Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Liver
P5914 - The Deadly Consequence of In-Hospital Infections in Acute and Subacute Liver Failure: A National Inpatient Sample Study (2016-2022)
Tuesday, October 28, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Usama Sakhawat, MD
United Health Services, Wilson Medical Center
BINGHAMTON, NY
Presenting Author(s)
Usama Sakhawat, MD1, Najam Gohar, MBBS2, Abdul Mateen, MBBS3, Harris Tahir Chaudhry, MBBS3, Haziq Ahmad, MBBS4, Faizan A. Malik, MD5, Tehmasp Rehman Mirza, MBBS6, Muhammad Junaid Zahid, MBBS3, Hinza Hassan, MBBS7, Taha Muhammad Hannan, MBBS3, Muhammad Usman Azeem, MBBS3, Ahmed Shehadah, MD8, Khandokar Talib, MD9, Toseef Javaid, MD1
1United Health Services, Wilson Medical Center, Johnson City, NY; 2Ameer Ud Din Medical College, Lahore, NY; 3Ameer Ud Din Medical College, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan; 4Sheikh Khalifa Bin Zayed Al Nahyan Medical and Dental College, Lahore, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan; 5Duke University, Durham, NC; 6MBBS, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan; 7Allama Iqbal Medical College, Lahore, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan; 8United Health Services, Wilson Medical Center, Binghamton, NY; 9United Health Services, Johnson City, NY
Introduction: Acute and subacute liver failure (ALF and SLF) are severe conditions characterized by rapid deterioration of liver function and are often accompanied by infections. However, the specific impact of infections on in-hospital outcomes in ALF and SLF patients remains underexplored. We evaluated the influence of infections on in-hospital outcomes in ALF and SLF patients using the National Inpatient Sample (NIS) database.
Methods: A retrospective study of the NIS database was performed using ICD-10-CM codes to identify hospitalizations for ALF and SLF. Hospitalizations were stratified by the presence or absence of infection. Weighted univariate Chi-square tests and t-tests were used to compare baseline characteristics and outcomes. Multivariable survey logistic and linear regression were used to evaluate the association between infection and in-hospital outcomes. All models were adjusted for potential confounders including demographics and comorbidities.
Results: There were 179,000 ALF and SLF hospitalizations, out of which 43,000 (24%) were associated with infection. Infections were more prevalent in females (58.41% with infections vs 43.55% without; p< 0.0001), patients over 70 years (24.42% vs 21.12%; p< 0.0001), those with congestive heart failure (15.96% vs 12.61%; p< 0.0001) and those with chronic liver disease (13.27% vs 11.71%; p=0.0001). Infected patients had increased in-hospital mortality (18.64% vs 7.49%, adjusted odds ratio, aOR 2.89; 95% confidence interval, CI 2.66-3.13; p< 0.0001), longer length of stay (LOS) by 3.95 days (95% CI 3.60-4.30; p< 0.0001), and higher total hospital charges by $72,991 (95% CI $64,567-$81,415; p< 0.0001). Infected patients also experienced significantly higher rates of complications including acute kidney injury (54.8% vs 36.9%), encephalopathy (22.2% vs 12.2%), mechanical ventilation requirement (19.6% vs 6.0%), arrhythmia (16.5% vs 13.0%), hepatorenal syndrome (14.9% vs 8.5%), and GI bleeding (10.6% vs 6.5%) (all p< 0.0001).
Discussion: Our study demonstrates that infection is a strong negative prognostic indicator in patients hospitalized with ALF and SLF, independently associated with significantly worse in-hospital outcomes. Early recognition and targeted antimicrobial management of infections are essential to improving prognosis. Further prospective studies are needed to evaluate whether timely antimicrobial interventions and preventive strategies can reduce morbidity and mortality in ALF and SLF patients.
