Tuesday Poster Session
Category: IBD
P5424 - The Risk of Emergent Colectomy for Ulcerative Colitis Has Increased Over Time
Tuesday, October 28, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall
- ML
Michael Ly, BA
University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill School of Medicine
Chapel Hill, NC
Presenting Author(s)
Michael Ly, BA1, Taylor Williams, MD, MS, MPH1, Sydney Power, MD1, Michael Dunn, MD1, Hans Herfarth, MD, PhD2, Millie D. Long, MD, FACG3, Edward L. Barnes, MD, MPH4
1University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill School of Medicine, Chapel Hill, NC; 2University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, NC, USA, Chapel Hill, NC; 3Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, NC, USA, Chapel Hill, NC; 4Multidisciplinary Inflammatory Bowel Diseases Center, Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, NC, USA, Chapel Hill, NC
Introduction: Although we have seen an emergence of new therapies for the treatment of ulcerative colitis (UC), there are concerns that patients and physicians prolong decisions regarding colectomy for severe disease to continue medical therapy. We evaluated trends in the proportion of emergent colectomies at our institution between 2003 and 2020.
Methods: In a retrospective cohort study, we evaluated emergent colectomies by time period. Emergent colectomy was defined as any colectomy that occurred subsequently from an Emergency Department admission. Time periods were assessed by availability of new medical therapies for the treatment of UC. We used Chi-square and Fisher exact testing for initial analyses followed by multivariable logistic regression to adjust for potential confounders, including social determinants of health such as the Area Deprivation Index among patients in the most recent time period.
Results: Among 717 patients, 101 (14%) underwent emergent colectomy. The highest percentage of patients undergoing emergent colectomy was demonstrated in the most recent period analyzed, 2017-2020 (33%, p< 0.001 for trend across time periods). Among 717 patients, 25 (3%) experienced perforation and 7 (1%) developed toxic megacolon, with no significant trends across time noted. Additionally, patients undergoing emergent colectomy were more likely to be of non-white race (23% vs. 10%, P< 0.001, Table 1). The number of advanced therapy exposures per patient increased significantly in more recent time periods (p< 0.001 for trend across time periods). In multivariable logistic regression, patients in later time periods demonstrated increased odds of emergent colectomy, after adjusting for race and Area Deprivation Index (2017-2020: aOR 3.57, 95% CI 1.5-8.2 and 2014-2016: aOR 3.66, 95% CI 1.7-7.9, Table 2).
Discussion: Despite advancements in UC therapies, our findings indicate an increasing trend in emergent colectomies over time. This suggests that patients may be delaying surgical intervention in favor of continuing medical management, allowing a progression to severe disease states. Non-white patients appear to be at higher risk for emergent colectomy, highlighting possible disparities access to UC-specific care. These results underscore the need for careful patient counseling about the risks of delaying surgery and emphasize the importance of consistent objective evaluation and timely decision-making to prevent severe complications.
