Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Liver
P5932 - Analysis of the Outcomes of Septic Shock Patients With and Without MASLD: A United States Population-Based Cohort Study
Tuesday, October 28, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Guy Loic Nguefang Tchoukeu, MD (he/him/his)
Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center
Odessa, TX
Presenting Author(s)
Guy Loic Nguefang Tchoukeu, MD1, Sarpong Boateng, MD, MPH2, Ikechukwu Elvis. Eze, MBBS3, Yussif Issaka, MBChB4, Joel Gabin Konlack Mekontso, MD5, Anjul Verma, MD1, Prince A. Ameyaw, MD6, Chimezirim Ezeano, MD, MPH7, Yazan Al Ajlouni, MD, Mphil8, Basile Njei, MD, PhD, MPH9
1Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center, Odessa, TX; 2Yale New Haven Health, Bridgeport, CT; 3Yale University, New Haven, CT; 4Bridgeport Hospital, Bridgeport, CT; 5New York City Health and Hospitals, South Brooklyn Health, New York, NY; 6Yale New Haven Health, Bridgeport Hospital, Bridgeport, CT; 7Aurora Healthcare, Aurora, WI; 8Montefiore Medical Center, New York, NY; 9VA Connecticut Healthcare System and Yale University, West Haven, CT
Introduction: Septic shock is a severe and life-threatening manifestation of sepsis that carries a high risk of morbidity and mortality. The impact of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) on septic shock prognosis remains underexplored. Identifying factors influencing outcomes in septic shock is critical for risk stratification and targeted management. This study aimed to assess the association between MASLD and in-hospital outcomes among patients with septic shock.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective cohort study using the National Inpatient Sample (2016–2020) and included adult patients (≥18 years) hospitalized with a primary diagnosis of septic shock, using ICD-10-CM codes. Patients were stratified by MASLD status; those with other chronic or acute liver diseases, including viral hepatitis, were excluded from the MASLD cohort. Patients were stratified by MASLD status; those with other chronic or acute liver diseases, including viral hepatitis, were excluded from the MASLD cohort. A 1:1 propensity score matching was performed based on demographics, comorbidities, and hospital characteristics. Outcomes included in-hospital mortality, acute kidney injury (AKI), cardiac arrest, and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). Multivariable logistic regression was performed to assess adjusted associations between MASLD and outcomes.
Results: The final sample included 17,382 patients (8,691 with MASLD and 8,691 without). Mean age was comparable (59.9 vs. 59.8 years), with no significant racial differences (p = 0.717). Unadjusted mortality was lower in the MASLD group (27.8% vs. 33.0%; p < 0.0001). However, on multivariable analysis, MASLD was associated with increased odds of in-hospital mortality (aOR 1.283, 95% CI: 1.203–1.369; p < 0.0001) and AKI (aOR 1.071, 95% CI: 1.005–1.143; p = 0.036). Conversely, MASLD was associated with lower odds of cardiac arrest (aOR 0.625, 95% CI: 0.554–0.705; p < 0.0001) and ARDS (aOR 0.834, 95% CI: 0.784–0.888; p < 0.0001).
Discussion: Among patients hospitalized with septic shock, MASLD was independently associated with higher odds of mortality and AKI, but paradoxically lower odds of cardiac arrest and ARDS. These findings underscore the need for further mechanistic studies and MASLD-specific risk stratification strategies in critical care settings.
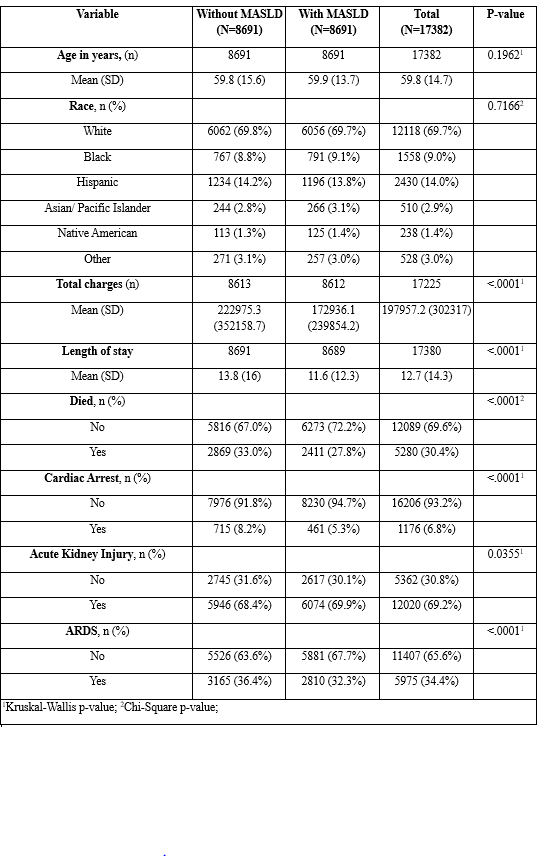
Figure: Baseline characteristics and outcomes of septic shock patients with and without MASLD
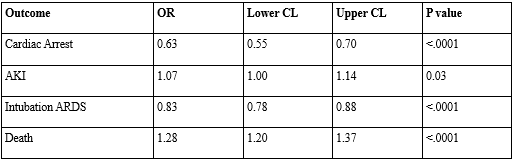
Figure: Adjusted Odds Ratios of Outcomes in Septic Shock Patients With MASLD Compared to Those Without MASLD
Disclosures:
Guy Loic Nguefang Tchoukeu indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sarpong Boateng indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ikechukwu Eze indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Yussif Issaka indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Joel Gabin Konlack Mekontso indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Anjul Verma indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Prince Ameyaw indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Chimezirim Ezeano indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Yazan Al Ajlouni indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Basile Njei indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Guy Loic Nguefang Tchoukeu, MD1, Sarpong