Tuesday Poster Session
Category: IBD
P5422 - GLP1-RA in Patients With Crohn's Disease Independently Associated With Reduction in SEMA-CD Score
Tuesday, October 28, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall
- VD
Vincent Dioguardi, MD
Thomas Jefferson University Hospital
Philadelphia, PA
Presenting Author(s)
Vincent Dioguardi, MD1, Joy Zhao, MD1, Cindy Xin Fang, BS2, Jasmine Lee, MD1, Hamzah Shariff, MD1, Caleb Song, BS3, Breanne McDermott, BS2, Vaishnavi Nara, BS2, Cuckoo Choudhary, MD4, Patricia L. Kozuch, MD1, Aakash Desai, MD5, Raina Shivashankar, MD1, Priya Sehgal, MD1
1Thomas Jefferson University Hospital, Philadelphia, PA; 2Sidney Kimmel Medical College at Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, PA; 3Sidney Kimmel Medical College At Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, PA; 4Thomas Jefferson University Hospital (Philadelphia, PA), Philadelphia, PA; 5Allegheny Health Network, Pittsburgh, PA
Introduction: Obesity in adults with IBD has been associated with increased risk of persistent disease activity in both Crohn’s Disease (CD) and Ulcerative Colitis (UC). Emerging evidence suggests that glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RA) are not only associated with weight loss but also with reduced systemic inflammation. This study aimed to describe endoscopic outcomes of patients with IBD treated with GLP-1RA.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective review of electronic health records, at a tertiary care center, from January 2018-January 2025. Adult patients with a history of CD or UC who were treated with GLP-1RA, for at least 3 months, were included. Patients received GLP-1RA therapy for either obesity or diabetes. The primary outcome was change in endoscopic disease activity, measured via SEMA-CD or Mayo score, one year prior to and one year post GLP-1RA therapy. Multivariable linear regression modeling was used to evaluate factors contributing to change in endoscopic disease activity. Co-variables included age, sex, change in IBD therapy and initiation of steroids (PO or IV).
