Tuesday Poster Session
Category: IBD
P5414 - Etrolizumab as Induction and Maintenance Therapy in Patients With Moderately to Severely Active Ulcerative Colitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Tuesday, October 28, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall
- MA
Mageda Al Areqi, MD
Raritan Bay Medical Center
Perth Amboy, NJ
Presenting Author(s)
Mohammed S. Beshr, MBBS1, Rana H. Shembesh, MBBCh2, Abdallah Khashan, MD3, Mageda Al Areqi, MD4, Bisher Sawaf, MD5, Muhammed Elhadi, MD6
1Sana’a University, Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences, Sana'a, Hadramawt, Yemen; 2Libyan International Medical University, Faculty of Medicine, Benghazi, Benghazi, Libya; 3Capital Health Regional Medical Center, Trenton, NJ; 4Raritan Bay Medical Center, Perth Amboy, NJ; 5University of Toledo Medical Center, Toledo, OH; 6College of Medicine, Korea University, Seongbuk, Seoul-t'ukpyolsi, Republic of Korea
Introduction: The treatment of ulcerative colitis remains crucial, and new advances in biologic treatments have further advanced the field. Etrolizumab, an anti-β7 integrin monoclonal antibody, has shown promising results in recent clinical trials. We aim in this meta-analysis to evaluate its efficacy as an induction and maintenance treatment option.
Methods: On November 15, 2024, a data search was conducted using PubMed, Scopus, and the Cochrane Library. Our inclusion criteria were any controlled clinical trials comparing the use of Etrolizumab to placebo in moderate-to-severe ulcerative colitis. The studied outcomes were clinical response, clinical remission, endoscopic improvements, endoscopic remission, and histologic remission. We used the odds ratio with the 95% confidence interval to estimate the effect size. A random-effects model was used.
Results: Out of 354 articles screened, only 5 were eligible, with a total of 1808 patients. Etrolizumab had a significant clinical response compared to placebo with an odds ratio of 1.60 [CI:1.23 to 2.09, p < 0.001]. Clinical remission was evaluated in both the induction and maintenance groups, and it was significantly higher in the induction group with an odds ratio of 2.85 [CI: 1.63 to 4.99, p < 0.001]. However, there was no significant difference in the maintenance group [OR: 1.43, CI: 0.91 to 2.23, p = 0.12]. In our evaluation of endoscopic improvement, etrolizumab showed significant improvement in both the induction and maintenance groups, with an odds ratio of 1.72 [CI: 1.24 to 2.40, p = 0.001] and 2.09 [CI: 1.37 to 3.20, p < 0.001], respectively. Similar results were observed for endoscopic remission, both the induction and maintenance groups had significant results, with an odds ratio of 2.50 [1.52 to 4.12, p < 0.001] and 2.27 [1.39 to 3.70, p = 0.001], respectively. Finally, histologic remission was only significant for the maintenance group. The odds ratios for induction and maintenance were 1.93 [CI: 1.01 to 3.68, p = 0.05] and 2.67 [CI: 1.61 to 4.41, p < 0.001], respectively.
Discussion: Etrolizumab is an effective option for both induction and maintenance treatment of moderate-to-severe ulcerative colitis. It has a positive impact on clinical response and remission, as well as on endoscopic and histologic endpoints.