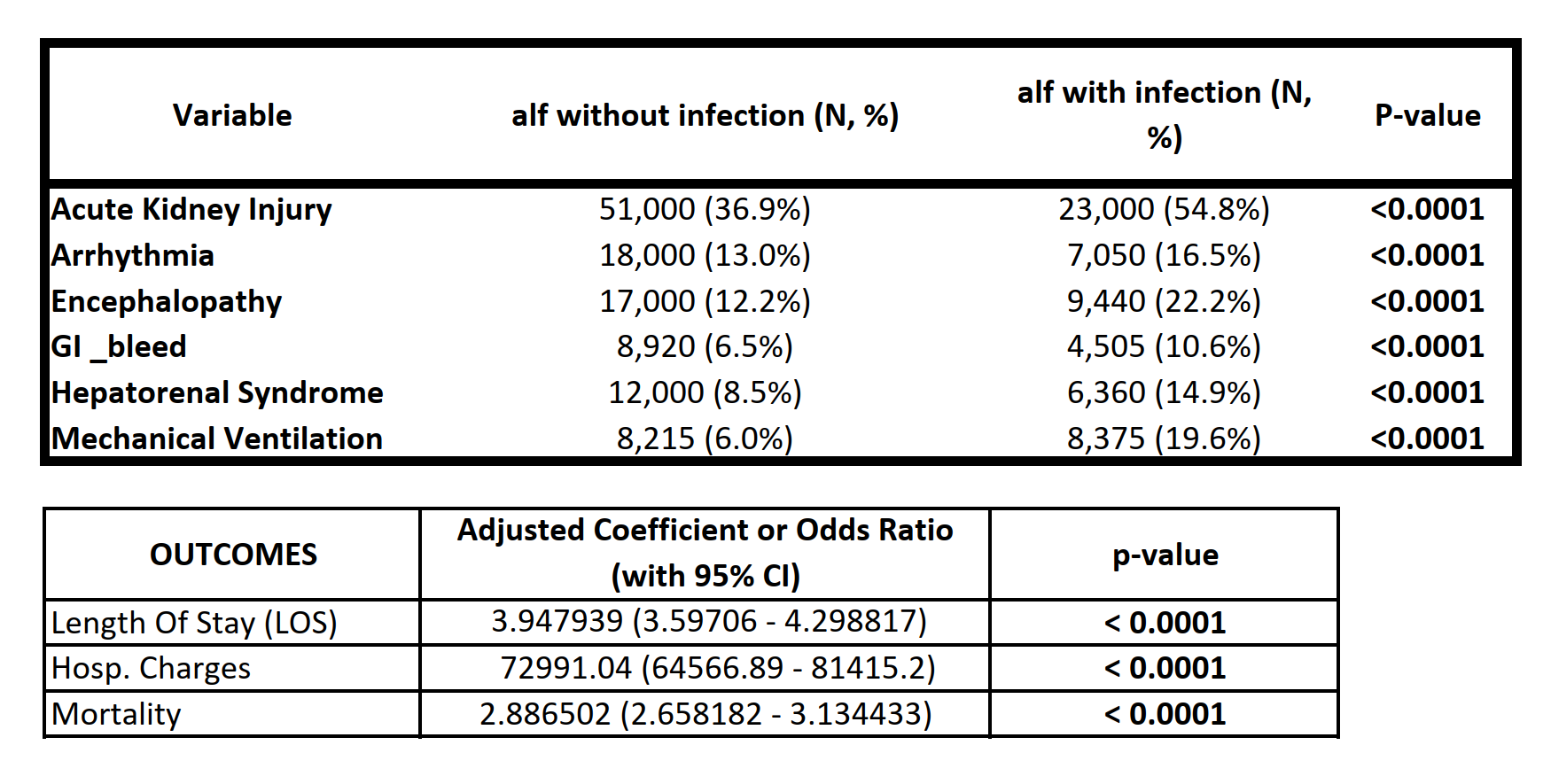
Figure: Figure 1- Baseline Characteristics
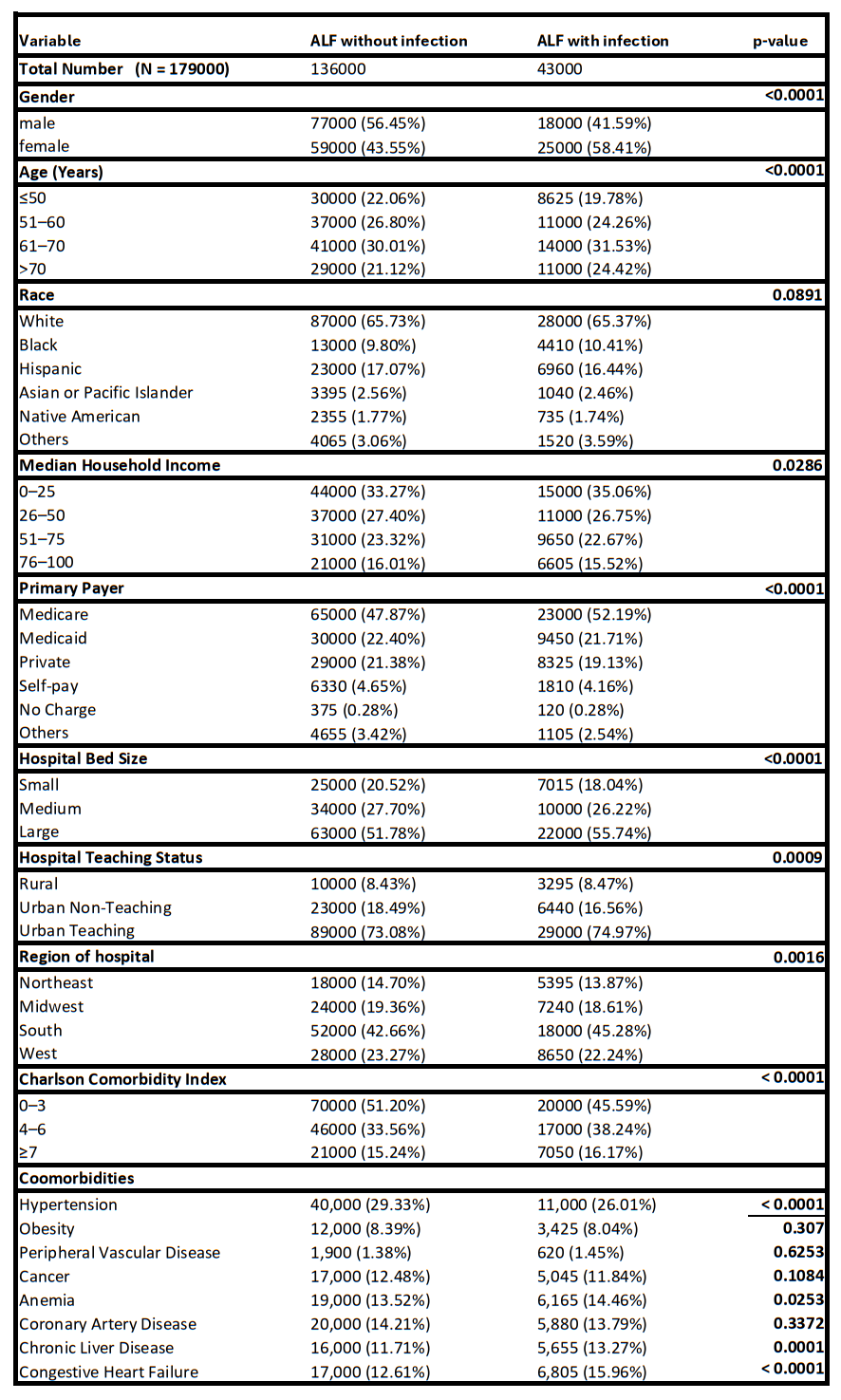
Figure: Figure 2- Complications and Outcomes
Disclosures:
Usama Sakhawat indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Najam Gohar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Abdul Mateen indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Harris Tahir Chaudhry indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Haziq Ahmad indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Faizan A. Malik indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Tehmasp Rehman Mirza indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Junaid Zahid indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hinza Hassan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Taha Muhammad Hannan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Usman Azeem indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ahmed Shehadah indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Khandokar Talib indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Toseef Javaid indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Usama Sakhawat, MD1, Najam Gohar, MBBS2, Abdul Mateen, MBBS3, Harris Tahir Chaudhry, MBBS3, Haziq Ahmad, MBBS4, Faizan A. Malik, MD5, Tehmasp Rehman Mirza, MBBS6, Muhammad Junaid Zahid, MBBS3, Hinza Hassan, MBBS7, Taha Muhammad Hannan, MBBS3, Muhammad Usman Azeem, MBBS3, Ahmed Shehadah, MD8, Khandokar Talib, MD9, Toseef Javaid, MD1. P5914 - The Deadly Consequence of In-Hospital Infections in Acute and Subacute Liver Failure: A National Inpatient Sample Study (2016-2022), ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1United Health Services, Wilson Medical Center, Johnson City, NY; 2Ameer Ud Din Medical College, Lahore, NY; 3Ameer Ud Din Medical College, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan; 4Sheikh Khalifa Bin Zayed Al Nahyan Medical and Dental College, Lahore, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan; 5Duke University, Durham, NC; 6MBBS, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan; 7Allama Iqbal Medical College, Lahore, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan; 8United Health Services, Wilson Medical Center, Binghamton, NY; 9United Health Services, Johnson City, NY
Introduction: Acute and subacute liver failure (ALF and SLF) are severe conditions characterized by rapid deterioration of liver function and are often accompanied by infections. However, the specific impact of infections on in-hospital outcomes in ALF and SLF patients remains underexplored. We evaluated the influence of infections on in-hospital outcomes in ALF and SLF patients using the National Inpatient Sample (NIS) database.