Results: We identified 180 CD and 174 UC patients treated with GLP1-RA. The majority received either semaglutide (57%) and were female (64%). Among the cohort, 32 (8.9%) patients had a documented CRP within 1 year prior to GLP-1RA as well as 6-12 months after with mean improvement of 7.1 mg/L (p=0.045). Amongst patients with CD, 23 (6.4%) had endoscopic data with a mean improvement in SEMA-CD score of 1.22 (p=0.047). On multivariable regression, adjusting for IBD therapy change and steroid initiation, we found that patients with CD on GLP-1RA exhibited a 5.05 point reduction in SEMA-CD score compared to CD patients not on GLP1RA therapy (p=0.004). In this regression, initiation of steroids was also associated with reduction in SEMA-CD score (p=0.003). This same improvement in disease activity was not seen in the UC cohort with endoscopic data available (n=22; 6.1%), with a reduction in Mayo score of 0.14, not significant (p=0.5).
Discussion: This study revealed an independent association between GLP-1RA therapy and improvement in SEMA-CD score, after taking into account change in IBD therapy (biologic change or escalation) and initiation of steroids (PO or IV). This study further supports the use of GLP-1RA therapy as an adjuvant therapy, for obesity or diabetes, in the IBD patient population with potential for optimization of inflammation.
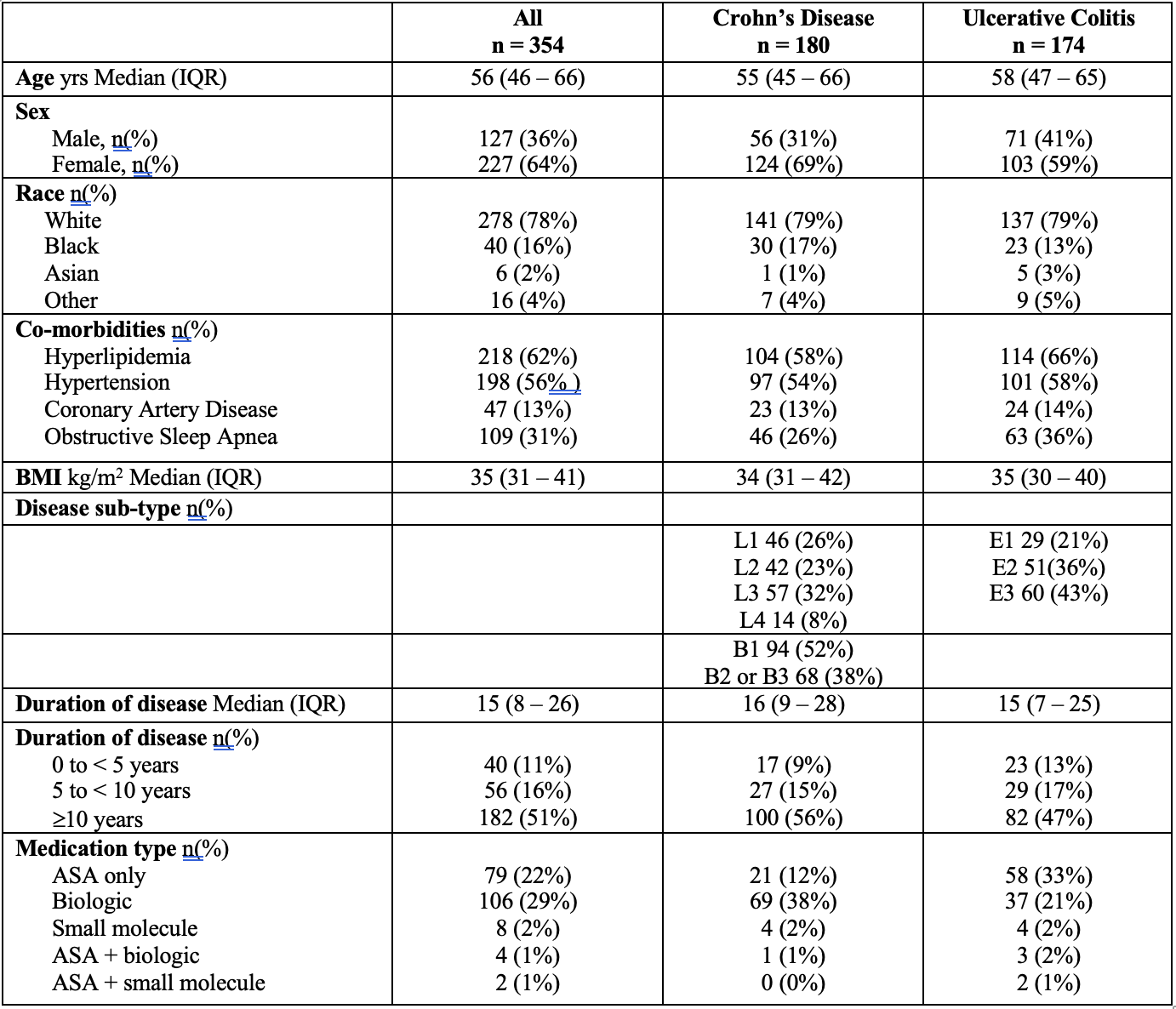
Figure: Table 1. Demographics of IBD-GLP1RA cohort.
Disease sub-type as per Montreal Classification. L1 = Terminal ileum, L2 = colon, L3 = Ileocolonic. B1 = nonstricturing/nonpenetrating, B2 = structuring, B3 = penetrating. P = perianal disease. E1 = proctitis, E2 = left colon, E3 = pan-colitis. ASA = 5-Aminosalicylic acid agent.
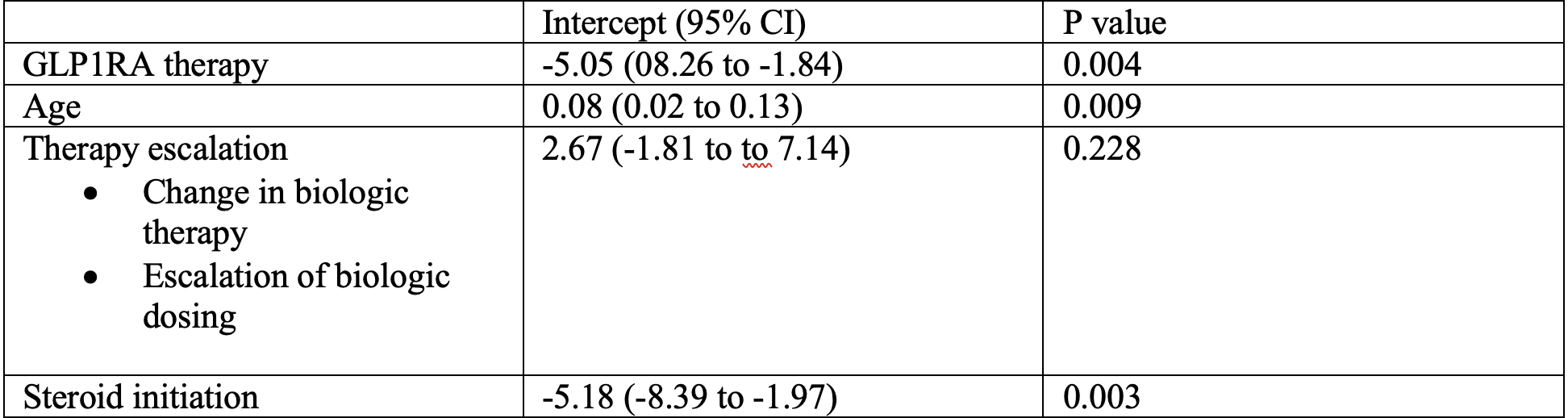
Figure: Table 2: Multivariable regression model examining factors contributing to change in SEMA-CD score one year prior and one year following GLP-1RA therapy initiation.
