Tuesday Poster Session
Category: IBD
P5343 - Impact of Micronutrient Deficiencies on Clinical Outcomes in Patients Hospitalized for Crohn’s Disease and Ulcerative Colitis: A Nationwide Analysis
Tuesday, October 28, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Maria Grba, DO (she/her/hers)
John H. Stroger, Jr. Hospital of Cook County
Chicago, IL
Presenting Author(s)
Maria Grba, DO1, Patricia Zarza Gulino, MD1, Bhanu Siva Mohan Pinnam, MD1, Denise Nunez, DO1, Saksham Kohli, MBBS1, Gedion Yilma Amdetsion, MD2, Abhin Sapkota, MBBS1, Daniel Guifarro Rivera, MD3, Alejandro Nieto Dominguez, MD2, Dushyant S. Dahiya, MD4, Smit Deliwala, MD5, Hema Sameera. Pinnam, 6, Kajali Mishra, MD2
1John H. Stroger, Jr. Hospital of Cook County, Chicago, IL; 2Cook County Health, Chicago, IL; 3Cook County Health and Hospital Systems, Chicago, IL; 4University of Kansas School of Medicine, Kansas City, KS; 5Emory University, Atlanta, GA; 6Jagadguru Sri Shivarathreeshwara Medical College, Mysuru, Karnataka, India
Introduction: Micronutrient deficiencies (MD) are prevalent in patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), but their impact on clinical outcomes is not well understood. This study evaluated the association between vitamin B12, folate, iron, vitamin D, and zinc deficiency and hospitalization outcomes in patients with Crohn’s disease (CD) and ulcerative colitis (UC).
Methods: Using the National Inpatient Sample from 2016–2021, we identified adult hospitalizations with CD or UC using The International Classification of Disease, Tenth Revision (ICD10) codes. Patients were further stratified by the presence of MD. Multivariate regression using STATA 18 was performed to compare inpatient outcomes while adjusting for demographics, comorbidities, and hospital characteristics.
Results: A total of 460,589 hospitalizations for IBD were identified (CD: 278,784, UC: 178,805). MD was present in 47,140 (16.7%) CD and 35,815 (20.0%) UC cases. In both CD and UC, patients with MD tended to be younger, female, and more often non-White. A greater proportion of patients with MD were Medicaid-insured and admitted to urban teaching hospitals. In both CD and UC groups, patients with MD had significantly higher rates of sepsis (3.8% vs. 2.99% in CD; 4.84% vs. 3.8% in UC), C. diff infection (2.43% vs. 1.70% in CD; 4.24% vs. 3.14% in UC), and VTE (1.44% vs. 0.88% in CD; 2.47% vs. 1.52% in UC). TPN use was significantly higher in both MD groups (5.94% vs. 3.40% in CD; 2.66% vs. 1.77% in UC). UC patients with MD had significantly higher rates of colectomy (4.80% vs. 3.32%), however, there was no statistical difference in CD patients. Additionally, patients with MD in both IBD groups had higher mean LOS (5.63 vs. 4.51 days in CD; 5.97 vs. 4.96 days in UC) and hospitalization charges (+7,904 in CD; +$8,440 in UC). Mortality, mechanical ventilation, and ICU admissions were not affected by MD status in either the CD or UC groups.
Discussion: In the presence of MD, patients with IBD face poorer outcomes with higher rates of infection, particularly C. diff, and longer hospitalization. Additionally, the risk of complications like sepsis, need for TPN, and surgical intervention were higher in these patients in the presence of MD, likely suggestive of poor disease control. Appropriate screening and interventions should be applied to promptly recognize and correct MD in patients with IBD. Further research in these directions can help improve outcomes and help achieve disease control and remission.
