Monday Poster Session
Category: Liver
P3751 - Impact of Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt (TIPS) vs Repeated Thoracocentesis on Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Hepatic Hydrothorax: A Retrospective Propensity-Matched Cohort Study
Monday, October 27, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Shefali Mody, MBBS (she/her/hers)
SUNY Upstate Medical University Hospital
Syracuse, NY
Presenting Author(s)
Shefali Mody, MBBS1, Azhar Hussain, MBBS1, Chidera Onwuzo, MBBS1, Avneet Kaur, MBBS1, Sushrut Ingawale, MD, DNB, MBBS2, Akanksha Togra, MD3, Aashay Dharia, MD4, Kalsoom Khalil, MBBS5, Ali Jaan, MD6, Umar Hayat, MD7, Jivan Lamichhane, MD1
1SUNY Upstate Medical University Hospital, Syracuse, NY; 2Quinnipiac University - Frank H Netter MD School of Medicine, Bridgeport, CT; 3Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center, El Paso, El Paso, TX; 4Brooklyn Hospital Center, Brooklyn, NY; 5Ameer Ud Din Medical College, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan; 6Unity Hospital, Rochester, NY; 7Geisinger Wyoming Valley Medical Center, Wilkes-Barre, PA
Introduction: Hepatic hydrothorax (HH) is a debilitating complication of advanced liver cirrhosis, often necessitating invasive interventions due to resistance to conventional medical therapies. While transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) has established efficacy in managing HH, repeated thoracentesis is more commonly used. This is largely due to lack of comparative safety and efficacy data on infection risk, impact on renal function, and hepatic encephalopathy. Our study aims to evaluate the impact of TIPS versus repeated thoracocentesis on these outcomes in patients with HH.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective 1:1 propensity-matched cohort study using US population based data from the TRINETX network including patients aged ≥ 18 years with HH and liver cirrhosis of any etiology. We excluded patients with CHF, nephrotic syndrome, CKD and pleural effusion due to other causes. Patients were divided into two cohorts: HH treated with TIPS, and HH treated with repeated thoracentesis (defined as ≥ 4 thoracenteses in 2 months). Multivariate regression analysis was employed to assess primary outcomes, including dehydration, sepsis, severe sepsis, septic shock, hepatic encephalopathy, acute kidney injury (AKI), hyponatremia, pneumothorax, and empyema within three months. Secondary outcomes like liver transplantation (LT) and spontaneous bacterial peritonitis (SBP) were also analyzed. 1:1 propensity matching was performed on variables such as demographics, use of medications (diuretics) and laboratory parameters to reduce confounding. Odds ratios and 95% CI were reported
Results: Propensity matched cohort analysis showed that patients treated with TIPS had a significantly lower incidence of developing sepsis(OR 0.473, 95% CI: 0.314–0.711), AKI(OR 0.515, 95% CI: 0.356–0.745), hyponatremia(OR 0.413, 95% CI: 0.194–0.880), pneumothorax(OR 0.257, 95% CI: 0.151–0.438), empyema (OR 0.293, 95% CI: 0.142–0.604), SBP(OR 0.497, 95% CI: 0.282–0.862), and need for LT (OR 0.374, 95% CI: 0.242–0.576) than those treated with repeated thoracentesis. However TIPS-treated patients had a significantly higher risk of hepatic encephalopathy (OR 2.031, 95% CI: 1.368–3.016).
Discussion: TIPS demonstrated significant benefits over repeated thoracentesis as it was associated with a lower risk of sepsis, AKI, hyponatremia, pneumothorax, empyema, SBP and need for LT in patients with HH. However the increased risk of hepatic encephalopathy associated with TIPS warrants careful patient selection and close monitoring.
