Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Biliary/Pancreas
P4428 - Stabilizing Mirizzi Syndrome With ERCP: Endoscopic Management as a Bridge to Delayed Cholecystectomy
Tuesday, October 28, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Hasan Jaber, MD (he/him/his)
University of Kansas School of Medicine
Wichita, KS
Presenting Author(s)
Hasan Jaber, MD1, Mahmoud Mahdi, MD1, Matthew Hoang, BS1, Nader Al Souky, MD1, David Maundu, MBChB, MSc-HCM, MSc-ID2, Janane Nasr, MD1, Thao Nguyen, DO1, W. Ransom. Kilgore, MD3
1University of Kansas School of Medicine, Wichita, KS; 2KU School of Medicine-Wichita, Wichita, KS; 3Ascension Saint Francis Hospital, Wichita, KS
Introduction: Mirizzi Syndrome (MS) is a rare complication of cholelithiasis, affecting 0.1% of the 20 million individuals with gallstones in the U.S. It is characterized by obstruction of the common hepatic or bile duct due to external compression from impacted gallstones in the cystic duct or gallbladder infundibulum. Clinically, patients present with obstructive jaundice and abdominal pain, which may mimic other conditions like choledocholithiasis or ascending cholangitis. MS is associated with gallbladder cancer in over 25% of cases.
Case Description/
Methods: A 40-year-old male with a history of alcohol use disorder, hemochromatosis, and cirrhosis presented with nausea, vomiting, pruritus, and worsening jaundice. ALP 349 U/L, AST 120 U/L, ALT 228 U/L, total bilirubin 5.5 mg/dL, WBC 12.4 ×10⁹/L. Hepatitis panel was negative. Abdominal ultrasound showed gallstones without acute cholecystitis and a dilated common bile duct (CBD). Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) showed mild intrahepatic ductal dilation and a hypointense filling defect in the gallbladder neck/cystic duct consistent with an impacted stone, causing extrinsic compression of the common hepatic duct and 7.28 mm dilated CBD (Figure 1). Surgery was initially planned but aborted due to severe inflammation and omental adhesions. Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) revealed a 2 cm stenosis of the common hepatic duct and failure of gallbladder filling (Figure 2). Sphincterotomy, biliary brushings, and placement of an 8.5 Fr x 9 cm biliary stent were performed. The patient experienced clinical improvement with resolution of symptoms and downtrending bilirubin levels. Pathology was negative for malignancy. Given ongoing biliary pathology and risk for recurrent obstruction, the patient was scheduled for robotic-assisted cholecystectomy following resolution of inflammation and stabilization with stenting.
Discussion: MS is a rare cause of obstructive jaundice and should be considered in patients with gallstones and biliary obstruction. With a potential malignancy rate up to 28%, thorough imaging and tissue evaluation are essential. Diagnosis is typically confirmed via imaging modalities like MRCP or ERCP. Surgical management is challenging due to inflammation around the gallbladder neck, increasing the risk of bile duct injury during laparoscopic procedures. As seen in this case, endoscopic management with ERCP can provide symptomatic relief and diagnostic clarification in patients not suitable for immediate surgery.
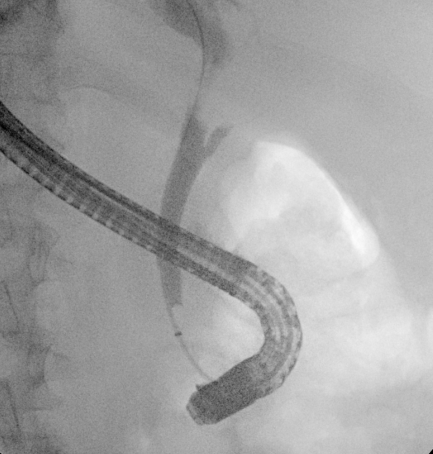
Figure: 7.28 mm Dilated CBD Found on MRCP
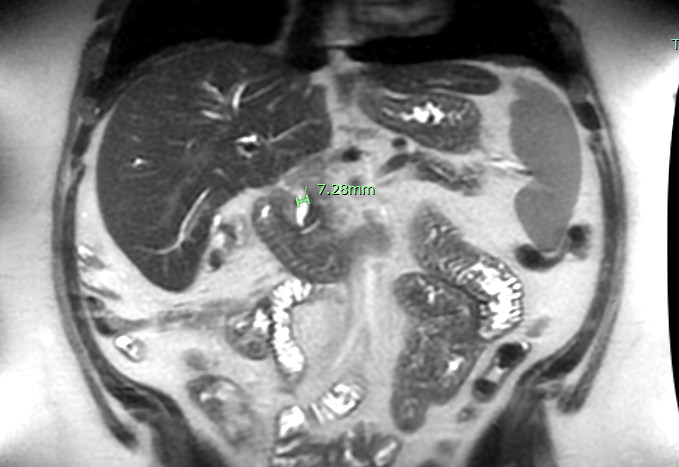
Figure: Stenosis of the Common Hepatic Duct and Failure of Gallbladder Filling Seen on ERCP
Disclosures:
Hasan Jaber indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mahmoud Mahdi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Matthew Hoang indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nader Al Souky indicated no relevant financial relationships.
