Tuesday Poster Session
Category: General Endoscopy
P5121 - Endoscopic Gastric Remodeling Plus GLP-1 Receptor Agonist versus Endoscopic Gastric Remodeling Alone for Weight Loss
Tuesday, October 28, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Vikash Kumar, MD
Creighton University School of Medicine
Phoenix, AZ
Presenting Author(s)
Sunny Kumar, MD1, Vikash Kumar, MD2, Anmol Mohan, MD3, Khyati Bidani, MD4, Elmkdad Mohammed, MD5, Divyesh Sejpal, MD, MS2, Dalbir Sandhu, MD2
1Wright Center for Graduate Medical Education, Scranton, PA; 2Creighton University School of Medicine, Phoenix, AZ; 3Carle Foundation hospital, Urbana, IL; 4Saint Peter's University Hospital / Rutgers Robert Wood Johnson Medical School, New Brunswick, NJ; 5The Wright Center for Graduate Medical Education, Scranton, PA
Introduction: Endoscopic gastric remodeling (EGR), particularly endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty (ESG), is an effective minimally invasive procedure for weight loss. While EGR alone has shown significant benefits, the added value of combining it with glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs) is still unclear. This study aims to evaluate and compare the effectiveness of EGR combined with GLP-1 RA therapy versus EGR alone in achieving weight loss
Methods: Online databases were searched up to May 2025 to identify eligible studies that reported quantitative weight loss outcomes following EGR with or without concomitant GLP-1 RA use. Random-effects models were used to estimate pooled mean differences (MDs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs). Heterogeneity was assessed using the Higgins I² statistic.
Results: This study comprised four studies with 1,526 participants. In the analysis of total body weight loss (TBWL), a numerical benefit was observed with combination therapy, approaching statistical significance (MD: 4.06%; 95% CI: -0.05 to 8.17; P = 0.05; I² = 93%). Similarly, for excessive weight loss (EWL), no significant difference was observed between groups (MD: 5.36%; 95% CI: -12.57 to 23.28; P = 0.56; I² = 93%). For BMI reduction, the pooled mean difference favored combination therapy but did not reach statistical significance (MD: 0.52 kg/m²; 95% CI: -1.63 to 2.68; P = 0.63; I² = 92%).
Discussion: EGR combined with GLP-1 RA therapy may provide incremental benefits in total body weight loss compared to EGR alone. However, the observed advantages in BMI and EWL were not statistically significant. Substantial heterogeneity across studies underscores the need for larger, well-designed randomized controlled trials to better define the synergistic potential of endoscopic and pharmacologic obesity treatments.
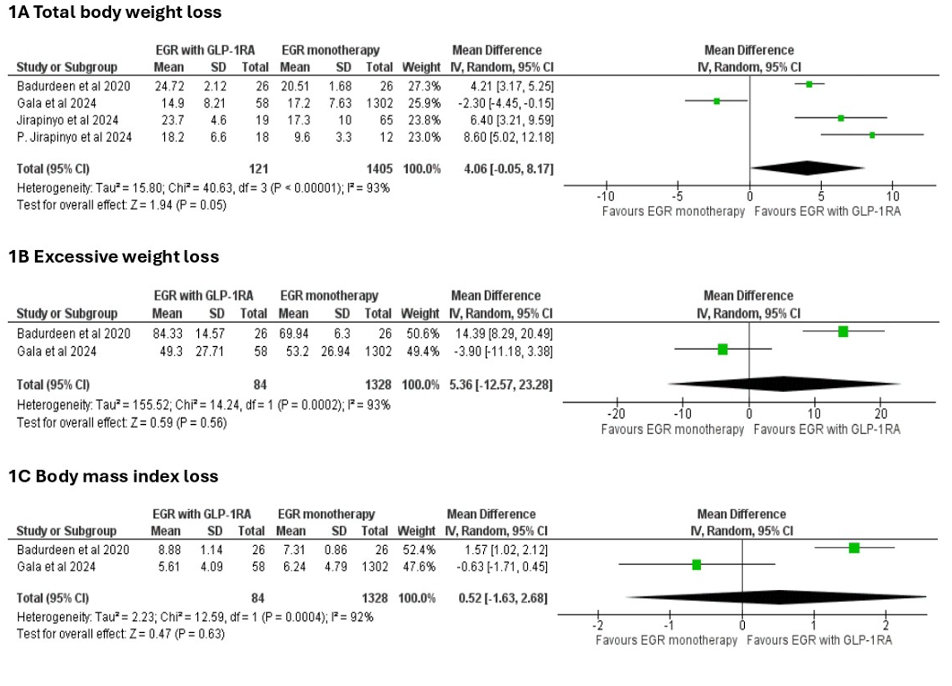
Figure: Outcomes of Endoscopic gastric remodeling plus GLP-1 receptor agonist versus endoscopic gastric remodeling alone for weight loss.