Disclosures:
Vincent Dioguardi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Joy Zhao indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Cindy Xin Fang indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jasmine Lee indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hamzah Shariff indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Caleb Song indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Breanne McDermott indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Vaishnavi Nara indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Cuckoo Choudhary indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Patricia Kozuch indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Aakash Desai indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Raina Shivashankar: Abbvie – Speakers Bureau. BMS – Speakers Bureau. Janssen – Grant/Research Support. Pfizer – Consultant.
Priya Sehgal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Vincent Dioguardi, MD1, Joy Zhao, MD1, Cindy Xin Fang, BS2, Jasmine Lee, MD1, Hamzah Shariff, MD1, Caleb Song, BS3, Breanne McDermott, BS2, Vaishnavi Nara, BS2, Cuckoo Choudhary, MD4, Patricia L. Kozuch, MD1, Aakash Desai, MD5, Raina Shivashankar, MD1, Priya Sehgal, MD1. P5422 - GLP1-RA in Patients With Crohn's Disease Independently Associated With Reduction in SEMA-CD Score, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Thomas Jefferson University Hospital, Philadelphia, PA; 2Sidney Kimmel Medical College at Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, PA; 3Sidney Kimmel Medical College At Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, PA; 4Thomas Jefferson University Hospital (Philadelphia, PA), Philadelphia, PA; 5Allegheny Health Network, Pittsburgh, PA
Introduction: Obesity in adults with IBD has been associated with increased risk of persistent disease activity in both Crohn’s Disease (CD) and Ulcerative Colitis (UC). Emerging evidence suggests that glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RA) are not only associated with weight loss but also with reduced systemic inflammation. This study aimed to describe endoscopic outcomes of patients with IBD treated with GLP-1RA.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective review of electronic health records, at a tertiary care center, from January 2018-January 2025. Adult patients with a history of CD or UC who were treated with GLP-1RA, for at least 3 months, were included. Patients received GLP-1RA therapy for either obesity or diabetes. The primary outcome was change in endoscopic disease activity, measured via SEMA-CD or Mayo score, one year prior to and one year post GLP-1RA therapy. Multivariable linear regression modeling was used to evaluate factors contributing to change in endoscopic disease activity. Co-variables included age, sex, change in IBD therapy and initiation of steroids (PO or IV).
Results: We identified 180 CD and 174 UC patients treated with GLP1-RA. The majority received either semaglutide (57%) and were female (64%). Among the cohort, 32 (8.9%) patients had a documented CRP within 1 year prior to GLP-1RA as well as 6-12 months after with mean improvement of 7.1 mg/L (p=0.045). Amongst patients with CD, 23 (6.4%) had endoscopic data with a mean improvement in SEMA-CD score of 1.22 (p=0.047). On multivariable regression, adjusting for IBD therapy change and steroid initiation, we found that patients with CD on GLP-1RA exhibited a 5.05 point reduction in SEMA-CD score compared to CD patients not on GLP1RA therapy (p=0.004). In this regression, initiation of steroids was also associated with reduction in SEMA-CD score (p=0.003). This same improvement in disease activity was not seen in the UC cohort with endoscopic data available (n=22; 6.1%), with a reduction in Mayo score of 0.14, not significant (p=0.5).
Discussion: This study revealed an independent association between GLP-1RA therapy and improvement in SEMA-CD score, after taking into account change in IBD therapy (biologic change or escalation) and initiation of steroids (PO or IV). This study further supports the use of GLP-1RA therapy as an adjuvant therapy, for obesity or diabetes, in the IBD patient population with potential for optimization of inflammation.

Figure: Table 1. Demographics of IBD-GLP1RA cohort.
Disease sub-type as per Montreal Classification. L1 = Terminal ileum, L2 = colon, L3 = Ileocolonic. B1 = nonstricturing/nonpenetrating, B2 = structuring, B3 = penetrating. P = perianal disease. E1 = proctitis, E2 = left colon, E3 = pan-colitis. ASA = 5-Aminosalicylic acid agent.

Figure: Table 2: Multivariable regression model examining factors contributing to change in SEMA-CD score one year prior and one year following GLP-1RA therapy initiation.
Disclosures:
Vincent Dioguardi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Joy Zhao indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Cindy Xin Fang indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jasmine Lee indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hamzah Shariff indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Caleb Song indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Breanne McDermott indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Vaishnavi Nara indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Cuckoo Choudhary indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Patricia Kozuch indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Aakash Desai indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Raina Shivashankar: Abbvie – Speakers Bureau. BMS – Speakers Bureau. Janssen – Grant/Research Support. Pfizer – Consultant.
Priya Sehgal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Vincent Dioguardi, MD1, Joy Zhao, MD1, Cindy Xin Fang, BS2, Jasmine Lee, MD1, Hamzah Shariff, MD1, Caleb Song, BS3, Breanne McDermott, BS2, Vaishnavi Nara, BS2, Cuckoo Choudhary, MD4, Patricia L. Kozuch, MD1, Aakash Desai, MD5, Raina Shivashankar, MD1, Priya Sehgal, MD1. P5422 - GLP1-RA in Patients With Crohn's Disease Independently Associated With Reduction in SEMA-CD Score, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.