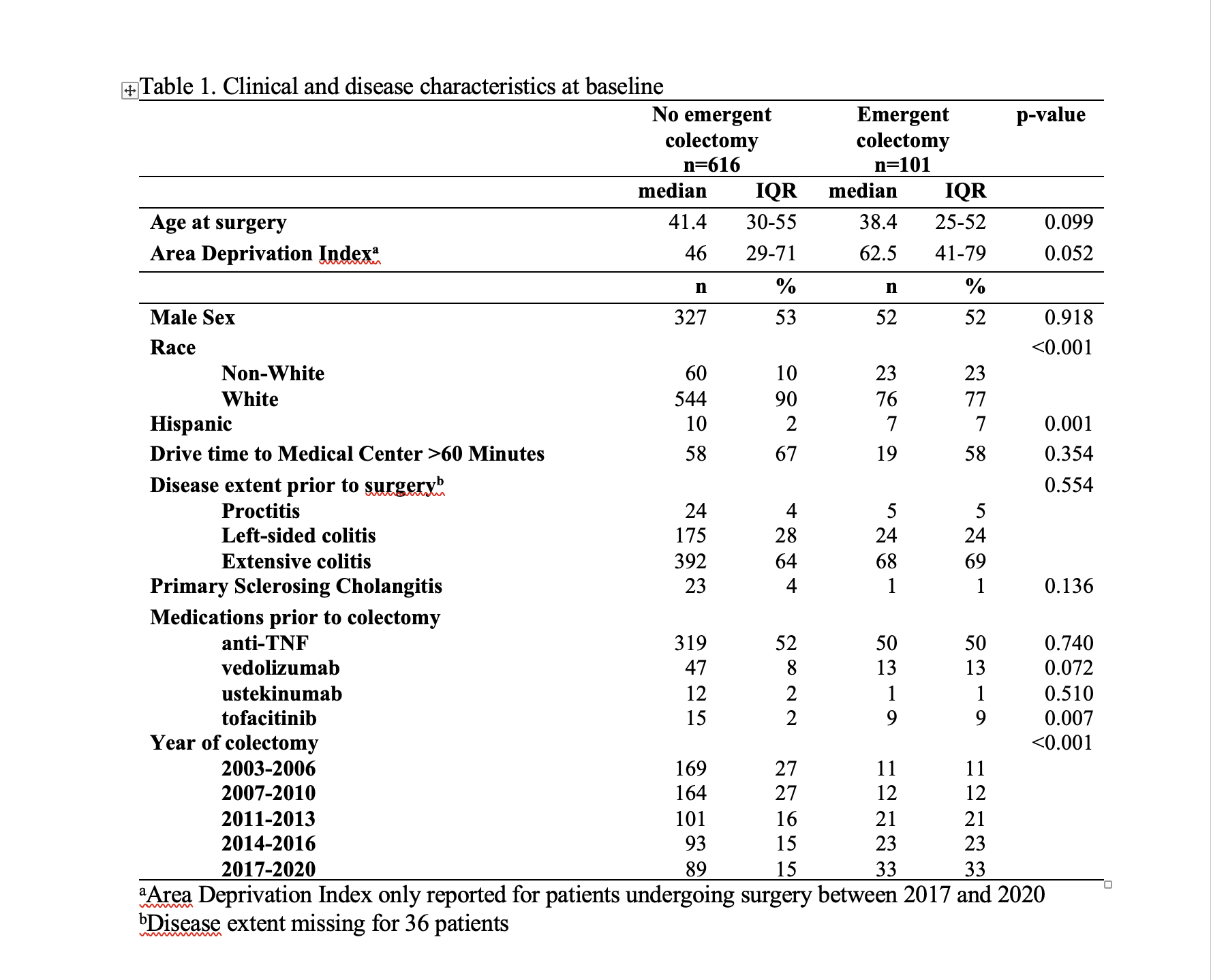
Figure: Table 1. Clinical and disease characteristics at baseline
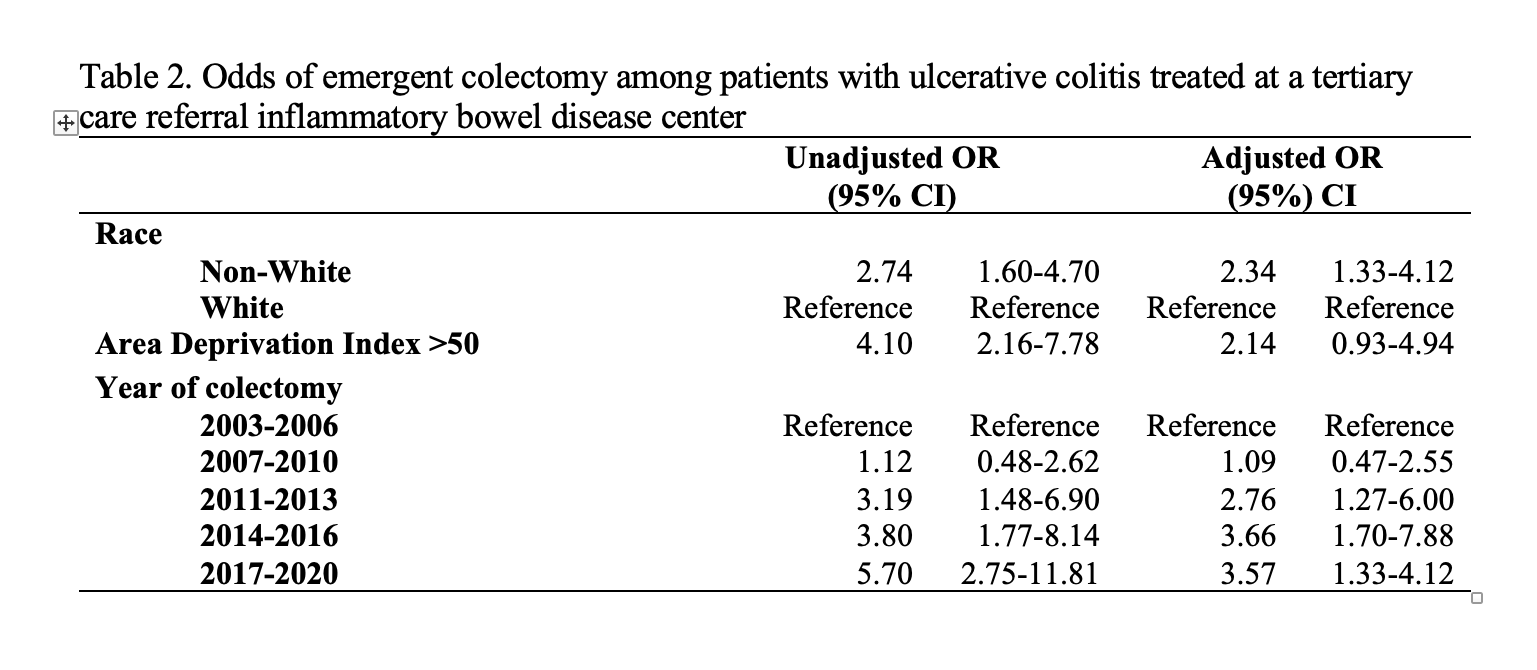
Figure: Table 2. Odds of emergent colectomy among patients with ulcerative colitis treated at a tertiary care referral inflammatory bowel disease center
Disclosures:
Michael Ly indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Taylor Williams indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sydney Power indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Michael Dunn indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hans Herfarth: Celltrion – Consultant. ExeGi – Consultant. Gilead – Consultant. Janssen – Consultant. Lilly – Grant/Research Support. Novo Nordisk – Grant/Research Support.
Millie Long: AbbVie – Consultant. Bristol Myers Squibb – Consultant. Celltrion – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Intercept – Consultant. Johnson & Johnson – Consultant. Lilly – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Merck – Consultant. Pfizer – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Prometheus – Consultant. Roivant – Consultant. Sanofi – Consultant. Spyre – Consultant. Takeda – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Target RWE – Consultant.
Edward Barnes: AbbVie, Inc. – Consultant. Boomerang – Consultant. Eli Lilly – Consultant. Eli Lilly – Grant/Research Support. Pfizer – Consultant. Sanofi – Consultant. Takeda – Consultant. Target RWE – Consultant.