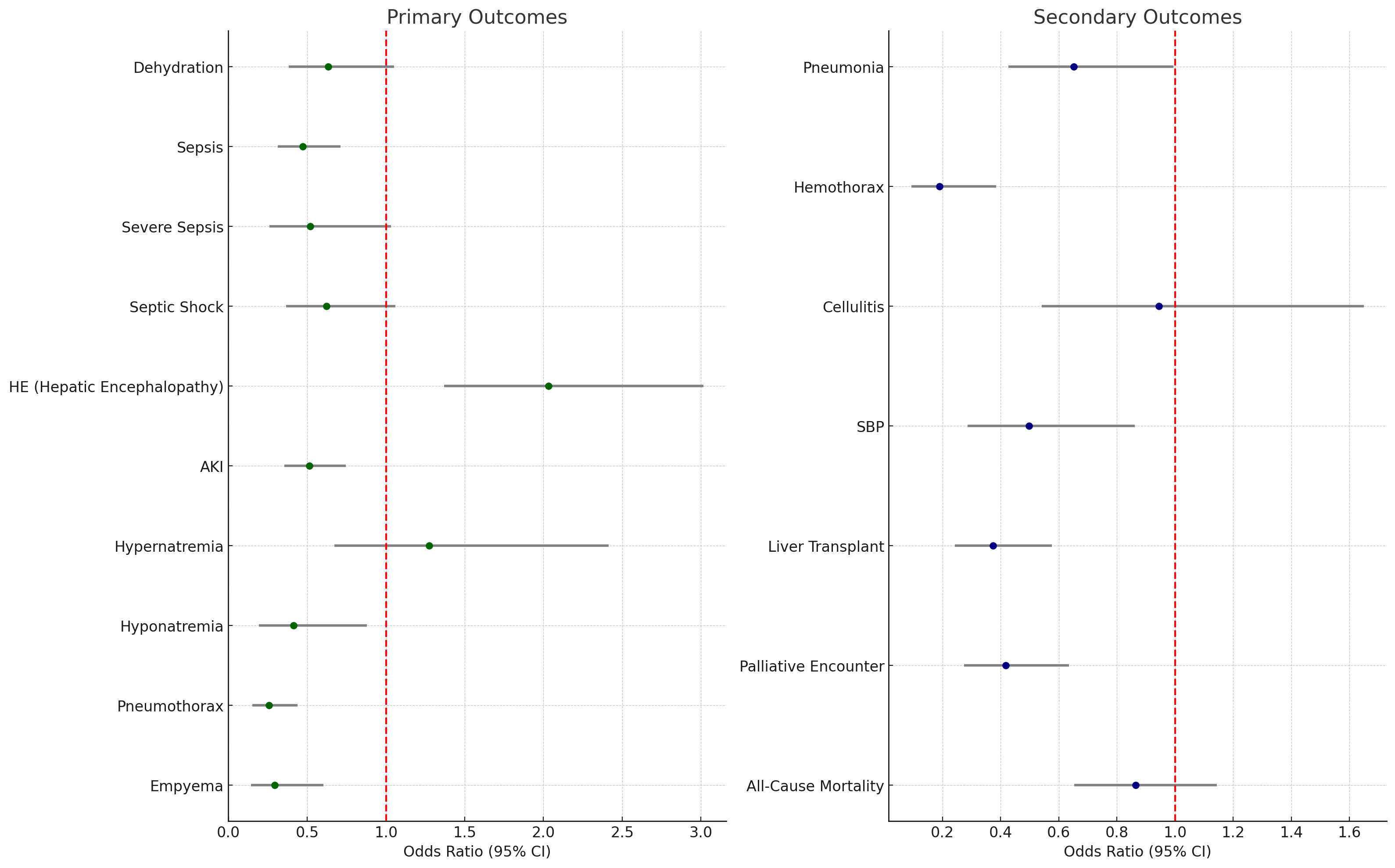
Figure: Table 1: Comparison of primary and secondary outcomes in hepatic hydrothorax patients treated with transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) vs. repeated thoracentesis
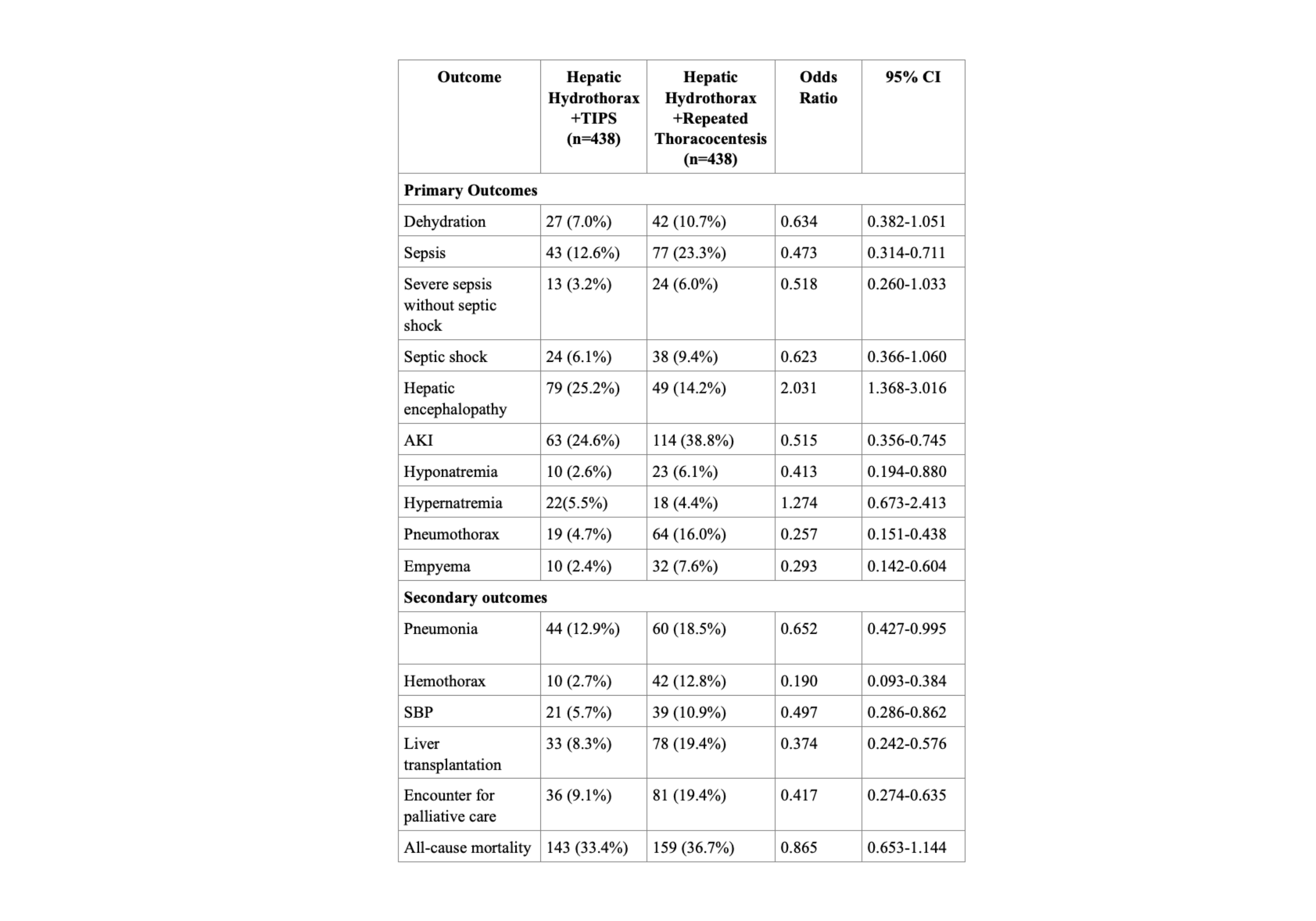
Figure: Figure 1: Forest plot comparing odds ratios for primary and secondary outcomes in hepatic hydrothorax patients treated with transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) vs. repeated thoracentesis
Disclosures:
Shefali Mody indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Azhar Hussain indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Chidera Onwuzo indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Avneet Kaur indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sushrut Ingawale indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Akanksha Togra indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Aashay Dharia indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kalsoom Khalil indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ali Jaan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Umar Hayat indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jivan Lamichhane indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Shefali Mody, MBBS1, Azhar Hussain, MBBS1, Chidera Onwuzo, MBBS1, Avneet Kaur, MBBS1, Sushrut Ingawale, MD, DNB, MBBS2, Akanksha Togra, MD3, Aashay Dharia, MD4, Kalsoom Khalil, MBBS5, Ali Jaan, MD6, Umar Hayat, MD7, Jivan Lamichhane, MD1. P3751 - Impact of Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt (TIPS) vs Repeated Thoracocentesis on Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Hepatic Hydrothorax: A Retrospective Propensity-Matched Cohort Study, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1SUNY Upstate Medical University Hospital, Syracuse, NY; 2Quinnipiac University - Frank H Netter MD School of Medicine, Bridgeport, CT; 3Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center, El Paso, El Paso, TX; 4Brooklyn Hospital Center, Brooklyn, NY; 5Ameer Ud Din Medical College, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan; 6Unity Hospital, Rochester, NY; 7Geisinger Wyoming Valley Medical Center, Wilkes-Barre, PA