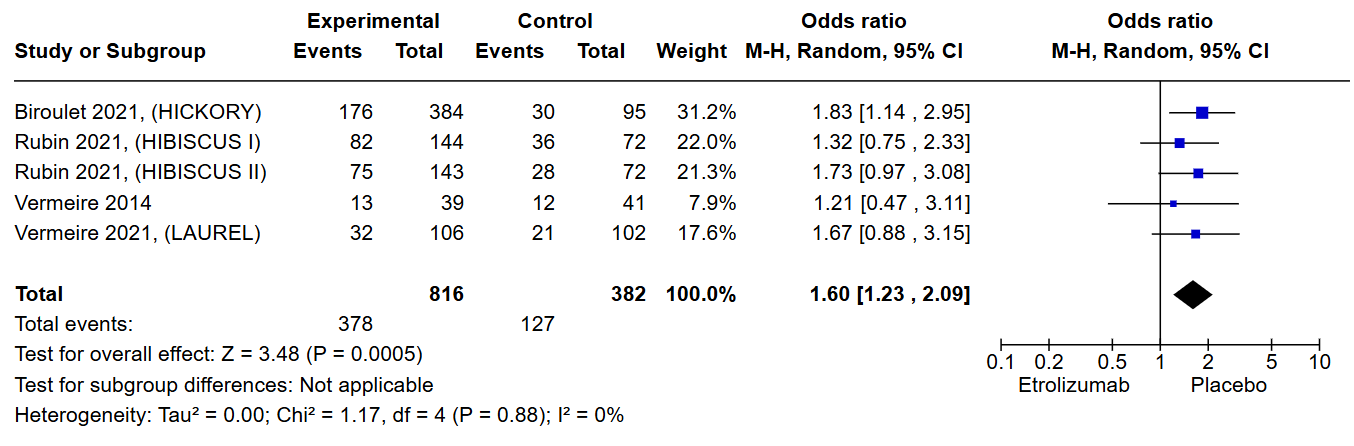
Figure: Figure 1: Clinical Response
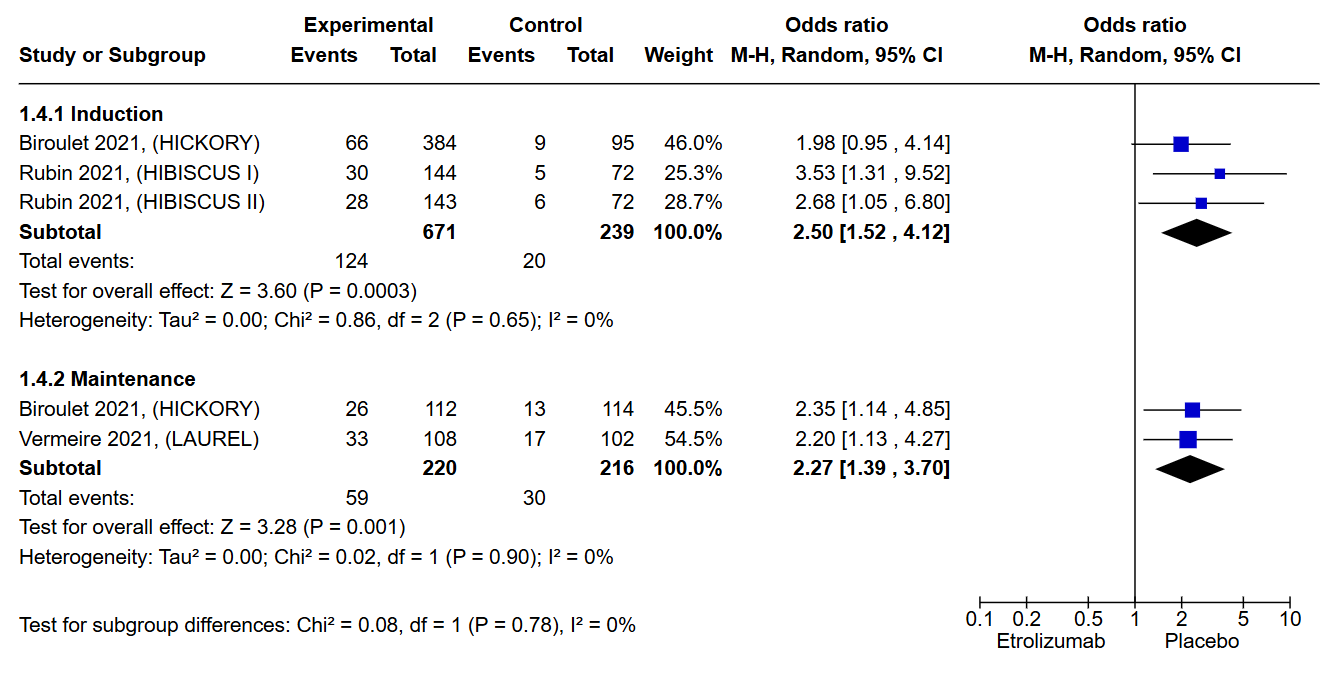
Figure: Figure 2: Endoscopic Remission
Disclosures:
Mohammed Beshr indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rana Shembesh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Abdallah Khashan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mageda Al Areqi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Bisher Sawaf indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammed Elhadi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohammed S. Beshr, MBBS1, Rana H. Shembesh, MBBCh2, Abdallah Khashan, MD3, Mageda Al Areqi, MD4, Bisher Sawaf, MD5, Muhammed Elhadi, MD6. P5414 - Etrolizumab as Induction and Maintenance Therapy in Patients With Moderately to Severely Active Ulcerative Colitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Sana’a University, Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences, Sana'a, Hadramawt, Yemen; 2Libyan International Medical University, Faculty of Medicine, Benghazi, Benghazi, Libya; 3Capital Health Regional Medical Center, Trenton, NJ; 4Raritan Bay Medical Center, Perth Amboy, NJ; 5University of Toledo Medical Center, Toledo, OH; 6College of Medicine, Korea University, Seongbuk, Seoul-t'ukpyolsi, Republic of Korea
Introduction: The treatment of ulcerative colitis remains crucial, and new advances in biologic treatments have further advanced the field. Etrolizumab, an anti-β7 integrin monoclonal antibody, has shown promising results in recent clinical trials. We aim in this meta-analysis to evaluate its efficacy as an induction and maintenance treatment option.
Methods: On November 15, 2024, a data search was conducted using PubMed, Scopus, and the Cochrane Library. Our inclusion criteria were any controlled clinical trials comparing the use of Etrolizumab to placebo in moderate-to-severe ulcerative colitis. The studied outcomes were clinical response, clinical remission, endoscopic improvements, endoscopic remission, and histologic remission. We used the odds ratio with the 95% confidence interval to estimate the effect size. A random-effects model was used.
