Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Esophagus
P4889 - Development and Validation of Predictive Models for Pathological Complete Response in Esophageal Adenocarcinoma Patients Receiving Neoadjuvant Chemoradiotherapy: A Decision Curve Analysis
Tuesday, October 28, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Woo Joo Lee, MD
AdventHealth Sebring
Sebring, FL
Presenting Author(s)
Woo Joo Lee, MD1, Muhammad Sohaib Asghar, MBBS1, Seon Hye Won, MD2, Abuoma Cherry Ekpendu, DO3, Marco Braaten, MD4, Pankajkumar Patel, MD5, Thomas Shimshak, MD6
1AdventHealth Sebring, Sebring, FL; 2Department of Family Medicine, Dongguk University Ilsan Hospital, Sebring, FL; 3ADVENTHEALTH SEBRING, Sebring, FL; 4Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis, St. Louis, MO; 5AdventHealth Sebring Department of Gastroenterology, Sebring, FL; 6AdventHealth, Sebring, FL
Introduction: Identifying esophageal adenocarcinoma (EAC) patients likely to achieve pathological complete response (pCR) after neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy (nCRT) could refine treatment strategies, potentially identifying candidates for organ preservation. We developed advanced predictive models for pCR and identified key predictive factors.
Methods: Data from 9,065 EAC patients (Stage I-III, cM0) treated with nCRT and esophagectomy (2018-2021) were extracted from the National Cancer Database (NCDB). Features included demographics, comorbidities, clinical stage, tumor grade, histology, lymphovascular invasion, RT dose, chemotherapy type, and diagnosis-to-surgery interval. Multi-Layer Perceptron (MLP), XGBoost, and logistic regression models were developed. Predictive accuracy was assessed by AUC and Brier score, and key predictive features were identified.
Results: The pCR rate was 19.7% (N=1,813 in test set). Both XGBoost and MLP models achieved an Area Under the Curve (AUC) of 0.715, outperforming logistic regression (AUC 0.707). XGBoost demonstrated superior calibration, as indicated by a lower Brier score (0.144), compared to MLP (Brier score 0.221) and Logistic Regression (Brier score 0.220). Using model-specific importance measures, lymphovascular invasion (LVI) status consistently ranked as a top predictor across all models. Other leading predictors for the MLP model included interval to surgery and positive clinical N-stage. For XGBoost, clinical T-stage (cT2) and a specific insurance type were prominent. Logistic regression's top contributors, aside from LVI, included diagnostic confirmation methods, median income quartile, and urban/rural classification.
Discussion: Advanced machine learning models, especially XGBoost, accurately predict pCR in EAC patients post-nCRT and demonstrate potential clinical utility. Identified predictors such as lymphovascular invasion, clinical stage, and treatment characteristics offer insights into patient subgroups with differing response likelihoods. If prospectively validated, these models could aid in shared decision-making and tailoring therapy.
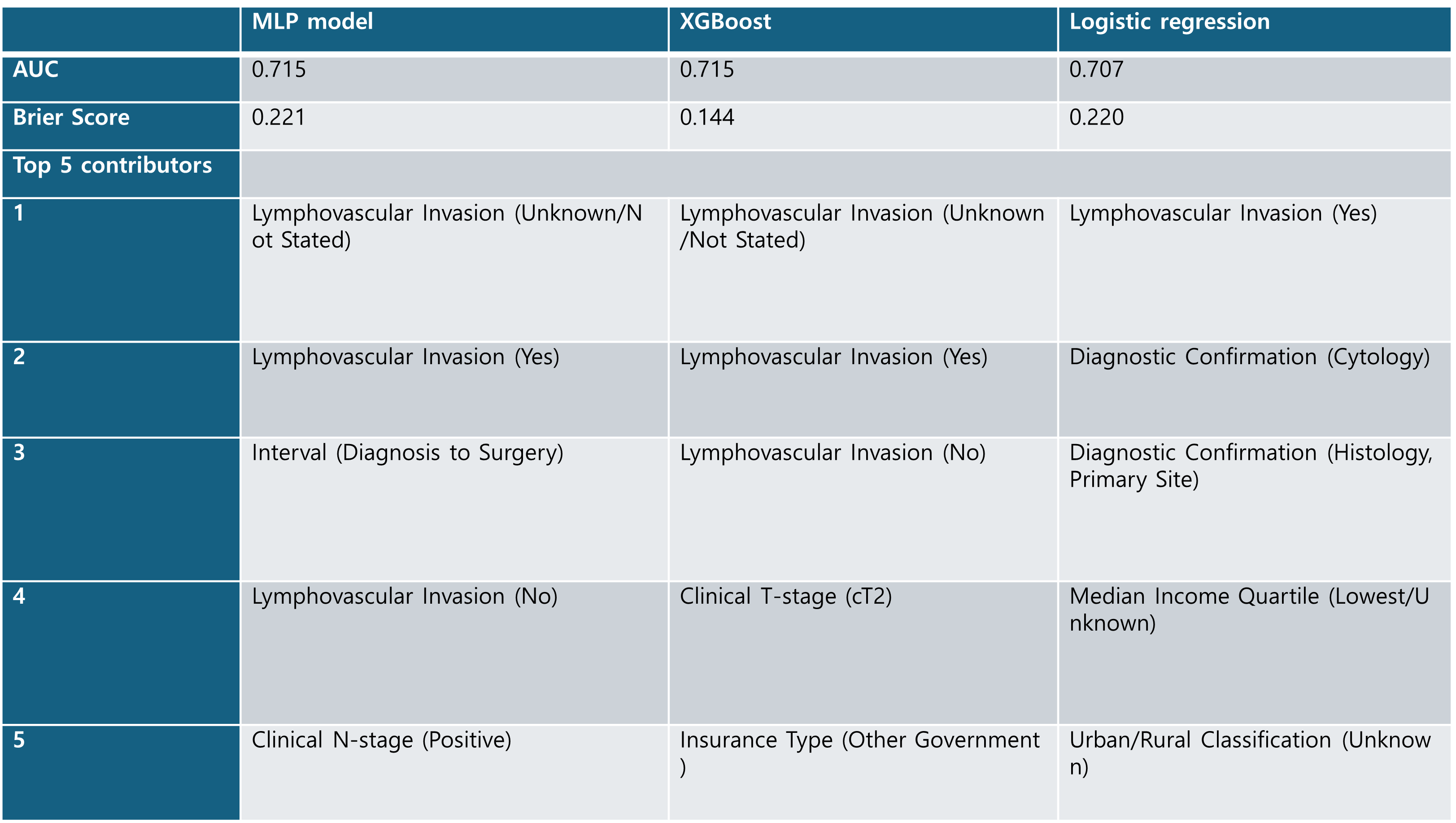
Figure: Table 1. Performance metrics (AUC, Brier Score) and top 5 predictors for the Multi-Layer Perceptron (MLP), XGBoost, and Logistic Regression models.