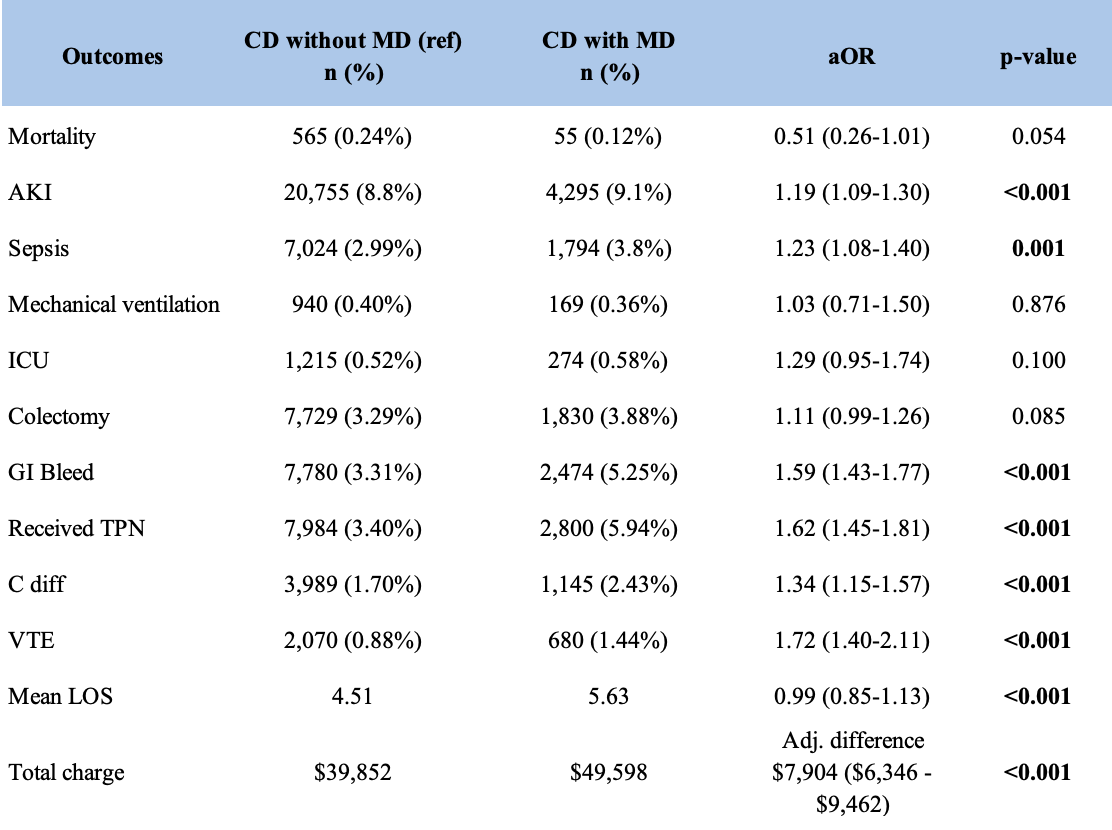
Figure: Outcomes, adverse events, and healthcare utilization in hospitalized patients with Crohn's disease, stratified by presence of absence of a micronutrient deficiency
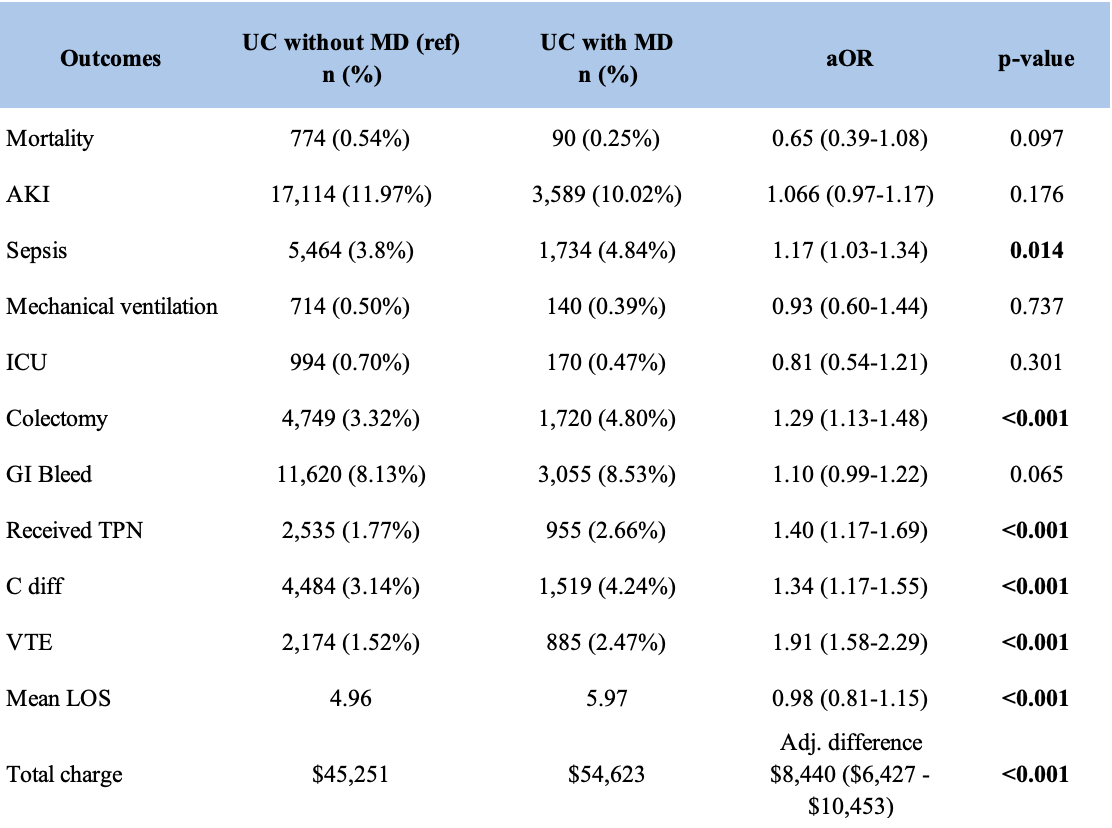
Figure: Outcomes, adverse events, and healthcare utilization in hospitalized patients with ulcerative colitis, stratified by presence of absence of a micronutrient deficiency
Disclosures:
Maria Grba indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Patricia Zarza Gulino indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Bhanu Siva Mohan Pinnam indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Denise Nunez indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Saksham Kohli indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Gedion Yilma Amdetsion indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Abhin Sapkota indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Daniel Guifarro Rivera indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Alejandro Nieto Dominguez indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Dushyant Dahiya indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Smit Deliwala indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hema Pinnam indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kajali Mishra indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Maria Grba, DO1, Patricia Zarza Gulino, MD1, Bhanu Siva Mohan Pinnam, MD1, Denise Nunez, DO1, Saksham Kohli, MBBS1, Gedion Yilma Amdetsion, MD2, Abhin Sapkota, MBBS1, Daniel Guifarro Rivera, MD3, Alejandro Nieto Dominguez, MD2, Dushyant S. Dahiya, MD4, Smit Deliwala, MD5, Hema Sameera. Pinnam, 6, Kajali Mishra, MD2. P5343 - Impact of Micronutrient Deficiencies on Clinical Outcomes in Patients Hospitalized for Crohn’s Disease and Ulcerative Colitis: A Nationwide Analysis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1John H. Stroger, Jr. Hospital of Cook County, Chicago, IL; 2Cook County Health, Chicago, IL; 3Cook County Health and Hospital Systems, Chicago, IL; 4University of Kansas School of Medicine, Kansas City, KS; 5Emory University, Atlanta, GA; 6Jagadguru Sri Shivarathreeshwara Medical College, Mysuru, Karnataka, India
Introduction: Micronutrient deficiencies (MD) are prevalent in patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), but their impact on clinical outcomes is not well understood. This study evaluated the association between vitamin B12, folate, iron, vitamin D, and zinc deficiency and hospitalization outcomes in patients with Crohn’s disease (CD) and ulcerative colitis (UC).
Methods: Using the National Inpatient Sample from 2016–2021, we identified adult hospitalizations with CD or UC using The International Classification of Disease, Tenth Revision (ICD10) codes. Patients were further stratified by the presence of MD. Multivariate regression using STATA 18 was performed to compare inpatient outcomes while adjusting for demographics, comorbidities, and hospital characteristics.