Results: Out of 354 articles screened, only 5 were eligible, with a total of 1808 patients. Etrolizumab had a significant clinical response compared to placebo with an odds ratio of 1.60 [CI:1.23 to 2.09, p < 0.001]. Clinical remission was evaluated in both the induction and maintenance groups, and it was significantly higher in the induction group with an odds ratio of 2.85 [CI: 1.63 to 4.99, p < 0.001]. However, there was no significant difference in the maintenance group [OR: 1.43, CI: 0.91 to 2.23, p = 0.12]. In our evaluation of endoscopic improvement, etrolizumab showed significant improvement in both the induction and maintenance groups, with an odds ratio of 1.72 [CI: 1.24 to 2.40, p = 0.001] and 2.09 [CI: 1.37 to 3.20, p < 0.001], respectively. Similar results were observed for endoscopic remission, both the induction and maintenance groups had significant results, with an odds ratio of 2.50 [1.52 to 4.12, p < 0.001] and 2.27 [1.39 to 3.70, p = 0.001], respectively. Finally, histologic remission was only significant for the maintenance group. The odds ratios for induction and maintenance were 1.93 [CI: 1.01 to 3.68, p = 0.05] and 2.67 [CI: 1.61 to 4.41, p < 0.001], respectively.
Discussion: Etrolizumab is an effective option for both induction and maintenance treatment of moderate-to-severe ulcerative colitis. It has a positive impact on clinical response and remission, as well as on endoscopic and histologic endpoints.

Figure: Figure 1: Clinical Response

Figure: Figure 2: Endoscopic Remission
Disclosures:
Mohammed Beshr indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rana Shembesh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Abdallah Khashan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mageda Al Areqi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Bisher Sawaf indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammed Elhadi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohammed S. Beshr, MBBS1, Rana H. Shembesh, MBBCh2, Abdallah Khashan, MD3, Mageda Al Areqi, MD4, Bisher Sawaf, MD5, Muhammed Elhadi, MD6. P5414 - Etrolizumab as Induction and Maintenance Therapy in Patients With Moderately to Severely Active Ulcerative Colitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
