Tuesday Poster Session
Category: GI Bleeding
P5276 - A Case of Late Onset Blue Rubber Bleb Nevus Syndrome
Tuesday, October 28, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Lukus Berber, MD (he/him/his)
Advocate Lutheran General
Des Plaines, IL
Presenting Author(s)
Lukus Berber, MD1, Olivia Foy, MD2
1Advocate Lutheran General, Des Plaines, IL; 2Advocate Lutheran General, Park Ridge, IL
Introduction: Blue rubber bleb nevus syndrome (BRBNS) is a rare congenital disorder caused by a mutation in the TEK gene, which disrupts normal cellular communication and leads to the development of abnormal blood vessels. The TEK gene expresses a TIE2 tyrosine kinase receptor predominantly present in the vascular endothelium. The TIE2 pathway, activated by angiopoietin 1 and 2, is responsible for angiogenesis and endothelial maintenance. Clinically, patients exhibit distinctive dome-shaped lesions, known as blebs, that can develop throughout the body but most commonly within the gastrointestinal tract. Patients most commonly present with severe iron deficiency anemia in the setting of recurrent GI hemorrhages.
Case Description/
Methods: 85 year old caucasian female with a past medical history of atrial fibrillation, HFpEF, CAD, COPD with chronic hypoxic respiratory failure on home oxygen, CKD3a, and HTN presented as a transfer from an outside hospital for a more rigorous investigation of ongoing blood loss anemia. She initially presented to an outside facility with dark stools and lower abdominal pain. She required pressor support and ultimately 19 units of pRBCs during her admission at the outside facility. She had a prolonged course with workup significant for: CT abdomen and pelvis with contrast extravasation in the small bowel, an EGD with several esophageal venous blebs, and finally a capsule endoscopy with active bleeding in the small bowel. Patient was treated with amicar and octreotide drip. Gastroenterology was consulted and recommended double balloon enteroscopy. Double balloon enteroscopy findings were significant for several nonbleeding venous blebs in the jejunum.
Discussion: BRBNS is an exceedingly rare disease with only a few hundred case reports published since 1860. There appears to be an autosomal dominant inheritance pattern linked to chromosome 9, but most cases are sporadic. Treatment with systemic therapies such as: sirolimus, corticosteroids, IVIG, INF-a, and vincristine have been utilized with reported success. However, dosing and duration of treatment have not been extensively studied. Supportive care with iron supplementation are standard for these patients. Some cases with severe gastrointestinal tract involvement may benefit from localized resection to prevent severe hemorrhage. Patients would benefit from pharmacotherapy trials with the drugs mentioned above in order to potentially reduce the long term complications of hospitalizations, blood transfusions, and bowel resections.
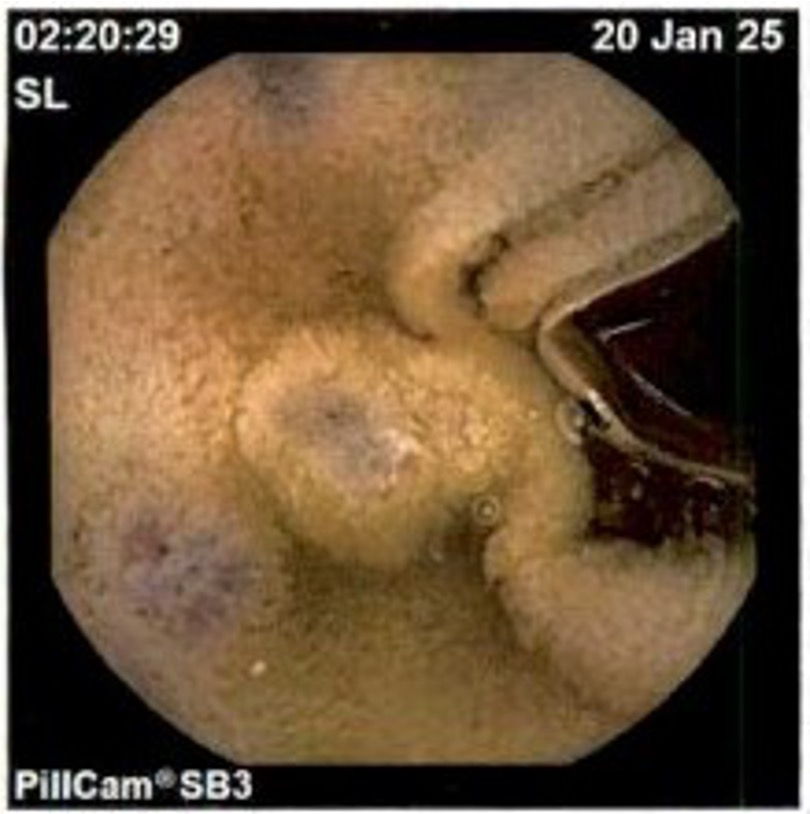
Figure: Pill endoscopy showing jejunal venous blebs
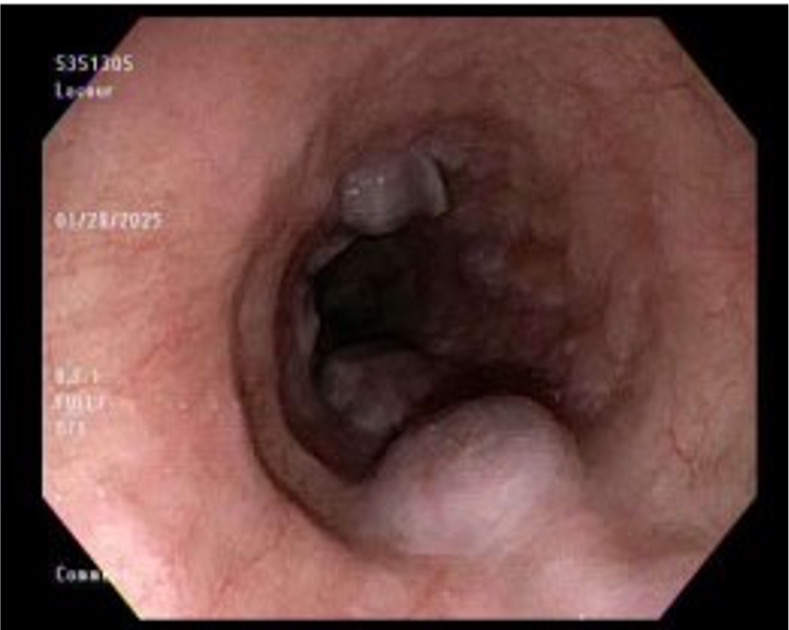
Figure: EGD showing esophageal venous blebs
Disclosures:
Lukus Berber indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Olivia Foy indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Lukus Berber, MD1, Olivia Foy, MD2. P5276 - A Case of Late Onset Blue Rubber Bleb Nevus Syndrome, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Advocate Lutheran General, Des Plaines, IL; 2Advocate Lutheran General, Park Ridge, IL
Introduction: Blue rubber bleb nevus syndrome (BRBNS) is a rare congenital disorder caused by a mutation in the TEK gene, which disrupts normal cellular communication and leads to the development of abnormal blood vessels. The TEK gene expresses a TIE2 tyrosine kinase receptor predominantly present in the vascular endothelium. The TIE2 pathway, activated by angiopoietin 1 and 2, is responsible for angiogenesis and endothelial maintenance. Clinically, patients exhibit distinctive dome-shaped lesions, known as blebs, that can develop throughout the body but most commonly within the gastrointestinal tract. Patients most commonly present with severe iron deficiency anemia in the setting of recurrent GI hemorrhages.
Case Description/
Methods: 85 year old caucasian female with a past medical history of atrial fibrillation, HFpEF, CAD, COPD with chronic hypoxic respiratory failure on home oxygen, CKD3a, and HTN presented as a transfer from an outside hospital for a more rigorous investigation of ongoing blood loss anemia. She initially presented to an outside facility with dark stools and lower abdominal pain. She required pressor support and ultimately 19 units of pRBCs during her admission at the outside facility. She had a prolonged course with workup significant for: CT abdomen and pelvis with contrast extravasation in the small bowel, an EGD with several esophageal venous blebs, and finally a capsule endoscopy with active bleeding in the small bowel. Patient was treated with amicar and octreotide drip. Gastroenterology was consulted and recommended double balloon enteroscopy. Double balloon enteroscopy findings were significant for several nonbleeding venous blebs in the jejunum.
Discussion: BRBNS is an exceedingly rare disease with only a few hundred case reports published since 1860. There appears to be an autosomal dominant inheritance pattern linked to chromosome 9, but most cases are sporadic. Treatment with systemic therapies such as: sirolimus, corticosteroids, IVIG, INF-a, and vincristine have been utilized with reported success. However, dosing and duration of treatment have not been extensively studied. Supportive care with iron supplementation are standard for these patients. Some cases with severe gastrointestinal tract involvement may benefit from localized resection to prevent severe hemorrhage. Patients would benefit from pharmacotherapy trials with the drugs mentioned above in order to potentially reduce the long term complications of hospitalizations, blood transfusions, and bowel resections.

Figure: Pill endoscopy showing jejunal venous blebs

Figure: EGD showing esophageal venous blebs
Disclosures:
Lukus Berber indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Olivia Foy indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Lukus Berber, MD1, Olivia Foy, MD2. P5276 - A Case of Late Onset Blue Rubber Bleb Nevus Syndrome, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
