Monday Poster Session
Category: Liver
P3770 - Fibro-GPT: A Large Language Model for Accurate Prediction of Advanced Fibrosis and Hepatic Decompensation in MASLD
Monday, October 27, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Basile Njei, MD, PhD, MPH
VA Connecticut Healthcare System and Yale University
West Haven, CT
Presenting Author(s)
Award: ACG Outstanding Research Award in the Liver Category
Award: ACG Presidential Poster Award
Basile Njei, MD, PhD, MPH1, Nelvis Njei, PharmD, MS2, Ysabel Ilagan-Ying, MD3, Omar Al Ta’ani, MD4, Sarpong Boateng, MD, MPH5, Yazan Al Ajlouni, MD, Mphil6, Bubu Banini, MD, PhD3
1VA Connecticut Healthcare System and Yale University, West Haven, CT; 2Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence, Ellicott City, MD; 3Yale University, New Haven, CT; 4Department of Internal Medicine, Allegheny Health Network, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, USA, Pittsburgh, PA; 5Yale New Haven Health, Bridgeport, CT; 6Montefiore Medical Center, New York, NY
Introduction: Recent advancements in generative artificial intelligence, particularly large language models (LLMs), offer promising avenues for enhancing the clinical prediction of advanced fibrosis (F3 or higher) in patients with metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD). We developed Fibro-GPT, a generative pre-trained transformer (GPT)-4-based LLM model, fine-tuned for structured medical data, to enhance detection of advanced fibrosis and assessed its prognostic value for incident hepatic decompensation.
Methods: Fibro-GPT was developed using NHANES 2017–2020 data from adults with MASLD (Table), including variables such as age, platelet count, HbA1c, eGFR, BMI, AST, and ALT. Inputs were formatted into standardized text prompts and analyzed via a secure Python interface, generating (1) a numerical risk estimate and (2) an explanatory summary. Fibrosis stage was determined using a two-step method: blood-based (FIB-4) followed by vibration-controlled transient elastography (VCTE). Fibro-GPT was trained on 162 MASLD cases and externally validated on 105 biopsy-confirmed MASLD patients, using liver histopathology as the reference standard. Predictive performance for 5-year incident hepatic decompensation was assessed in an additional 337 biopsy-confirmed MASLD patients. To evaluate the economic impact, we modeled a U.S. population-wide screening scenario comparing Fibro-GPT to FIB-4 as a first-line tool for detecting advanced fibrosis in MASLD.
Results: Fibro-GPT achieved an AUROC of 0.91 in the derivation cohort, with 84% sensitivity and 86% specificity, significantly outperforming FIB-4 (AUROC 0.62; P < 0.001). Validation on biopsy-confirmed cases showed sustained performance (AUROC 0.90 vs. FIB-4 AUROC 0.75; P < 0.001). For predicting 5-year incident hepatic decompensation, Fibro-GPT achieved AUROC 0.85, with 91% sensitivity and 67% specificity (Figure). Cost analysis revealed that Fibro-GPT’s superior accuracy resulted in a 25% reduction in unnecessary VCTEs and an 18% reduction in liver biopsies compared to FIB-4, translating into estimated annual savings of $150-200 million in the U.S.
Discussion: Fibro-GPT is a highly accurate, LLM-based tool that significantly improves detection of advanced fibrosis and predicts hepatic decompensation in MASLD. Its superior performance, interpretability, and potential cost savings underscore its value for integration into clinical workflows to improve risk stratification and management in MASLD patients.