Introduction: Hepatic hydrothorax (HH) is a debilitating complication of advanced liver cirrhosis, often necessitating invasive interventions due to resistance to conventional medical therapies. While transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) has established efficacy in managing HH, repeated thoracentesis is more commonly used. This is largely due to lack of comparative safety and efficacy data on infection risk, impact on renal function, and hepatic encephalopathy. Our study aims to evaluate the impact of TIPS versus repeated thoracocentesis on these outcomes in patients with HH.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective 1:1 propensity-matched cohort study using US population based data from the TRINETX network including patients aged ≥ 18 years with HH and liver cirrhosis of any etiology. We excluded patients with CHF, nephrotic syndrome, CKD and pleural effusion due to other causes. Patients were divided into two cohorts: HH treated with TIPS, and HH treated with repeated thoracentesis (defined as ≥ 4 thoracenteses in 2 months). Multivariate regression analysis was employed to assess primary outcomes, including dehydration, sepsis, severe sepsis, septic shock, hepatic encephalopathy, acute kidney injury (AKI), hyponatremia, pneumothorax, and empyema within three months. Secondary outcomes like liver transplantation (LT) and spontaneous bacterial peritonitis (SBP) were also analyzed. 1:1 propensity matching was performed on variables such as demographics, use of medications (diuretics) and laboratory parameters to reduce confounding. Odds ratios and 95% CI were reported
Results: Propensity matched cohort analysis showed that patients treated with TIPS had a significantly lower incidence of developing sepsis(OR 0.473, 95% CI: 0.314–0.711), AKI(OR 0.515, 95% CI: 0.356–0.745), hyponatremia(OR 0.413, 95% CI: 0.194–0.880), pneumothorax(OR 0.257, 95% CI: 0.151–0.438), empyema (OR 0.293, 95% CI: 0.142–0.604), SBP(OR 0.497, 95% CI: 0.282–0.862), and need for LT (OR 0.374, 95% CI: 0.242–0.576) than those treated with repeated thoracentesis. However TIPS-treated patients had a significantly higher risk of hepatic encephalopathy (OR 2.031, 95% CI: 1.368–3.016).
