Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Liver
P5929 - Safety and Efficacy of Efruxifermin in Patients With Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Tuesday, October 28, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Calvin Ghimire, MD (he/him/his)
Princeton Community Hospital/West Virginia University
Princeton, WV
Presenting Author(s)
Amira M. Taha, 1, Ahmed Saad Elsaeidy, 2, Marwa Muhammed. Abdeljawad, BSc3, Sadish Sharma, MBBS4, Mohamed Tarek Hasan, 5, Hanaa Abdelmoneim Kamel, MBBCh6, Calvin Ghimire, MD7
1Fayoum University, Faculty of Medicine, Fayoum, Al Fayyum, Egypt; 2Benha University, Benha, Al Qalyubiyah, Egypt; 3MARS global, Giza, Al Jizah, Egypt; 4College of Medical Sciences, Bharatpur, Bharatpur, Bagmati, Nepal; 5, Al-Azhar University, Cairo, Al Minufiyah, Egypt; 6Rheumatology Department, Al Haram Hospital, El Omraniya, Al Jizah, Egypt; 7Princeton Community Hospital/West Virginia University, Princeton, WV
Introduction: Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) is an advanced form of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, closely linked with metabolic syndromes. Despite its prevalence, effective treatments are limited. This meta-analysis aimed to assess Efruxifermin's efficacy and safety in NASH patients.
Methods: We conducted an extensive search in PubMed, Scopus, Cochrane, and Web of Science until 30 October 2023, focusing on randomized clinical trials comparing Eefruxifermin to placebo in NASH patients. Dichotomous data were analyzed as risk ratio (RR) and 95% confidence interval (CI) using R software for data analysi
Results: Three randomized controlled trials (RCTs) were included. Efruxifermin compared to placebo showed a significant improvement in liver fibrosis (≥1 stages) and no worsening of NASH at doses of 28 mg (RR = 22.5; 95% CI: 3.19, 158.72) and 50 mg (RR = 18.22; 95% CI: 3.44, 96.56). Improvement in liver fibrosis (≥1 stage) and resolution of NASH were observed at 28 mg (RR = 6.39; 95% CI: 1.78, 23.01) and 50 mg (RR = 7.49; 95% CI: 2.29, 24.57). The 70 mg dosage showed no significant benefits. No significant increase in serious adverse events was noted across all dosages.
Discussion: Our analysis indicated Efruxifermin, especially at doses of 28 mg and 50 mg, as a promising therapeutic agent for NASH with significant improvements in liver fibrosis and NASH markers with a manageable safety profile. These findings highlight Efruxifermin's potential as a key intervention in the treatment of NASH, warranting further investigation and clinical application.
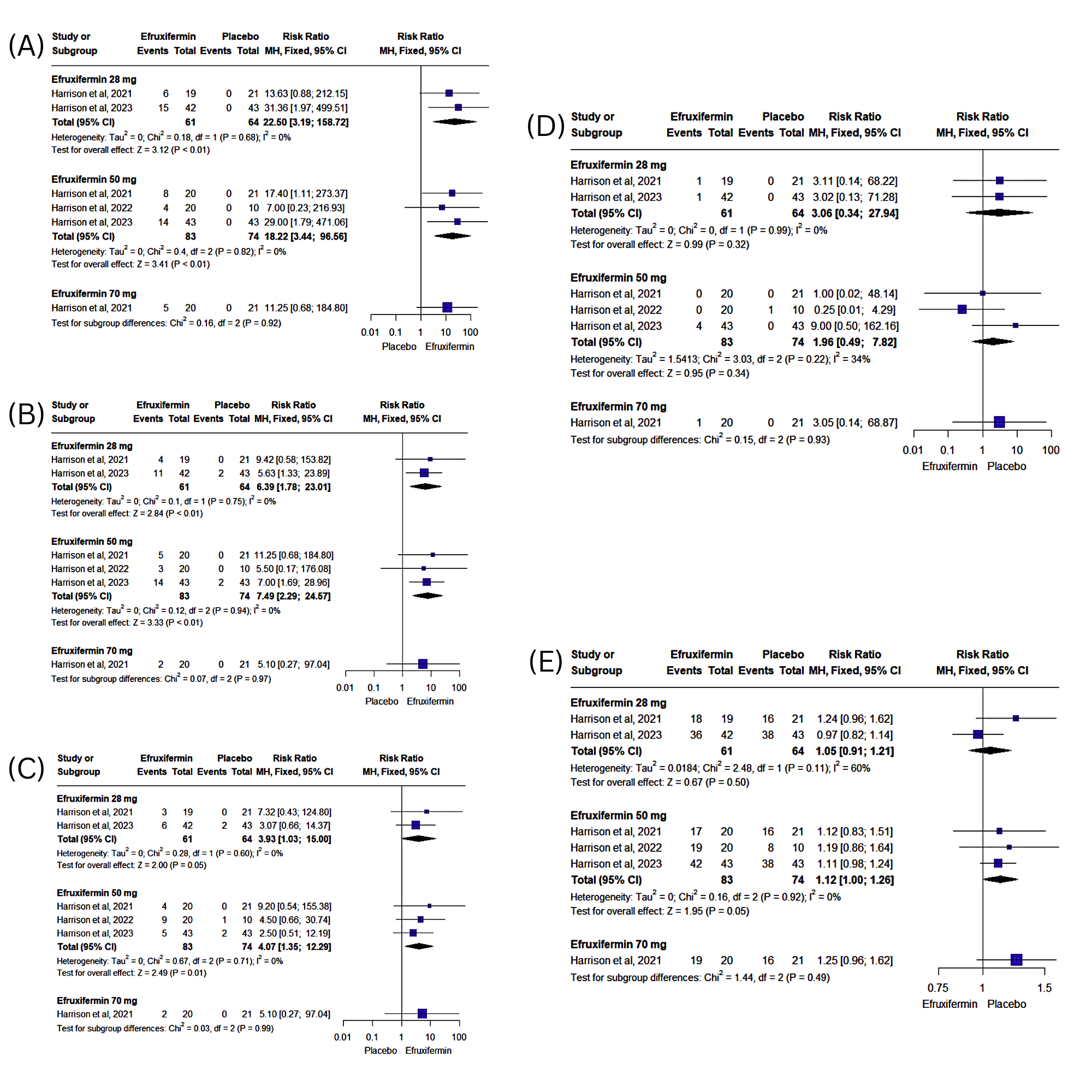
Figure: Forest Plots
Disclosures:
Amira M. Taha indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ahmed Saad Elsaeidy indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Marwa Abdeljawad indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sadish Sharma indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohamed Tarek Hasan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hanaa Abdelmoneim Kamel indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Calvin Ghimire indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Amira