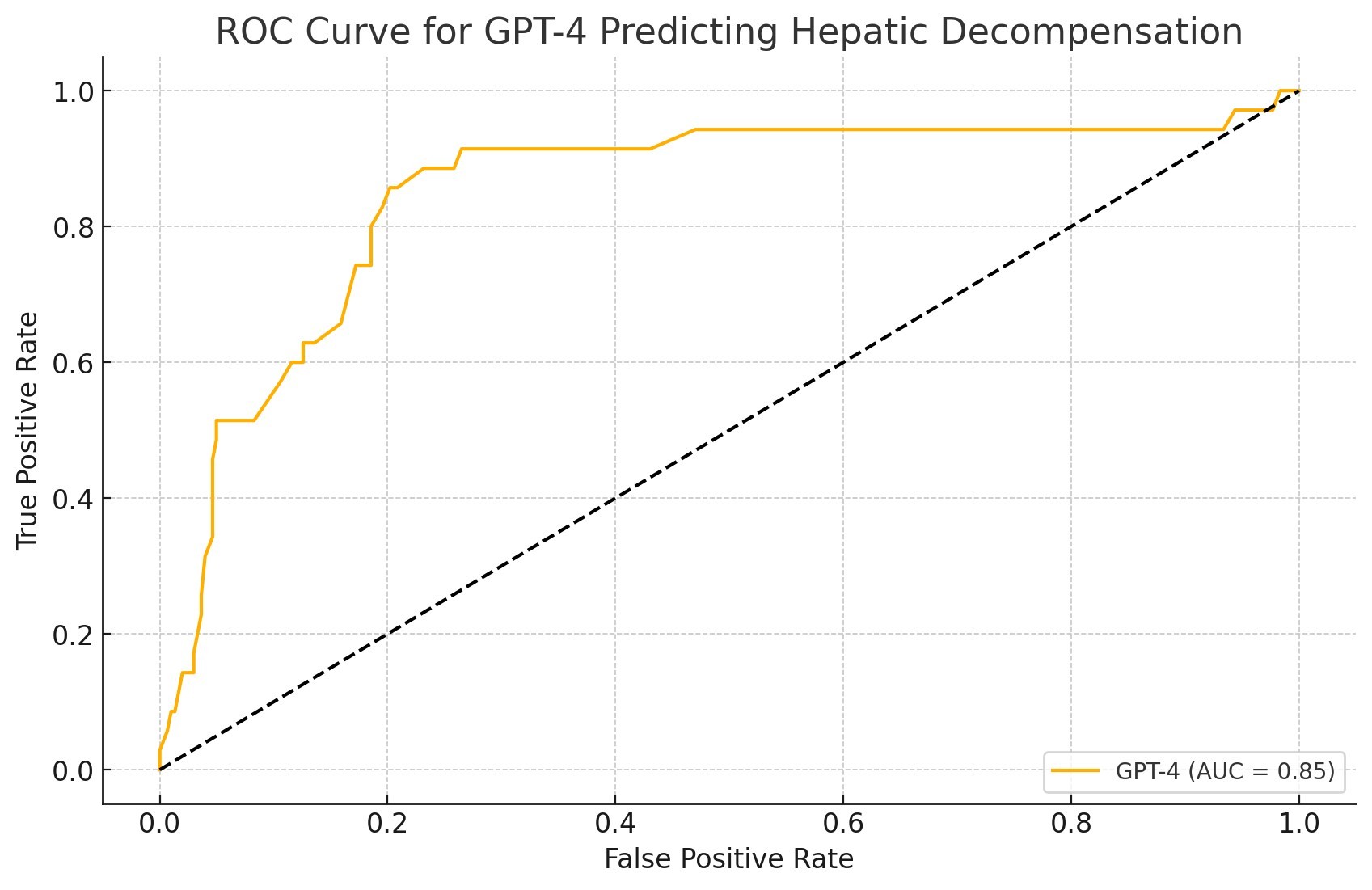
Figure: Baseline Characteristics of Participants in the Derivation Cohort (NHANES 2017-2020)
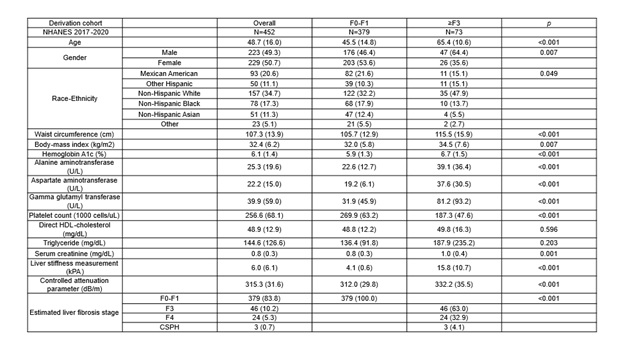
Figure: ROC curve for Fibro-GPT for prediction of 5-year hepatic decompensation in biopsy-confirmed MASLD.