David Maundu indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Janane Nasr indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Thao Nguyen indicated no relevant financial relationships.
W. Kilgore: Vanda Pharmaceuticals – Grant/Research Support.
Hasan Jaber, MD1, Mahmoud Mahdi, MD1, Matthew Hoang, BS1, Nader Al Souky, MD1, David Maundu, MBChB, MSc-HCM, MSc-ID2, Janane Nasr, MD1, Thao Nguyen, DO1, W. Ransom. Kilgore, MD3. P4428 - Stabilizing Mirizzi Syndrome With ERCP: Endoscopic Management as a Bridge to Delayed Cholecystectomy, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1University of Kansas School of Medicine, Wichita, KS; 2KU School of Medicine-Wichita, Wichita, KS; 3Ascension Saint Francis Hospital, Wichita, KS
Introduction: Mirizzi Syndrome (MS) is a rare complication of cholelithiasis, affecting 0.1% of the 20 million individuals with gallstones in the U.S. It is characterized by obstruction of the common hepatic or bile duct due to external compression from impacted gallstones in the cystic duct or gallbladder infundibulum. Clinically, patients present with obstructive jaundice and abdominal pain, which may mimic other conditions like choledocholithiasis or ascending cholangitis. MS is associated with gallbladder cancer in over 25% of cases.
Case Description/
Methods: A 40-year-old male with a history of alcohol use disorder, hemochromatosis, and cirrhosis presented with nausea, vomiting, pruritus, and worsening jaundice. ALP 349 U/L, AST 120 U/L, ALT 228 U/L, total bilirubin 5.5 mg/dL, WBC 12.4 ×10⁹/L. Hepatitis panel was negative. Abdominal ultrasound showed gallstones without acute cholecystitis and a dilated common bile duct (CBD). Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) showed mild intrahepatic ductal dilation and a hypointense filling defect in the gallbladder neck/cystic duct consistent with an impacted stone, causing extrinsic compression of the common hepatic duct and 7.28 mm dilated CBD (Figure 1). Surgery was initially planned but aborted due to severe inflammation and omental adhesions. Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) revealed a 2 cm stenosis of the common hepatic duct and failure of gallbladder filling (Figure 2). Sphincterotomy, biliary brushings, and placement of an 8.5 Fr x 9 cm biliary stent were performed. The patient experienced clinical improvement with resolution of symptoms and downtrending bilirubin levels. Pathology was negative for malignancy. Given ongoing biliary pathology and risk for recurrent obstruction, the patient was scheduled for robotic-assisted cholecystectomy following resolution of inflammation and stabilization with stenting.
Discussion: MS is a rare cause of obstructive jaundice and should be considered in patients with gallstones and biliary obstruction. With a potential malignancy rate up to 28%, thorough imaging and tissue evaluation are essential. Diagnosis is typically confirmed via imaging modalities like MRCP or ERCP. Surgical management is challenging due to inflammation around the gallbladder neck, increasing the risk of bile duct injury during laparoscopic procedures. As seen in this case, endoscopic management with ERCP can provide symptomatic relief and diagnostic clarification in patients not suitable for immediate surgery.

Figure: 7.28 mm Dilated CBD Found on MRCP

Figure: Stenosis of the Common Hepatic Duct and Failure of Gallbladder Filling Seen on ERCP
Disclosures:
Hasan Jaber indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mahmoud Mahdi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Matthew Hoang indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nader Al Souky indicated no relevant financial relationships.
David Maundu indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Janane Nasr indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Thao Nguyen indicated no relevant financial relationships.
W. Kilgore: Vanda Pharmaceuticals – Grant/Research Support.
Hasan Jaber, MD1, Mahmoud Mahdi, MD1, Matthew Hoang, BS1, Nader Al Souky, MD1, David Maundu, MBChB, MSc-HCM, MSc-ID2, Janane Nasr, MD1, Thao Nguyen, DO1, W. Ransom. Kilgore, MD3. P4428 - Stabilizing Mirizzi Syndrome With ERCP: Endoscopic Management as a Bridge to Delayed Cholecystectomy, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
