Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Interventional Endoscopy
P5680 - Long-Term Outcomes of Transoral Outlet Reduction for Weight Regain After Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Tuesday, October 28, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Samreen Jawaid, MD
Indiana University School of Medicine
Indianapolis, IN
Presenting Author(s)
Fortunato S. Principe-Meneses, MD1, Luis G.. Azanedo-Garcia, MD2, Ambar Godoy, MD3, Daniel Guifarro Rivera, MD4, Samreen Jawaid, MD3, Leandro Sierra, MD5, Mirian Ramirez-Rojas, 6, Renato Beas, MD7, Dalton A. Norwood, MD8, Eleazar E.. Montalvan-Sanchez, MD9
1Universidad Peruana de Ciencias Aplicadas (UPC), Lima, Lima, Peru; 2Universidad Peruana de Ciencias Aplicadas, Lima, Perú., Orlando, FL; 3Indiana University, Indianapolis, IN; 4Cook County Health and Hospital Systems, Chicago, IL; 5Department of Internal Medicine, Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH; 6Ruth Lilly Medical Library, Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis, IN; 7Washington University in St Louis, St. Louis, MO; 8University of Alabama at Birmingham, Birmingham, AL; 9Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, CT
Introduction: Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB) is a well-established bariatric procedure; however, weight regain remains a significant concern, affecting up to 30% of patients. Transoral outlet reduction (TORe) is an endoscopic intervention that reduces the size of the gastrojejunal anastomosis (GJA) to address post-RYGB weight regain. We conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis to evaluate long term effectiveness of TORe in this population.
Methods: A comprehensive search of six databases (Pubmed, Embase, Scopus, Web of Science, CINAHL and Cochrane Library) was performed until 2024. Studies reporting ≥12 months of follow-up after TORe for weight regain post-RYGB were included. Primary outcomes were the percentage of excess weight loss (%EWL). Secondary outcomes included reduction in GJA diameter and serious adverse events requiring surgery. A random-effects model was used to pool estimates. Heterogeneity was assessed using the I² statistic.
Results: Nine studies including 1,167 post-RYGB patients were analyzed. Most were female, aged 40–52. Serious adverse events requiring surgery were rare (1–3 patients/study). Pooled mean %EWL was 24.28% (95% CI: 19.55–29.01; p< 0.05) at 12 months (Figure 1A1), 19.65% (95% CI: 7.87–31.43; p< 0.05) at 24 months (Figure 1A2), and 10.74% (95% CI: −1.47 to 22.94; p=0.08) at 36 months (Figure 1B1). TORe significantly reduced GJA diameter by 17.11 mm (95% CI: 13.37–20.85; p< 0.05) (Figure 1B2). Study identification and selection process is summarized in the PRISMA diagram (Figure 2).
Discussion: TORe is a safe and effective endoscopic treatment for weight regain following RYGB, demonstrating durable outcomes with significant weight loss through 12 and 24 months. Although weight loss at 36 months showed a positive trend, it did not reach statistical significance, highlighting the need for further long-term studies. TORe is associated with a low rate of serious adverse events. This meta-analysis is unique as it evaluates long-term outcomes beyond one year, reinforcing the sustained benefit of TORe as a minimally invasive alternative to surgical revision. These findings support its role in the long-term management of post-bypass weight regain.
Figure: Forest-plot showing the effect of Mean Percentage of Excess Body Weight (%) Loss at 12, 24 and 36 months and change in Gastrojejunal Anastomosis (GJA).