Michael Ly, BA1, Taylor Williams, MD, MS, MPH1, Sydney Power, MD1, Michael Dunn, MD1, Hans Herfarth, MD, PhD2, Millie D. Long, MD, FACG3, Edward L. Barnes, MD, MPH4. P5424 - The Risk of Emergent Colectomy for Ulcerative Colitis Has Increased Over Time, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill School of Medicine, Chapel Hill, NC; 2University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, NC, USA, Chapel Hill, NC; 3Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, NC, USA, Chapel Hill, NC; 4Multidisciplinary Inflammatory Bowel Diseases Center, Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, NC, USA, Chapel Hill, NC
Introduction: Although we have seen an emergence of new therapies for the treatment of ulcerative colitis (UC), there are concerns that patients and physicians prolong decisions regarding colectomy for severe disease to continue medical therapy. We evaluated trends in the proportion of emergent colectomies at our institution between 2003 and 2020.
Methods: In a retrospective cohort study, we evaluated emergent colectomies by time period. Emergent colectomy was defined as any colectomy that occurred subsequently from an Emergency Department admission. Time periods were assessed by availability of new medical therapies for the treatment of UC. We used Chi-square and Fisher exact testing for initial analyses followed by multivariable logistic regression to adjust for potential confounders, including social determinants of health such as the Area Deprivation Index among patients in the most recent time period.
Results: Among 717 patients, 101 (14%) underwent emergent colectomy. The highest percentage of patients undergoing emergent colectomy was demonstrated in the most recent period analyzed, 2017-2020 (33%, p< 0.001 for trend across time periods). Among 717 patients, 25 (3%) experienced perforation and 7 (1%) developed toxic megacolon, with no significant trends across time noted. Additionally, patients undergoing emergent colectomy were more likely to be of non-white race (23% vs. 10%, P< 0.001, Table 1). The number of advanced therapy exposures per patient increased significantly in more recent time periods (p< 0.001 for trend across time periods). In multivariable logistic regression, patients in later time periods demonstrated increased odds of emergent colectomy, after adjusting for race and Area Deprivation Index (2017-2020: aOR 3.57, 95% CI 1.5-8.2 and 2014-2016: aOR 3.66, 95% CI 1.7-7.9, Table 2).
Discussion: Despite advancements in UC therapies, our findings indicate an increasing trend in emergent colectomies over time. This suggests that patients may be delaying surgical intervention in favor of continuing medical management, allowing a progression to severe disease states. Non-white patients appear to be at higher risk for emergent colectomy, highlighting possible disparities access to UC-specific care. These results underscore the need for careful patient counseling about the risks of delaying surgery and emphasize the importance of consistent objective evaluation and timely decision-making to prevent severe complications.

Figure: Table 1. Clinical and disease characteristics at baseline

Figure: Table 2. Odds of emergent colectomy among patients with ulcerative colitis treated at a tertiary care referral inflammatory bowel disease center
Disclosures:
Michael Ly indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Taylor Williams indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sydney Power indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Michael Dunn indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hans Herfarth: Celltrion – Consultant. ExeGi – Consultant. Gilead – Consultant. Janssen – Consultant. Lilly – Grant/Research Support. Novo Nordisk – Grant/Research Support.
Millie Long: AbbVie – Consultant. Bristol Myers Squibb – Consultant. Celltrion – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Intercept – Consultant. Johnson & Johnson – Consultant. Lilly – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Merck – Consultant. Pfizer – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Prometheus – Consultant. Roivant – Consultant. Sanofi – Consultant. Spyre – Consultant. Takeda – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Target RWE – Consultant.
Edward Barnes: AbbVie, Inc. – Consultant. Boomerang – Consultant. Eli Lilly – Consultant. Eli Lilly – Grant/Research Support. Pfizer – Consultant. Sanofi – Consultant. Takeda – Consultant. Target RWE – Consultant.
Michael Ly, BA1, Taylor Williams, MD, MS, MPH1, Sydney Power, MD1, Michael Dunn, MD1, Hans Herfarth, MD, PhD2, Millie D. Long, MD, FACG3, Edward L. Barnes, MD, MPH4. P5424 - The Risk of Emergent Colectomy for Ulcerative Colitis Has Increased Over Time, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
