Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Liver
P5913 - Systemic Inflammation Response Index (SIRI) as an Independent Predictor of In-Hospital Mortality in Critically Ill Cirrhotic Patients: A MIMIC-IV Based Study
Tuesday, October 28, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Usama Sakhawat, MD
United Health Services, Wilson Medical Center
BINGHAMTON, NY
Presenting Author(s)
Usama Sakhawat, MD1, Ahmed Shehadah, MD2, Anfal Hamza, MBBS3, Atif Nawaz Malik, MBBS3, Muhammad Sufyan, MBBS4, Muhammad Hammad Iqbal, MBBS5, Arbaz Hassan, MBBS3, Allah Dad, MD6, Muhammad Tasawar. Latif, MD7, Ahsan A. Nawaz, 8, Faseeh Haider, MD9, Faizan Ahmad, MD10, Kinza Bakht, MBBS11, Tehmasp Rehman Mirza, MBBS12, Rama Hassan, MBBS13, Moheudin Khan, MD1, Abdul Basit, MBBS14, Amanke Oranu, MD2
1United Health Services, Wilson Medical Center, Johnson City, NY; 2United Health Services, Wilson Medical Center, Binghamton, NY; 3Sheikh Zayed Medical College, Rahim Yar Khan, Pakistan, Rahim Yar Khan, Punjab, Pakistan; 4Quaid-e-Azam Medical College, Bahawalpur, Bahawalpur, Punjab, Pakistan; 5Sheikh Zayed Medical College, RYK, Rahim Yar Khan, Punjab, Pakistan; 6Shiekh Zayed Medical College Rahim Yar Khan, Pakistan, Kot Addu, Punjab, Pakistan; 7Yale New Haven Hospital, Middlebury, CT; 8Holy Family Hospital, Rawalpindi, Bhakkar, Punjab, Pakistan; 9Allama Iqbal Medical college, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan; 10Duke University, Durham, NC; 11Sheikh Zayed Medical College Rahim Yar Khan, Muzaffargarh, Punjab, Pakistan; 12MBBS, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan; 13Akhtar Saeed Medical and Dental College, Lahore, Binghamton, NY; 14Quaid-e-Azam Medical College, Bahwalpur, Punjab, Pakistan
Introduction: The incidence of liver cirrhosis (LC) remains high throughout the world, posing a serious threat to human health, with repeated inflammation, repair and fibrosis being the pivotal factors in the entire pathophysiologic process. Systemic inflammatory response index (SIRI) is the novel indicator for poor prognosis of liver cirrhosis. The aim of this study was to evaluate its prognostic value and the correlation between SIRI and mortality in critically ill liver cirrhosis patients.
Methods: This retrospective study analyzed critically ill cirrhotic patients admitted to the ICU (2008–2019) using the MIMIC-IV database. Patient demographics, comorbid conditions, laboratory results, and mortality data were extracted. The systemic inflammation response index (calculated as = neutrophils × monocytes / lymphocytes) was calculated in Excel and categorized as high (≥4.35) or low (≤4.35). Patients with missing baseline labs were excluded. Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS v26. Descriptive statistics (mean and SD, frequency and percentages), chi-square tests, and multivariate regression (adjusted for confounders) assessed associations and mortality risk. ROC curves evaluated predictive value, and Kaplan–Meier analysis (log-rank test) compared survival. A p-value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results: Of 2,344 critically ill cirrhotic patients (61.2% male, mean age 58.7±12.9 years), 28.5% (668) died in-hospital. Non-survivors were older (61.2±11.7 vs. 57.7±13.3, p< 0.001) and had more comorbidities (renal disease, severe liver disease, heart failure). Mortality group had higher SIRI (6.8 [5.3–9.2] vs. 4.2 [3.1–6.2], p< 0.001), SOFA, and APSIII scores, and lower albumin and calcium. Multivariable logistic regression confirmed SIRI as an independent mortality predictor (OR 1.007, 95% CI: p=0.027) alongside lower SpO₂, temperature, albumin, higher SOFA, and older age (AUC=0.799). ROC analysis showed SIRI’s modest predictive ability (AUC=0.61, cutoff 4.35, 69.3% sensitivity, 53.3% specificity). Kaplan-Meier analysis confirmed worse survival for SIRI ≥4.35 (log-rank p< 0.001).
Discussion: High SIRI (≥4.35) was significantly associated with raised in-hospital mortality in the critically ill cirrhotic patients and independently predicted mortality with moderate discriminatory ability. Moreover, Kaplan–Meier analysis demonstrated poorer survival in the high SIRI group.