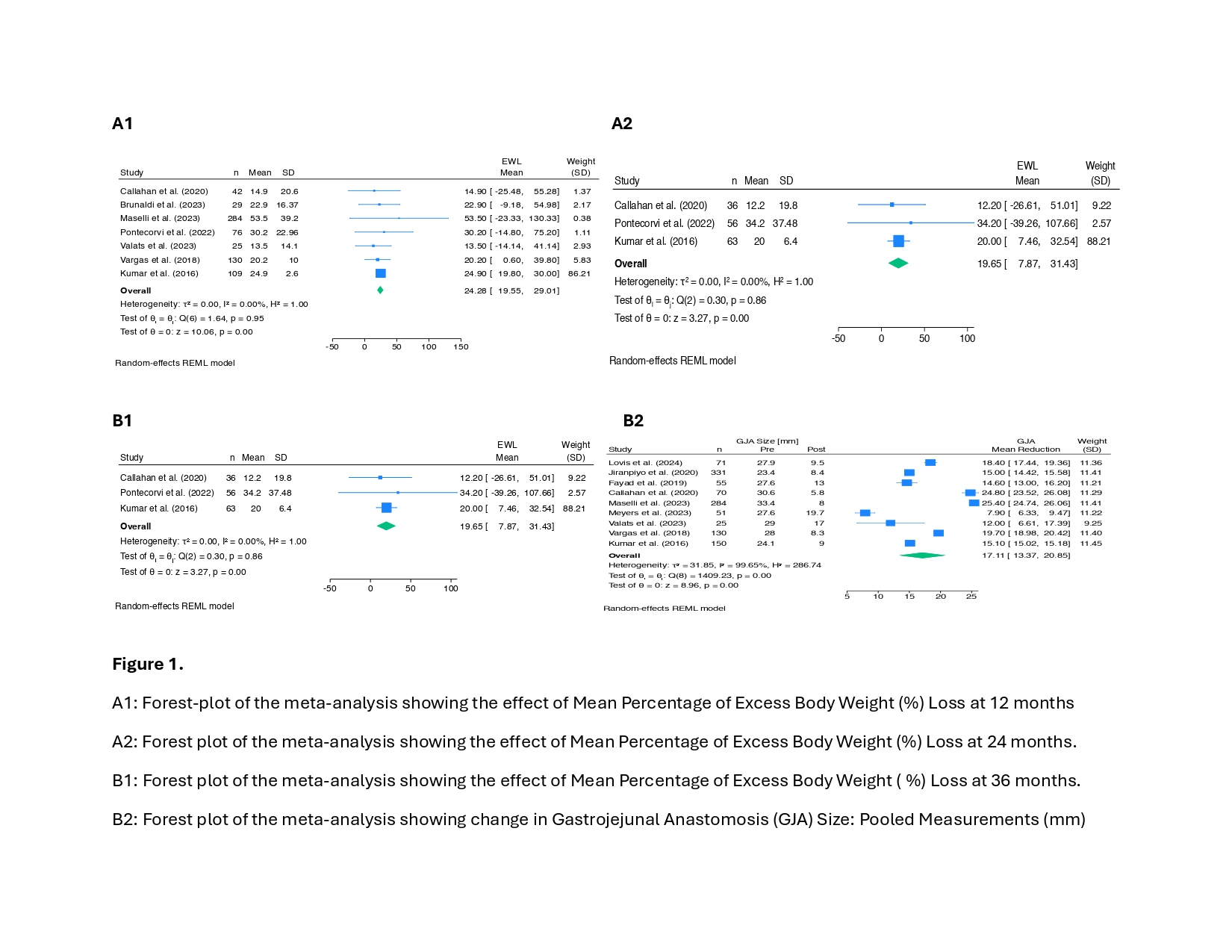
Figure: PRISMA flow diagram of study identification, screening, eligibility, and inclusion
Disclosures:
Fortunato S. Principe-Meneses indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Luis Azanedo-Garcia indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ambar Godoy indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Daniel Guifarro Rivera indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Samreen Jawaid indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Leandro Sierra indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mirian Ramirez-Rojas indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Renato Beas indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Dalton Norwood indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Eleazar Montalvan-Sanchez indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Fortunato S. Principe-Meneses, MD1, Luis G.. Azanedo-Garcia, MD2, Ambar Godoy, MD3, Daniel Guifarro Rivera, MD4, Samreen Jawaid, MD3, Leandro Sierra, MD5, Mirian Ramirez-Rojas, 6, Renato Beas, MD7, Dalton A. Norwood, MD8, Eleazar E.. Montalvan-Sanchez, MD9. P5680 - Long-Term Outcomes of Transoral Outlet Reduction for Weight Regain After Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Universidad Peruana de Ciencias Aplicadas (UPC), Lima, Lima, Peru; 2Universidad Peruana de Ciencias Aplicadas, Lima, Perú., Orlando, FL; 3Indiana University, Indianapolis, IN; 4Cook County Health and Hospital Systems, Chicago, IL; 5Department of Internal Medicine, Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH; 6Ruth Lilly Medical Library, Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis, IN; 7Washington University in St Louis, St. Louis, MO; 8University of Alabama at Birmingham, Birmingham, AL; 9Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, CT
Introduction: Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB) is a well-established bariatric procedure; however, weight regain remains a significant concern, affecting up to 30% of patients. Transoral outlet reduction (TORe) is an endoscopic intervention that reduces the size of the gastrojejunal anastomosis (GJA) to address post-RYGB weight regain. We conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis to evaluate long term effectiveness of TORe in this population.