Discussion: TIPS demonstrated significant benefits over repeated thoracentesis as it was associated with a lower risk of sepsis, AKI, hyponatremia, pneumothorax, empyema, SBP and need for LT in patients with HH. However the increased risk of hepatic encephalopathy associated with TIPS warrants careful patient selection and close monitoring.

Figure: Table 1: Comparison of primary and secondary outcomes in hepatic hydrothorax patients treated with transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) vs. repeated thoracentesis

Figure: Figure 1: Forest plot comparing odds ratios for primary and secondary outcomes in hepatic hydrothorax patients treated with transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) vs. repeated thoracentesis
Disclosures:
Shefali Mody indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Azhar Hussain indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Chidera Onwuzo indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Avneet Kaur indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sushrut Ingawale indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Akanksha Togra indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Aashay Dharia indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kalsoom Khalil indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ali Jaan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Umar Hayat indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jivan Lamichhane indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Shefali Mody, MBBS1, Azhar Hussain, MBBS1, Chidera Onwuzo, MBBS1, Avneet Kaur, MBBS1, Sushrut Ingawale, MD, DNB, MBBS2, Akanksha Togra, MD3, Aashay Dharia, MD4, Kalsoom Khalil, MBBS5, Ali Jaan, MD6, Umar Hayat, MD7, Jivan Lamichhane, MD1. P3751 - Impact of Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt (TIPS) vs Repeated Thoracocentesis on Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Hepatic Hydrothorax: A Retrospective Propensity-Matched Cohort Study, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