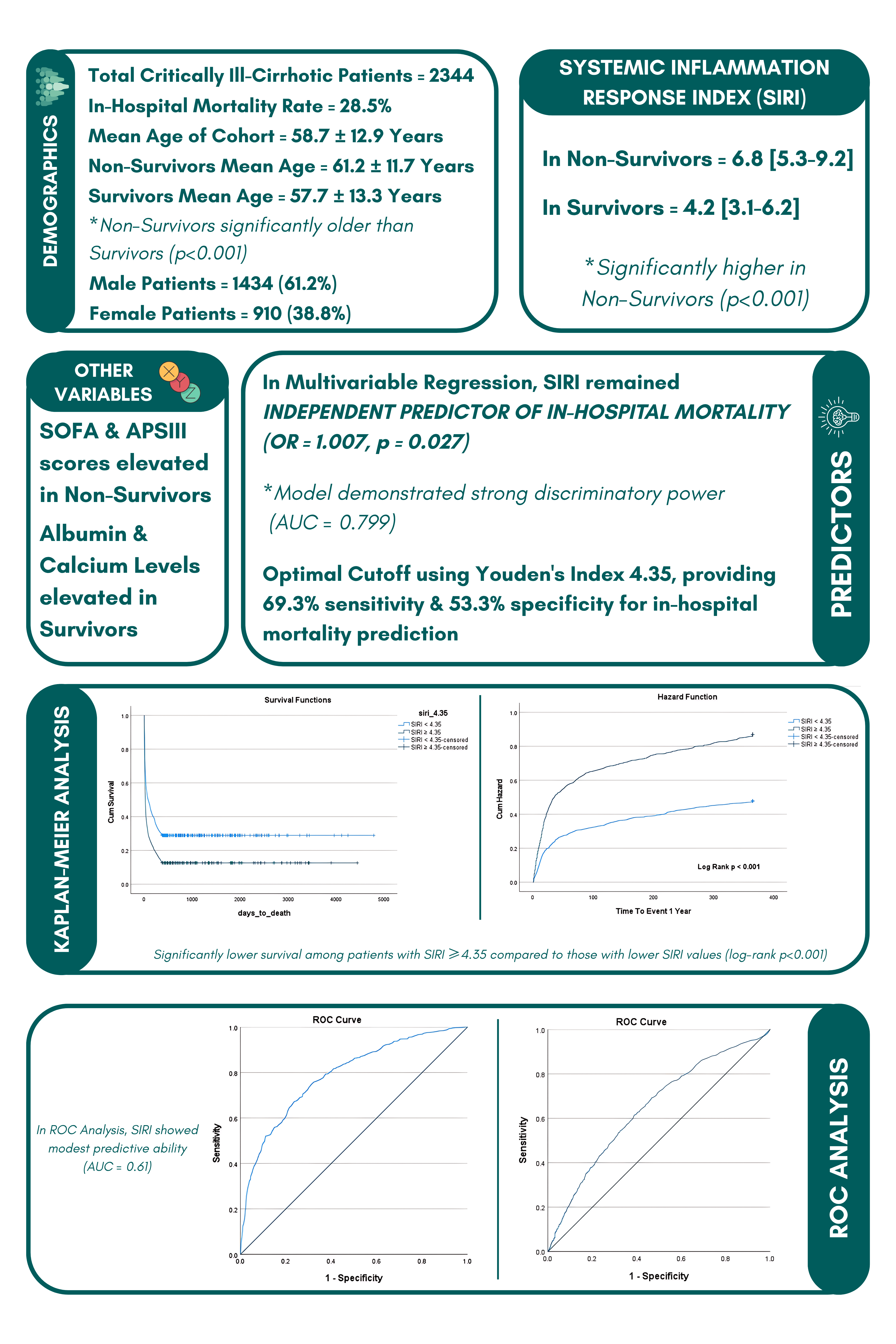
Figure: Illustration and Analysis
Disclosures:
Usama Sakhawat indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ahmed Shehadah indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Anfal Hamza indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Atif Nawaz Malik indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Sufyan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Hammad Iqbal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Arbaz Hassan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Allah Dad indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Latif indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ahsan Nawaz indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Faseeh Haider indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Faizan Ahmad indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kinza Bakht indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Tehmasp Rehman Mirza indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rama Hassan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Moheudin Khan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Abdul Basit indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Amanke Oranu indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Usama Sakhawat, MD1, Ahmed Shehadah, MD2, Anfal Hamza, MBBS3, Atif Nawaz Malik, MBBS3, Muhammad Sufyan, MBBS4, Muhammad Hammad Iqbal, MBBS5, Arbaz Hassan, MBBS3, Allah Dad, MD6, Muhammad Tasawar. Latif, MD7, Ahsan A. Nawaz, 8, Faseeh Haider, MD9, Faizan Ahmad, MD10, Kinza Bakht, MBBS11, Tehmasp Rehman Mirza, MBBS12, Rama Hassan, MBBS13, Moheudin Khan, MD1, Abdul Basit, MBBS14, Amanke Oranu, MD2. P5913 - Systemic Inflammation Response Index (SIRI) as an Independent Predictor of In-Hospital Mortality in Critically Ill Cirrhotic Patients: A MIMIC-IV Based Study, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1United Health Services, Wilson Medical Center, Johnson City, NY; 2United Health Services, Wilson Medical Center, Binghamton, NY; 3Sheikh Zayed Medical College, Rahim Yar Khan, Pakistan, Rahim Yar Khan, Punjab, Pakistan; 4Quaid-e-Azam Medical College, Bahawalpur, Bahawalpur, Punjab, Pakistan; 5Sheikh Zayed Medical College, RYK, Rahim Yar Khan, Punjab, Pakistan; 6Shiekh Zayed Medical College Rahim Yar Khan, Pakistan, Kot Addu, Punjab, Pakistan; 7Yale New Haven Hospital, Middlebury, CT; 8Holy Family Hospital, Rawalpindi, Bhakkar, Punjab, Pakistan; 9Allama Iqbal Medical college, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan; 10Duke University, Durham, NC; 11Sheikh Zayed Medical College Rahim Yar Khan, Muzaffargarh, Punjab, Pakistan; 12MBBS, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan; 13Akhtar Saeed Medical and Dental College, Lahore, Binghamton, NY; 14Quaid-e-Azam Medical College, Bahwalpur, Punjab, Pakistan
Introduction: The incidence of liver cirrhosis (LC) remains high throughout the world, posing a serious threat to human health, with repeated inflammation, repair and fibrosis being the pivotal factors in the entire pathophysiologic process. Systemic inflammatory response index (SIRI) is the novel indicator for poor prognosis of liver cirrhosis. The aim of this study was to evaluate its prognostic value and the correlation between SIRI and mortality in critically ill liver cirrhosis patients.
