TTE features of PPHTN compared to CLD patients without TTE features of PPHTN. D – Odds ratio of autoimmune hepatitis in CLD patients with TTE features of PPHTN compared to CLD patients without TTE features of PPHTN. PPHTN compared to CLD patients without TTE features of PPHTN. D – Odds ratio of autoimmune hepatitis in CLD patients with TTE features of PPHTN compared to CLD patients without TTE features of PPHTN.
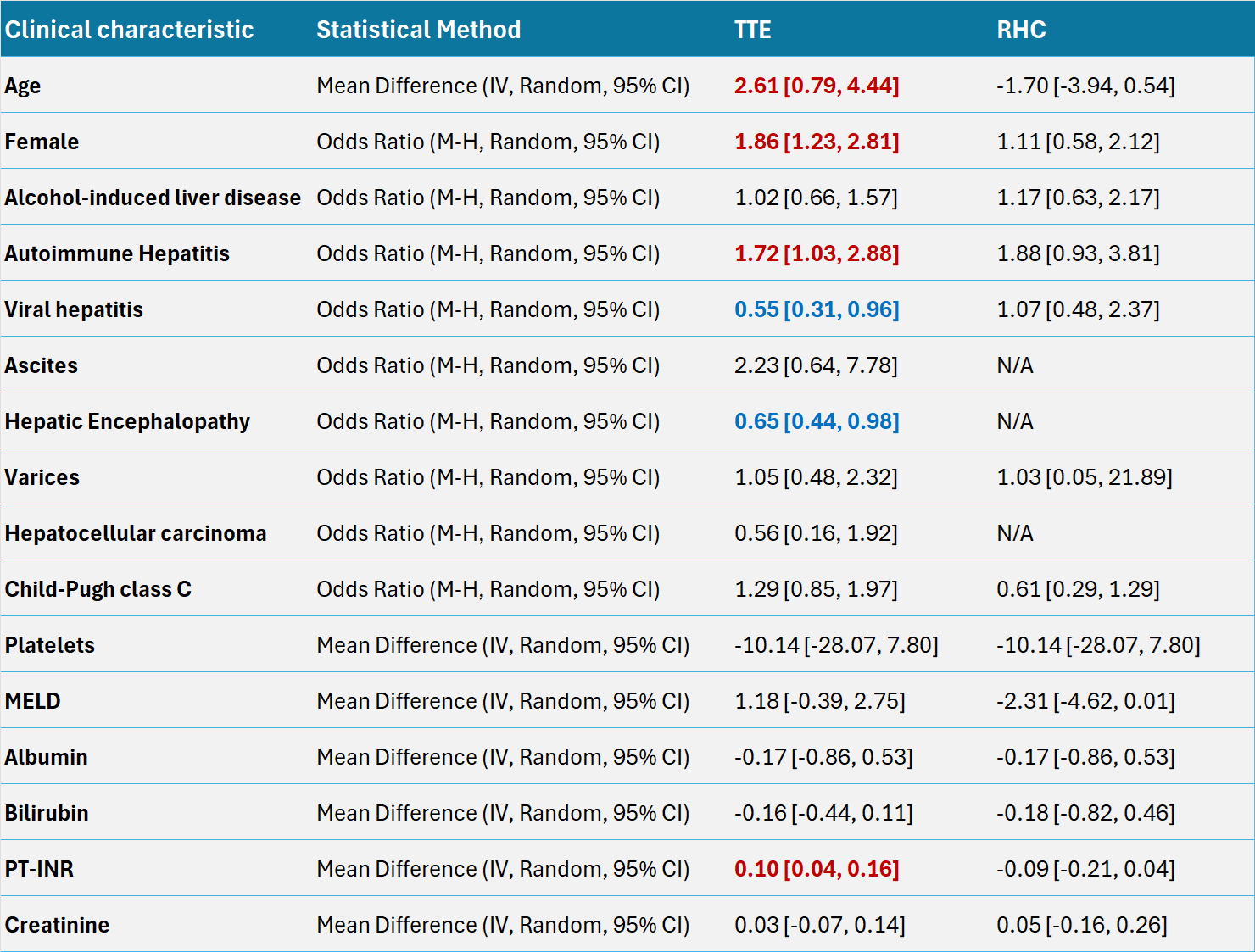
Figure: Table 1. Odds ratios/Mean differences of other demographic, clinical, and laboratory characteristics in CLD patients with and without PPHTN.