Boateng, MD, MPH2, Ikechukwu Elvis. Eze, MBBS3, Yussif Issaka, MBChB4, Joel Gabin Konlack Mekontso, MD5, Anjul Verma, MD1, Prince A. Ameyaw, MD6, Chimezirim Ezeano, MD, MPH7, Yazan Al Ajlouni, MD, Mphil8, Basile Njei, MD, PhD, MPH9. P5932 - Analysis of the Outcomes of Septic Shock Patients With and Without MASLD: A United States Population-Based Cohort Study, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center, Odessa, TX; 2Yale New Haven Health, Bridgeport, CT; 3Yale University, New Haven, CT; 4Bridgeport Hospital, Bridgeport, CT; 5New York City Health and Hospitals, South Brooklyn Health, New York, NY; 6Yale New Haven Health, Bridgeport Hospital, Bridgeport, CT; 7Aurora Healthcare, Aurora, WI; 8Montefiore Medical Center, New York, NY; 9VA Connecticut Healthcare System and Yale University, West Haven, CT
Introduction: Septic shock is a severe and life-threatening manifestation of sepsis that carries a high risk of morbidity and mortality. The impact of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) on septic shock prognosis remains underexplored. Identifying factors influencing outcomes in septic shock is critical for risk stratification and targeted management. This study aimed to assess the association between MASLD and in-hospital outcomes among patients with septic shock.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective cohort study using the National Inpatient Sample (2016–2020) and included adult patients (≥18 years) hospitalized with a primary diagnosis of septic shock, using ICD-10-CM codes. Patients were stratified by MASLD status; those with other chronic or acute liver diseases, including viral hepatitis, were excluded from the MASLD cohort. Patients were stratified by MASLD status; those with other chronic or acute liver diseases, including viral hepatitis, were excluded from the MASLD cohort. A 1:1 propensity score matching was performed based on demographics, comorbidities, and hospital characteristics. Outcomes included in-hospital mortality, acute kidney injury (AKI), cardiac arrest, and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). Multivariable logistic regression was performed to assess adjusted associations between MASLD and outcomes.
Results: The final sample included 17,382 patients (8,691 with MASLD and 8,691 without). Mean age was comparable (59.9 vs. 59.8 years), with no significant racial differences (p = 0.717). Unadjusted mortality was lower in the MASLD group (27.8% vs. 33.0%; p < 0.0001). However, on multivariable analysis, MASLD was associated with increased odds of in-hospital mortality (aOR 1.283, 95% CI: 1.203–1.369; p < 0.0001) and AKI (aOR 1.071, 95% CI: 1.005–1.143; p = 0.036). Conversely, MASLD was associated with lower odds of cardiac arrest (aOR 0.625, 95% CI: 0.554–0.705; p < 0.0001) and ARDS (aOR 0.834, 95% CI: 0.784–0.888; p < 0.0001).
Discussion: Among patients hospitalized with septic shock, MASLD was independently associated with higher odds of mortality and AKI, but paradoxically lower odds of cardiac arrest and ARDS. These findings underscore the need for further mechanistic studies and MASLD-specific risk stratification strategies in critical care settings.

Figure: Baseline characteristics and outcomes of septic shock patients with and without MASLD

Figure: Adjusted Odds Ratios of Outcomes in Septic Shock Patients With MASLD Compared to Those Without MASLD
Disclosures:
Guy Loic Nguefang Tchoukeu indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sarpong Boateng indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ikechukwu Eze indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Yussif Issaka indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Joel Gabin Konlack Mekontso indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Anjul Verma indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Prince Ameyaw indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Chimezirim Ezeano indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Yazan Al Ajlouni indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Basile Njei indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Guy Loic Nguefang Tchoukeu, MD1, Sarpong Boateng, MD, MPH2, Ikechukwu Elvis. Eze, MBBS3, Yussif Issaka, MBChB4, Joel Gabin Konlack Mekontso, MD5, Anjul Verma, MD1, Prince A. Ameyaw, MD6, Chimezirim Ezeano, MD, MPH7, Yazan Al Ajlouni, MD, Mphil8, Basile Njei, MD, PhD, MPH9. P5932 - Analysis of the Outcomes of Septic Shock Patients With and Without MASLD: A United States Population-Based Cohort Study, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