M. Taha, 1, Ahmed Saad Elsaeidy, 2, Marwa Muhammed. Abdeljawad, BSc3, Sadish Sharma, MBBS4, Mohamed Tarek Hasan, 5, Hanaa Abdelmoneim Kamel, MBBCh6, Calvin Ghimire, MD7. P5929 - Safety and Efficacy of Efruxifermin in Patients With Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Fayoum University, Faculty of Medicine, Fayoum, Al Fayyum, Egypt; 2Benha University, Benha, Al Qalyubiyah, Egypt; 3MARS global, Giza, Al Jizah, Egypt; 4College of Medical Sciences, Bharatpur, Bharatpur, Bagmati, Nepal; 5, Al-Azhar University, Cairo, Al Minufiyah, Egypt; 6Rheumatology Department, Al Haram Hospital, El Omraniya, Al Jizah, Egypt; 7Princeton Community Hospital/West Virginia University, Princeton, WV
Introduction: Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) is an advanced form of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, closely linked with metabolic syndromes. Despite its prevalence, effective treatments are limited. This meta-analysis aimed to assess Efruxifermin's efficacy and safety in NASH patients.
Methods: We conducted an extensive search in PubMed, Scopus, Cochrane, and Web of Science until 30 October 2023, focusing on randomized clinical trials comparing Eefruxifermin to placebo in NASH patients. Dichotomous data were analyzed as risk ratio (RR) and 95% confidence interval (CI) using R software for data analysi
Results: Three randomized controlled trials (RCTs) were included. Efruxifermin compared to placebo showed a significant improvement in liver fibrosis (≥1 stages) and no worsening of NASH at doses of 28 mg (RR = 22.5; 95% CI: 3.19, 158.72) and 50 mg (RR = 18.22; 95% CI: 3.44, 96.56). Improvement in liver fibrosis (≥1 stage) and resolution of NASH were observed at 28 mg (RR = 6.39; 95% CI: 1.78, 23.01) and 50 mg (RR = 7.49; 95% CI: 2.29, 24.57). The 70 mg dosage showed no significant benefits. No significant increase in serious adverse events was noted across all dosages.
Discussion: Our analysis indicated Efruxifermin, especially at doses of 28 mg and 50 mg, as a promising therapeutic agent for NASH with significant improvements in liver fibrosis and NASH markers with a manageable safety profile. These findings highlight Efruxifermin's potential as a key intervention in the treatment of NASH, warranting further investigation and clinical application.

Figure: Forest Plots
Disclosures:
Amira M. Taha indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ahmed Saad Elsaeidy indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Marwa Abdeljawad indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sadish Sharma indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohamed Tarek Hasan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hanaa Abdelmoneim Kamel indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Calvin Ghimire indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Amira M. Taha, 1, Ahmed Saad Elsaeidy, 2, Marwa Muhammed. Abdeljawad, BSc3, Sadish Sharma, MBBS4, Mohamed Tarek Hasan, 5, Hanaa Abdelmoneim Kamel, MBBCh6, Calvin Ghimire, MD7. P5929 - Safety and Efficacy of Efruxifermin in Patients With Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