OR – Odds ratio, MD – Mean difference
Disclosures:
Tareq Alsaleh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Amir Harb indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Parikshit Chapagain indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Bassel Dakkak indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nihal Khan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohamad Khaled Almujarkesh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ayman Koteish indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Tareq Alsaleh, MD1, Amir Harb, DO1, Parikshit Chapagain, MD1, Bassel Dakkak, MD2, Nihal Khan, MD1, Mohamad Khaled Almujarkesh, MD3, Ayman Koteish, MD4. P3813 - Prevalence and Risk Factors of Portopulmonary Hypertension in Chronic Liver Disease: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Department of Internal Medicine, AdventHealth Orlando, Orlando, FL; 2Marshall University Joan C. Edwards School of Medicine, Huntington, WV; 3Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, AdventHealth Orlando, Orlando, FL; 4Gastroenterology, Transplant Hepatology, AdventHealth Orlando, Orlando, FL
Introduction: Portopulmonary hypertension (PPHTN) is a serious complication of chronic liver disease (CLD), characterized by pulmonary arterial hypertension in the presence of portal hypertension. In patients undergoing liver transplantation, it is associated with higher perioperative mortality, highlighting the significance of its early detection. Diagnostic modalities include transthoracic echocardiogram (TTE) and right heart catheterization (RHC). We conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis to report the prevalence and risk factors for development of PPHTN in CLD.
Methods: A systematic review of the literature from PubMed, EMBASE, Scopus, Web of Science, and Ovid was conducted from inception to April 2025 for studies reporting on PPHTN in CLD patients. We included studies comparing characteristics of CLD patients with PPHTN to those without PPHTN. Outcomes of interest included prevalence and risk factors for PPHTN. Standard meta-analysis methods were followed using the random-effects model. Treatment effect estimates were expressed as odds ratio (OR) and 95% confidence interval (CI). Heterogeneity was assessed using the I2% statistic.
Results: A total of 44 studies were included, comprising 14,025 CLD patients. These included 19 retrospective cohort, 14 prospective, 8 case-control, and 3 cross-sectional studies. Males comprised 53.1% of the study population. The pooled prevalence of PPHTN on TTE was 10.7% (95% CI 7.3-14.2; I2=94.2%), whereas the pooled prevalence of PPHTN confirmed by RHC was 2% (95% CI 1.3-2.6; I2=86.9%). Patients with PPHTN diagnosed by TTE had significantly higher odds of being female (OR 1.86; 95% CI 1.23-2.81; P=0.003) and having autoimmune hepatitis (AIH) (OR 1.72; 95% CI 1.03-2.88; P=0.002) (Figure 1).
Additionally, features of PPHTN on TTE were significantly associated with higher mean age and INR levels, but lower odds of viral hepatitis and hepatic encephalopathy. Other potential factors showed no statistically significant association (Table 1).
Discussion: This meta-analysis demonstrates that age, female sex, and AIH are significant risk factors for pulmonary hypertension on TTE, a finding suggestive of PPHTN. Lower screening threshold in these populations may aid earlier diagnosis, treatment, and improved outcomes. Although AIH showed a positive trend, no significant risk factors were identified for PPHTN confirmed by RHC. The lack of significance may be due to the small number of RHCs and inherent study limitations.

Figure: Figure 1. A – Pooled prevalence of TTE features of PPHTN in CLD. B – Pooled prevalence of PPHTN confirmed by RHC in CLD. C – Odds ratio of female sex in CLD patients with Figure 1. A – Prevalence of TTE features of PPHTN in CLD. B – Prevalence of PPHTN confirmed by RHC in CLD. C – Odds ratio of female sex in CLD patients with TTE features of PPHTN compared to CLD patients without TTE features of PPHTN. D – Odds ratio of autoimmune hepatitis in CLD patients with TTE features of PPHTN compared to CLD patients without TTE features of PPHTN. PPHTN compared to CLD patients without TTE features of PPHTN. D – Odds ratio of autoimmune hepatitis in CLD patients with TTE features of PPHTN compared to CLD patients without TTE features of PPHTN.

Figure: Table 1. Odds ratios/Mean differences of other demographic, clinical, and laboratory characteristics in CLD patients with and without PPHTN.
OR – Odds ratio, MD – Mean difference
Disclosures:
Tareq Alsaleh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Amir Harb indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Parikshit Chapagain indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Bassel Dakkak indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nihal Khan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohamad Khaled Almujarkesh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ayman Koteish indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Tareq Alsaleh, MD1, Amir Harb, DO1, Parikshit Chapagain, MD1, Bassel Dakkak, MD2, Nihal Khan, MD1, Mohamad Khaled Almujarkesh, MD3, Ayman Koteish, MD4. P3813 - Prevalence and Risk Factors of Portopulmonary Hypertension in Chronic Liver Disease: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