Disclosures:
Basile Njei indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nelvis Njei indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ysabel Ilagan-Ying indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Omar Al Ta’ani indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sarpong Boateng indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Yazan Al Ajlouni indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Bubu Banini indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Basile Njei, MD, PhD, MPH1, Nelvis Njei, PharmD, MS2, Ysabel Ilagan-Ying, MD3, Omar Al Ta’ani, MD4, Sarpong Boateng, MD, MPH5, Yazan Al Ajlouni, MD, Mphil6, Bubu Banini, MD, PhD3. P3770 - Fibro-GPT: A Large Language Model for Accurate Prediction of Advanced Fibrosis and Hepatic Decompensation in MASLD, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
Award: ACG Presidential Poster Award
Basile Njei, MD, PhD, MPH1, Nelvis Njei, PharmD, MS2, Ysabel Ilagan-Ying, MD3, Omar Al Ta’ani, MD4, Sarpong Boateng, MD, MPH5, Yazan Al Ajlouni, MD, Mphil6, Bubu Banini, MD, PhD3
1VA Connecticut Healthcare System and Yale University, West Haven, CT; 2Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence, Ellicott City, MD; 3Yale University, New Haven, CT; 4Department of Internal Medicine, Allegheny Health Network, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, USA, Pittsburgh, PA; 5Yale New Haven Health, Bridgeport, CT; 6Montefiore Medical Center, New York, NY
Introduction: Recent advancements in generative artificial intelligence, particularly large language models (LLMs), offer promising avenues for enhancing the clinical prediction of advanced fibrosis (F3 or higher) in patients with metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD). We developed Fibro-GPT, a generative pre-trained transformer (GPT)-4-based LLM model, fine-tuned for structured medical data, to enhance detection of advanced fibrosis and assessed its prognostic value for incident hepatic decompensation.
Methods: Fibro-GPT was developed using NHANES 2017–2020 data from adults with MASLD (Table), including variables such as age, platelet count, HbA1c, eGFR, BMI, AST, and ALT. Inputs were formatted into standardized text prompts and analyzed via a secure Python interface, generating (1) a numerical risk estimate and (2) an explanatory summary. Fibrosis stage was determined using a two-step method: blood-based (FIB-4) followed by vibration-controlled transient elastography (VCTE). Fibro-GPT was trained on 162 MASLD cases and externally validated on 105 biopsy-confirmed MASLD patients, using liver histopathology as the reference standard. Predictive performance for 5-year incident hepatic decompensation was assessed in an additional 337 biopsy-confirmed MASLD patients. To evaluate the economic impact, we modeled a U.S. population-wide screening scenario comparing Fibro-GPT to FIB-4 as a first-line tool for detecting advanced fibrosis in MASLD.
Results: Fibro-GPT achieved an AUROC of 0.91 in the derivation cohort, with 84% sensitivity and 86% specificity, significantly outperforming FIB-4 (AUROC 0.62; P < 0.001). Validation on biopsy-confirmed cases showed sustained performance (AUROC 0.90 vs. FIB-4 AUROC 0.75; P < 0.001). For predicting 5-year incident hepatic decompensation, Fibro-GPT achieved AUROC 0.85, with 91% sensitivity and 67% specificity (Figure). Cost analysis revealed that Fibro-GPT’s superior accuracy resulted in a 25% reduction in unnecessary VCTEs and an 18% reduction in liver biopsies compared to FIB-4, translating into estimated annual savings of $150-200 million in the U.S.
Discussion: Fibro-GPT is a highly accurate, LLM-based tool that significantly improves detection of advanced fibrosis and predicts hepatic decompensation in MASLD. Its superior performance, interpretability, and potential cost savings underscore its value for integration into clinical workflows to improve risk stratification and management in MASLD patients.

Figure: Baseline Characteristics of Participants in the Derivation Cohort (NHANES 2017-2020)

Figure: ROC curve for Fibro-GPT for prediction of 5-year hepatic decompensation in biopsy-confirmed MASLD.
Disclosures:
Basile Njei indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nelvis Njei indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ysabel Ilagan-Ying indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Omar Al Ta’ani indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sarpong Boateng indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Yazan Al Ajlouni indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Bubu Banini indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Basile Njei, MD, PhD, MPH1, Nelvis Njei, PharmD, MS2, Ysabel Ilagan-Ying, MD3, Omar Al Ta’ani, MD4, Sarpong Boateng, MD, MPH5, Yazan Al Ajlouni, MD, Mphil6, Bubu Banini, MD, PhD3. P3770 - Fibro-GPT: A Large Language Model for Accurate Prediction of Advanced Fibrosis and Hepatic Decompensation in MASLD, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.