Disclosures:
Woo Joo Lee indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Sohaib Asghar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Seon Hye Won indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Abuoma Cherry Ekpendu indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Marco Braaten indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Pankajkumar Patel indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Thomas Shimshak indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Woo Joo Lee, MD1, Muhammad Sohaib Asghar, MBBS1, Seon Hye Won, MD2, Abuoma Cherry Ekpendu, DO3, Marco Braaten, MD4, Pankajkumar Patel, MD5, Thomas Shimshak, MD6. P4889 - Development and Validation of Predictive Models for Pathological Complete Response in Esophageal Adenocarcinoma Patients Receiving Neoadjuvant Chemoradiotherapy: A Decision Curve Analysis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1AdventHealth Sebring, Sebring, FL; 2Department of Family Medicine, Dongguk University Ilsan Hospital, Sebring, FL; 3ADVENTHEALTH SEBRING, Sebring, FL; 4Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis, St. Louis, MO; 5AdventHealth Sebring Department of Gastroenterology, Sebring, FL; 6AdventHealth, Sebring, FL
Introduction: Identifying esophageal adenocarcinoma (EAC) patients likely to achieve pathological complete response (pCR) after neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy (nCRT) could refine treatment strategies, potentially identifying candidates for organ preservation. We developed advanced predictive models for pCR and identified key predictive factors.
Methods: Data from 9,065 EAC patients (Stage I-III, cM0) treated with nCRT and esophagectomy (2018-2021) were extracted from the National Cancer Database (NCDB). Features included demographics, comorbidities, clinical stage, tumor grade, histology, lymphovascular invasion, RT dose, chemotherapy type, and diagnosis-to-surgery interval. Multi-Layer Perceptron (MLP), XGBoost, and logistic regression models were developed. Predictive accuracy was assessed by AUC and Brier score, and key predictive features were identified.
Results: The pCR rate was 19.7% (N=1,813 in test set). Both XGBoost and MLP models achieved an Area Under the Curve (AUC) of 0.715, outperforming logistic regression (AUC 0.707). XGBoost demonstrated superior calibration, as indicated by a lower Brier score (0.144), compared to MLP (Brier score 0.221) and Logistic Regression (Brier score 0.220). Using model-specific importance measures, lymphovascular invasion (LVI) status consistently ranked as a top predictor across all models. Other leading predictors for the MLP model included interval to surgery and positive clinical N-stage. For XGBoost, clinical T-stage (cT2) and a specific insurance type were prominent. Logistic regression's top contributors, aside from LVI, included diagnostic confirmation methods, median income quartile, and urban/rural classification.
Discussion: Advanced machine learning models, especially XGBoost, accurately predict pCR in EAC patients post-nCRT and demonstrate potential clinical utility. Identified predictors such as lymphovascular invasion, clinical stage, and treatment characteristics offer insights into patient subgroups with differing response likelihoods. If prospectively validated, these models could aid in shared decision-making and tailoring therapy.

Figure: Table 1. Performance metrics (AUC, Brier Score) and top 5 predictors for the Multi-Layer Perceptron (MLP), XGBoost, and Logistic Regression models.
Disclosures:
Woo Joo Lee indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Sohaib Asghar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Seon Hye Won indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Abuoma Cherry Ekpendu indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Marco Braaten indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Pankajkumar Patel indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Thomas Shimshak indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Woo Joo Lee, MD1, Muhammad Sohaib Asghar, MBBS1, Seon Hye Won, MD2, Abuoma Cherry Ekpendu, DO3, Marco Braaten, MD4, Pankajkumar Patel, MD5, Thomas Shimshak, MD6. P4889 - Development and Validation of Predictive Models for Pathological Complete Response in Esophageal Adenocarcinoma Patients Receiving Neoadjuvant Chemoradiotherapy: A Decision Curve Analysis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