Disclosures:
Sunny Kumar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Vikash Kumar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Anmol Mohan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Khyati Bidani indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Elmkdad Mohammed indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Divyesh Sejpal: Boston Scientific – Consultant. Olympus – Grant/Research Support.
Dalbir Sandhu indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sunny Kumar, MD1, Vikash Kumar, MD2, Anmol Mohan, MD3, Khyati Bidani, MD4, Elmkdad Mohammed, MD5, Divyesh Sejpal, MD, MS2, Dalbir Sandhu, MD2. P5121 - Endoscopic Gastric Remodeling Plus GLP-1 Receptor Agonist versus Endoscopic Gastric Remodeling Alone for Weight Loss, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Wright Center for Graduate Medical Education, Scranton, PA; 2Creighton University School of Medicine, Phoenix, AZ; 3Carle Foundation hospital, Urbana, IL; 4Saint Peter's University Hospital / Rutgers Robert Wood Johnson Medical School, New Brunswick, NJ; 5The Wright Center for Graduate Medical Education, Scranton, PA
Introduction: Endoscopic gastric remodeling (EGR), particularly endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty (ESG), is an effective minimally invasive procedure for weight loss. While EGR alone has shown significant benefits, the added value of combining it with glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs) is still unclear. This study aims to evaluate and compare the effectiveness of EGR combined with GLP-1 RA therapy versus EGR alone in achieving weight loss
Methods: Online databases were searched up to May 2025 to identify eligible studies that reported quantitative weight loss outcomes following EGR with or without concomitant GLP-1 RA use. Random-effects models were used to estimate pooled mean differences (MDs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs). Heterogeneity was assessed using the Higgins I² statistic.
Results: This study comprised four studies with 1,526 participants. In the analysis of total body weight loss (TBWL), a numerical benefit was observed with combination therapy, approaching statistical significance (MD: 4.06%; 95% CI: -0.05 to 8.17; P = 0.05; I² = 93%). Similarly, for excessive weight loss (EWL), no significant difference was observed between groups (MD: 5.36%; 95% CI: -12.57 to 23.28; P = 0.56; I² = 93%). For BMI reduction, the pooled mean difference favored combination therapy but did not reach statistical significance (MD: 0.52 kg/m²; 95% CI: -1.63 to 2.68; P = 0.63; I² = 92%).
Discussion: EGR combined with GLP-1 RA therapy may provide incremental benefits in total body weight loss compared to EGR alone. However, the observed advantages in BMI and EWL were not statistically significant. Substantial heterogeneity across studies underscores the need for larger, well-designed randomized controlled trials to better define the synergistic potential of endoscopic and pharmacologic obesity treatments.

Figure: Outcomes of Endoscopic gastric remodeling plus GLP-1 receptor agonist versus endoscopic gastric remodeling alone for weight loss.
Disclosures:
Sunny Kumar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Vikash Kumar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Anmol Mohan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Khyati Bidani indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Elmkdad Mohammed indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Divyesh Sejpal: Boston Scientific – Consultant. Olympus – Grant/Research Support.
Dalbir Sandhu indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sunny Kumar, MD1, Vikash Kumar, MD2, Anmol Mohan, MD3, Khyati Bidani, MD4, Elmkdad Mohammed, MD5, Divyesh Sejpal, MD, MS2, Dalbir Sandhu, MD2. P5121 - Endoscopic Gastric Remodeling Plus GLP-1 Receptor Agonist versus Endoscopic Gastric Remodeling Alone for Weight Loss, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