Methods: A comprehensive search of six databases (Pubmed, Embase, Scopus, Web of Science, CINAHL and Cochrane Library) was performed until 2024. Studies reporting ≥12 months of follow-up after TORe for weight regain post-RYGB were included. Primary outcomes were the percentage of excess weight loss (%EWL). Secondary outcomes included reduction in GJA diameter and serious adverse events requiring surgery. A random-effects model was used to pool estimates. Heterogeneity was assessed using the I² statistic.
Results: Nine studies including 1,167 post-RYGB patients were analyzed. Most were female, aged 40–52. Serious adverse events requiring surgery were rare (1–3 patients/study). Pooled mean %EWL was 24.28% (95% CI: 19.55–29.01; p< 0.05) at 12 months (Figure 1A1), 19.65% (95% CI: 7.87–31.43; p< 0.05) at 24 months (Figure 1A2), and 10.74% (95% CI: −1.47 to 22.94; p=0.08) at 36 months (Figure 1B1). TORe significantly reduced GJA diameter by 17.11 mm (95% CI: 13.37–20.85; p< 0.05) (Figure 1B2). Study identification and selection process is summarized in the PRISMA diagram (Figure 2).
Discussion: TORe is a safe and effective endoscopic treatment for weight regain following RYGB, demonstrating durable outcomes with significant weight loss through 12 and 24 months. Although weight loss at 36 months showed a positive trend, it did not reach statistical significance, highlighting the need for further long-term studies. TORe is associated with a low rate of serious adverse events. This meta-analysis is unique as it evaluates long-term outcomes beyond one year, reinforcing the sustained benefit of TORe as a minimally invasive alternative to surgical revision. These findings support its role in the long-term management of post-bypass weight regain.

Figure: Forest-plot showing the effect of Mean Percentage of Excess Body Weight (%) Loss at 12, 24 and 36 months and change in Gastrojejunal Anastomosis (GJA).

Figure: PRISMA flow diagram of study identification, screening, eligibility, and inclusion
Disclosures:
Fortunato S. Principe-Meneses indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Luis Azanedo-Garcia indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ambar Godoy indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Daniel Guifarro Rivera indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Samreen Jawaid indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Leandro Sierra indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mirian Ramirez-Rojas indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Renato Beas indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Dalton Norwood indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Eleazar Montalvan-Sanchez indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Fortunato S. Principe-Meneses, MD1, Luis G.. Azanedo-Garcia, MD2, Ambar Godoy, MD3, Daniel Guifarro Rivera, MD4, Samreen Jawaid, MD3, Leandro Sierra, MD5, Mirian Ramirez-Rojas, 6, Renato Beas, MD7, Dalton A. Norwood, MD8, Eleazar E.. Montalvan-Sanchez, MD9. P5680 - Long-Term Outcomes of Transoral Outlet Reduction for Weight Regain After Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.