Methods: This retrospective study analyzed critically ill cirrhotic patients admitted to the ICU (2008–2019) using the MIMIC-IV database. Patient demographics, comorbid conditions, laboratory results, and mortality data were extracted. The systemic inflammation response index (calculated as = neutrophils × monocytes / lymphocytes) was calculated in Excel and categorized as high (≥4.35) or low (≤4.35). Patients with missing baseline labs were excluded. Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS v26. Descriptive statistics (mean and SD, frequency and percentages), chi-square tests, and multivariate regression (adjusted for confounders) assessed associations and mortality risk. ROC curves evaluated predictive value, and Kaplan–Meier analysis (log-rank test) compared survival. A p-value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results: Of 2,344 critically ill cirrhotic patients (61.2% male, mean age 58.7±12.9 years), 28.5% (668) died in-hospital. Non-survivors were older (61.2±11.7 vs. 57.7±13.3, p< 0.001) and had more comorbidities (renal disease, severe liver disease, heart failure). Mortality group had higher SIRI (6.8 [5.3–9.2] vs. 4.2 [3.1–6.2], p< 0.001), SOFA, and APSIII scores, and lower albumin and calcium. Multivariable logistic regression confirmed SIRI as an independent mortality predictor (OR 1.007, 95% CI: p=0.027) alongside lower SpO₂, temperature, albumin, higher SOFA, and older age (AUC=0.799). ROC analysis showed SIRI’s modest predictive ability (AUC=0.61, cutoff 4.35, 69.3% sensitivity, 53.3% specificity). Kaplan-Meier analysis confirmed worse survival for SIRI ≥4.35 (log-rank p< 0.001).
Discussion: High SIRI (≥4.35) was significantly associated with raised in-hospital mortality in the critically ill cirrhotic patients and independently predicted mortality with moderate discriminatory ability. Moreover, Kaplan–Meier analysis demonstrated poorer survival in the high SIRI group.

Figure: Illustration and Analysis
Disclosures:
Usama Sakhawat indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ahmed Shehadah indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Anfal Hamza indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Atif Nawaz Malik indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Sufyan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Hammad Iqbal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Arbaz Hassan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Allah Dad indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Latif indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ahsan Nawaz indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Faseeh Haider indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Faizan Ahmad indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kinza Bakht indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Tehmasp Rehman Mirza indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rama Hassan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Moheudin Khan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Abdul Basit indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Amanke Oranu indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Usama Sakhawat, MD1, Ahmed Shehadah, MD2, Anfal Hamza, MBBS3, Atif Nawaz Malik, MBBS3, Muhammad Sufyan, MBBS4, Muhammad Hammad Iqbal, MBBS5, Arbaz Hassan, MBBS3, Allah Dad, MD6, Muhammad Tasawar. Latif, MD7, Ahsan A. Nawaz, 8, Faseeh Haider, MD9, Faizan Ahmad, MD10, Kinza Bakht, MBBS11, Tehmasp Rehman Mirza, MBBS12, Rama Hassan, MBBS13, Moheudin Khan, MD1, Abdul Basit, MBBS14, Amanke Oranu, MD2. P5913 - Systemic Inflammation Response Index (SIRI) as an Independent Predictor of In-Hospital Mortality in Critically Ill Cirrhotic Patients: A MIMIC-IV Based Study, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