Results: A total of 460,589 hospitalizations for IBD were identified (CD: 278,784, UC: 178,805). MD was present in 47,140 (16.7%) CD and 35,815 (20.0%) UC cases. In both CD and UC, patients with MD tended to be younger, female, and more often non-White. A greater proportion of patients with MD were Medicaid-insured and admitted to urban teaching hospitals. In both CD and UC groups, patients with MD had significantly higher rates of sepsis (3.8% vs. 2.99% in CD; 4.84% vs. 3.8% in UC), C. diff infection (2.43% vs. 1.70% in CD; 4.24% vs. 3.14% in UC), and VTE (1.44% vs. 0.88% in CD; 2.47% vs. 1.52% in UC). TPN use was significantly higher in both MD groups (5.94% vs. 3.40% in CD; 2.66% vs. 1.77% in UC). UC patients with MD had significantly higher rates of colectomy (4.80% vs. 3.32%), however, there was no statistical difference in CD patients. Additionally, patients with MD in both IBD groups had higher mean LOS (5.63 vs. 4.51 days in CD; 5.97 vs. 4.96 days in UC) and hospitalization charges (+7,904 in CD; +$8,440 in UC). Mortality, mechanical ventilation, and ICU admissions were not affected by MD status in either the CD or UC groups.
Discussion: In the presence of MD, patients with IBD face poorer outcomes with higher rates of infection, particularly C. diff, and longer hospitalization. Additionally, the risk of complications like sepsis, need for TPN, and surgical intervention were higher in these patients in the presence of MD, likely suggestive of poor disease control. Appropriate screening and interventions should be applied to promptly recognize and correct MD in patients with IBD. Further research in these directions can help improve outcomes and help achieve disease control and remission.

Figure: Outcomes, adverse events, and healthcare utilization in hospitalized patients with Crohn's disease, stratified by presence of absence of a micronutrient deficiency

Figure: Outcomes, adverse events, and healthcare utilization in hospitalized patients with ulcerative colitis, stratified by presence of absence of a micronutrient deficiency
Disclosures:
Maria Grba indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Patricia Zarza Gulino indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Bhanu Siva Mohan Pinnam indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Denise Nunez indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Saksham Kohli indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Gedion Yilma Amdetsion indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Abhin Sapkota indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Daniel Guifarro Rivera indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Alejandro Nieto Dominguez indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Dushyant Dahiya indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Smit Deliwala indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hema Pinnam indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kajali Mishra indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Maria Grba, DO1, Patricia Zarza Gulino, MD1, Bhanu Siva Mohan Pinnam, MD1, Denise Nunez, DO1, Saksham Kohli, MBBS1, Gedion Yilma Amdetsion, MD2, Abhin Sapkota, MBBS1, Daniel Guifarro Rivera, MD3, Alejandro Nieto Dominguez, MD2, Dushyant S. Dahiya, MD4, Smit Deliwala, MD5, Hema Sameera. Pinnam, 6, Kajali Mishra, MD2. P5343 - Impact of Micronutrient Deficiencies on Clinical Outcomes in Patients Hospitalized for Crohn’s Disease and Ulcerative Colitis: A Nationwide Analysis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.