Methods: A retrospective study of the NIS database was performed using ICD-10-CM codes to identify hospitalizations for ALF and SLF. Hospitalizations were stratified by the presence or absence of infection. Weighted univariate Chi-square tests and t-tests were used to compare baseline characteristics and outcomes. Multivariable survey logistic and linear regression were used to evaluate the association between infection and in-hospital outcomes. All models were adjusted for potential confounders including demographics and comorbidities.
Results: There were 179,000 ALF and SLF hospitalizations, out of which 43,000 (24%) were associated with infection. Infections were more prevalent in females (58.41% with infections vs 43.55% without; p< 0.0001), patients over 70 years (24.42% vs 21.12%; p< 0.0001), those with congestive heart failure (15.96% vs 12.61%; p< 0.0001) and those with chronic liver disease (13.27% vs 11.71%; p=0.0001). Infected patients had increased in-hospital mortality (18.64% vs 7.49%, adjusted odds ratio, aOR 2.89; 95% confidence interval, CI 2.66-3.13; p< 0.0001), longer length of stay (LOS) by 3.95 days (95% CI 3.60-4.30; p< 0.0001), and higher total hospital charges by $72,991 (95% CI $64,567-$81,415; p< 0.0001). Infected patients also experienced significantly higher rates of complications including acute kidney injury (54.8% vs 36.9%), encephalopathy (22.2% vs 12.2%), mechanical ventilation requirement (19.6% vs 6.0%), arrhythmia (16.5% vs 13.0%), hepatorenal syndrome (14.9% vs 8.5%), and GI bleeding (10.6% vs 6.5%) (all p< 0.0001).
Discussion: Our study demonstrates that infection is a strong negative prognostic indicator in patients hospitalized with ALF and SLF, independently associated with significantly worse in-hospital outcomes. Early recognition and targeted antimicrobial management of infections are essential to improving prognosis. Further prospective studies are needed to evaluate whether timely antimicrobial interventions and preventive strategies can reduce morbidity and mortality in ALF and SLF patients.

Figure: Figure 1- Baseline Characteristics

Figure: Figure 2- Complications and Outcomes
Disclosures:
Usama Sakhawat indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Najam Gohar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Abdul Mateen indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Harris Tahir Chaudhry indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Haziq Ahmad indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Faizan A. Malik indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Tehmasp Rehman Mirza indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Junaid Zahid indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hinza Hassan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Taha Muhammad Hannan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Usman Azeem indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ahmed Shehadah indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Khandokar Talib indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Toseef Javaid indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Usama Sakhawat, MD1, Najam Gohar, MBBS2, Abdul Mateen, MBBS3, Harris Tahir Chaudhry, MBBS3, Haziq Ahmad, MBBS4, Faizan A. Malik, MD5, Tehmasp Rehman Mirza, MBBS6, Muhammad Junaid Zahid, MBBS3, Hinza Hassan, MBBS7, Taha Muhammad Hannan, MBBS3, Muhammad Usman Azeem, MBBS3, Ahmed Shehadah, MD8, Khandokar Talib, MD9, Toseef Javaid, MD1. P5914 - The Deadly Consequence of In-Hospital Infections in Acute and Subacute Liver Failure: A National Inpatient Sample Study (2016-2022), ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
